Polystyrene beads are the raw, small, spherical particles used in the production of various molded products, whereas Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) consists of these beads that have been expanded and fused to form lightweight, rigid foam materials. EPS is widely utilized for insulation, packaging, and cushioning due to its excellent thermal resistance and shock-absorbing properties. Polystyrene beads provide the foundational raw material that transforms into EPS through a controlled expansion process, optimizing durability and performance in finished applications.
Table of Comparison
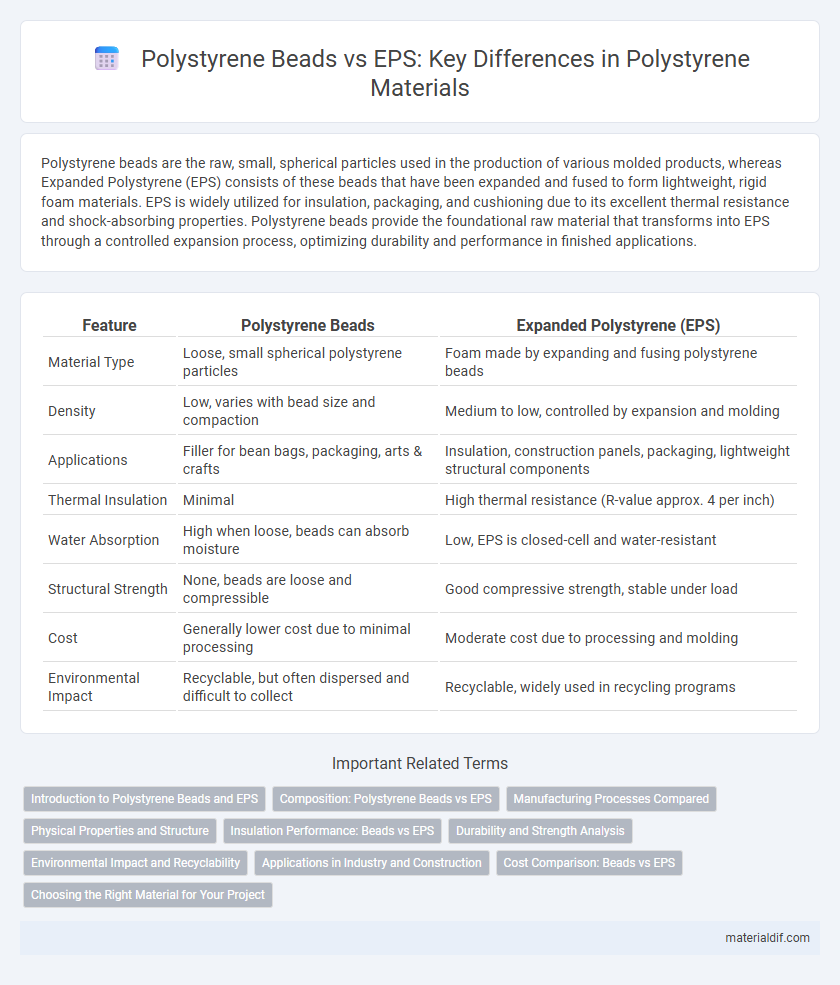
| Feature | Polystyrene Beads | Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Loose, small spherical polystyrene particles | Foam made by expanding and fusing polystyrene beads |
| Density | Low, varies with bead size and compaction | Medium to low, controlled by expansion and molding |
| Applications | Filler for bean bags, packaging, arts & crafts | Insulation, construction panels, packaging, lightweight structural components |
| Thermal Insulation | Minimal | High thermal resistance (R-value approx. 4 per inch) |
| Water Absorption | High when loose, beads can absorb moisture | Low, EPS is closed-cell and water-resistant |
| Structural Strength | None, beads are loose and compressible | Good compressive strength, stable under load |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to minimal processing | Moderate cost due to processing and molding |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, but often dispersed and difficult to collect | Recyclable, widely used in recycling programs |
Introduction to Polystyrene Beads and EPS
Polystyrene beads are small, spherical particles commonly used as raw material for molded products and insulation, valued for their lightweight and cushioning properties. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a foam material created by expanding polystyrene beads through steam heating, resulting in a rigid, low-density structure with excellent thermal insulation. Both forms originate from the same polymer but differ primarily in their processing, physical form, and typical applications such as packaging, construction, and insulation.
