Polystyrene blocks offer superior structural strength and are ideal for applications requiring solid insulation or crafting durable models. In contrast, polystyrene pellets provide excellent flexibility and lightweight properties, making them suitable for filling, packaging, and molding complex shapes. Choosing between blocks and pellets depends on the specific project's need for rigidity versus adaptability.
Table of Comparison
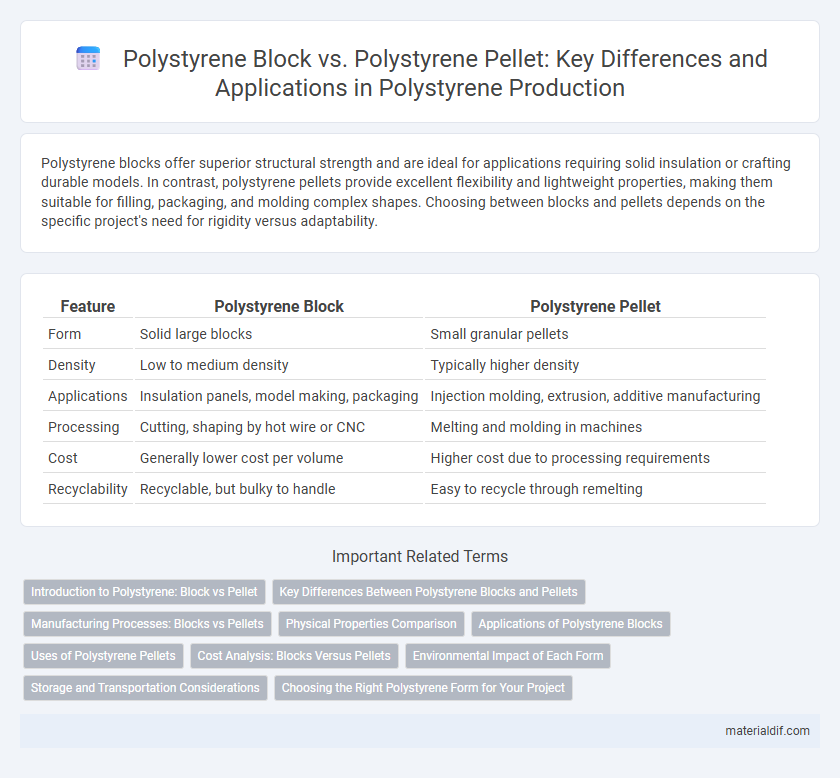
| Feature | Polystyrene Block | Polystyrene Pellet |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Solid large blocks | Small granular pellets |
| Density | Low to medium density | Typically higher density |
| Applications | Insulation panels, model making, packaging | Injection molding, extrusion, additive manufacturing |
| Processing | Cutting, shaping by hot wire or CNC | Melting and molding in machines |
| Cost | Generally lower cost per volume | Higher cost due to processing requirements |
| Recyclability | Recyclable, but bulky to handle | Easy to recycle through remelting |
Introduction to Polystyrene: Block vs Pellet
Polystyrene blocks are large, solid forms primarily used for insulation, model making, and packaging due to their rigidity and ease of cutting, whereas polystyrene pellets are small, granular pieces commonly used as raw material in plastic manufacturing and molding processes. The block form offers structural stability and can be shaped with precision, while pellets provide versatility for melting and reforming into various products. Understanding the differences between polystyrene block and pellet allows for optimized application in industries such as construction, packaging, and plastics production.
Key Differences Between Polystyrene Blocks and Pellets
Polystyrene blocks are large, rigid foam sheets commonly used for insulation and structural applications due to their high compressive strength and ease of shaping. In contrast, polystyrene pellets are small, granular raw materials primarily used in injection molding and extrusion processes for manufacturing plastic products. The key differences lie in their physical form, processing methods, and end-use applications, with blocks serving as building materials and pellets functioning as feedstock for plastic fabrication.
Manufacturing Processes: Blocks vs Pellets
Polystyrene block manufacturing involves polymerizing styrene monomers in large molds, producing dense, solid blocks that are later cut or shaped for various applications. In contrast, polystyrene pellets are created through a polymerization process followed by extrusion and chopping, resulting in small, uniform granules ideal for melting and molding in injection or blow molding. The block process yields material suited for machining and insulation, while pellet production supports mass manufacturing of items with complex geometries.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polystyrene blocks exhibit higher density and enhanced structural rigidity compared to polystyrene pellets, making them ideal for applications requiring solid, stable forms. Polystyrene pellets, being granular and low in bulk density, offer greater flexibility for molding and extrusion processes due to their uniform melting and flow characteristics. The thermal insulation value of polystyrene blocks generally surpasses that of pellets, attributed to their compact structure and reduced air gaps.
Applications of Polystyrene Blocks
Polystyrene blocks are widely used in insulation for construction due to their excellent thermal resistance and structural rigidity, making them ideal for wall, roof, and foundation insulation. Their larger, solid form allows for easy cutting and shaping, which is essential in custom architectural applications and model prototyping. Compared to polystyrene pellets, blocks offer superior stability and durability in applications requiring consistent shape and mechanical strength.
Uses of Polystyrene Pellets
Polystyrene pellets are extensively used as raw material for manufacturing various plastic products, including packaging materials, insulation panels, and disposable containers due to their lightweight and thermal insulation properties. These pellets offer easy melting and molding capabilities, making them ideal for injection molding and extrusion processes in producing consumer goods, automotive parts, and electronic housings. Their versatility in recycling also promotes sustainable production cycles compared to polystyrene blocks, which are primarily utilized in construction and architectural applications for insulation and structural support.
Cost Analysis: Blocks Versus Pellets
Polystyrene blocks generally offer lower cost per volume compared to polystyrene pellets due to reduced manufacturing complexity and lower transportation expenses. Pellets require additional processing steps such as melting and molding, which increase labor and energy costs. Cost analysis favors blocks for large-scale insulation projects, while pellets may be more economical for customized or small-batch applications.
Environmental Impact of Each Form
Polystyrene blocks generate less waste during manufacturing compared to polystyrene pellets, which often result in microplastic pollution due to their small size and ease of dispersion in the environment. Polystyrene pellets pose a higher risk of ingestion by marine and terrestrial wildlife, leading to toxic buildup and ecosystem disruption. Recycling efficiency is greater for polystyrene blocks because their solid form allows for easier collection and processing, reducing environmental contamination.
Storage and Transportation Considerations
Polystyrene block offers advantages in storage efficiency due to its compact, solid form, reducing space requirements compared to expandable polystyrene pellets, which are lightweight but occupy larger volumes. Transportation costs for polystyrene blocks tend to be lower, as they can be stacked and packed more densely, whereas pellets often require specialized containment to prevent spillage and contamination. Proper handling protocols for pellets include sealed containers and moisture protection, ensuring product integrity during shipping and storage.
Choosing the Right Polystyrene Form for Your Project
Polystyrene block offers superior insulation and structural integrity, making it ideal for large-scale construction and design projects requiring durability and precise shaping. Polystyrene pellets provide greater flexibility for molding and packaging applications where lightweight and shock absorption are critical. Selecting the right polystyrene form depends on project requirements like strength, insulation, molding capability, and cost-effectiveness.
Polystyrene Block vs Polystyrene Pellet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com