Composition: Polystyrene Beads vs EPS
Polystyrene beads consist of small, spherical particles of polystyrene polymer used in various applications, whereas Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is formed by expanding these beads with steam to create a lightweight, rigid foam. The composition of polystyrene beads remains in a raw, granular state, allowing flexibility in molding and shaping, while EPS is a consolidated foam composed primarily of 98%-99% air trapped within the expanded beads. This difference in structure results in contrasting physical properties, with EPS exhibiting enhanced thermal insulation and cushioning capabilities due to its cellular composition.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Polystyrene beads are produced through suspension polymerization, creating small, uniform spheres ideal for molding and insulation applications. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is manufactured by pre-expanding these beads with steam, followed by molding and curing into rigid foam blocks with enhanced thermal insulation properties. The key difference in manufacturing lies in EPS's additional expansion and fusion steps, transforming raw beads into lightweight, durable foam materials widely used in packaging and construction.
Physical Properties and Structure
Polystyrene beads are small, spherical particles used as a raw material in the production of expanded polystyrene (EPS), which is a foam composed of these beads fused together. Physically, polystyrene beads are dense and solid, whereas EPS exhibits a lightweight, porous structure due to the air trapped within the expanded beads, giving it excellent insulation properties. The microstructure of polystyrene beads is compact and uniform, while EPS features a cellular, foam-like matrix that enhances its impact resistance and thermal insulation capabilities.
Insulation Performance: Beads vs EPS
Polystyrene beads exhibit superior insulation performance compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) due to their spherical shape, which creates a denser and more uniform cellular structure, effectively reducing thermal conductivity. EPS, while lightweight and cost-effective, contains larger, irregular air pockets that can lead to higher thermal bridging and reduced energy efficiency. The enhanced insulation properties of polystyrene beads make them preferable in applications requiring maximum thermal resistance and durability.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Polystyrene beads exhibit higher density and compressive strength compared to Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), resulting in enhanced durability under mechanical stress. EPS's open-cell structure makes it less resistant to impacts and deformation, reducing its lifespan in demanding applications. Polystyrene beads' uniform size and compact arrangement contribute to superior structural integrity and longevity in insulation and packaging uses.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene beads, commonly used in packaging and insulation, have a lower density than expanded polystyrene (EPS), resulting in reduced material consumption but challenging recycling processes due to their small size and tendency to scatter. EPS, characterized by its rigid, foam-like structure, offers better recyclability through specialized densification and compaction methods, facilitating more efficient material recovery and reuse. Both materials pose environmental concerns as they degrade slowly in ecosystems, but advancements in recycling technologies and increased collection efforts have improved EPS's sustainability profile compared to loose polystyrene beads.
Applications in Industry and Construction
Polystyrene beads are commonly used as a raw material in the production of expanded polystyrene (EPS), providing lightweight and insulating properties ideal for packaging, insulation panels, and lightweight concrete in construction. EPS, composed of fused polystyrene beads, offers superior thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and compressive strength, making it essential in building envelopes, flooring systems, and insulation boards. Industrial applications leverage polystyrene beads for moldable products and flotation devices, while EPS's structural rigidity and durability expand its use in sustainable construction and energy-efficient building solutions.
Cost Comparison: Beads vs EPS
Polystyrene beads typically cost less per unit volume compared to expanded polystyrene (EPS) sheets, offering savings in bulk purchases for insulation and packaging applications. The manufacturing process of polystyrene beads involves less energy-intensive expansion, contributing to their lower market price relative to pre-formed EPS blocks. However, EPS provides better structural integrity, which can justify its higher cost in construction and product protection scenarios.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Polystyrene beads offer superior moldability and are ideal for projects requiring detailed shapes, while expanded polystyrene (EPS) provides excellent thermal insulation and impact resistance for construction and packaging. EPS is lightweight with a closed-cell structure that enhances moisture resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications. Selecting between polystyrene beads and EPS depends on the specific project requirements such as flexibility, durability, and insulation needs.
Polystyrene Beads vs EPS Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com