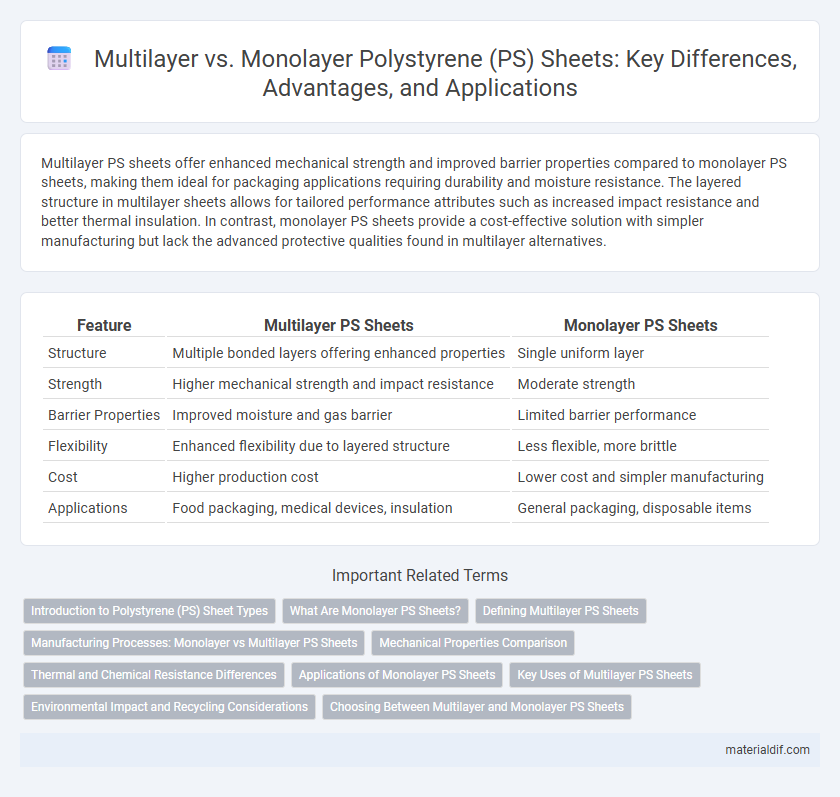
Multilayer PS sheets offer enhanced mechanical strength and improved barrier properties compared to monolayer PS sheets, making them ideal for packaging applications requiring durability and moisture resistance. The layered structure in multilayer sheets allows for tailored performance attributes such as increased impact resistance and better thermal insulation. In contrast, monolayer PS sheets provide a cost-effective solution with simpler manufacturing but lack the advanced protective qualities found in multilayer alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Multilayer PS Sheets | Monolayer PS Sheets |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Multiple bonded layers offering enhanced properties | Single uniform layer |
| Strength | Higher mechanical strength and impact resistance | Moderate strength |
| Barrier Properties | Improved moisture and gas barrier | Limited barrier performance |
| Flexibility | Enhanced flexibility due to layered structure | Less flexible, more brittle |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower cost and simpler manufacturing |
| Applications | Food packaging, medical devices, insulation | General packaging, disposable items |
Introduction to Polystyrene (PS) Sheet Types
Multilayer polystyrene (PS) sheets consist of several bonded layers that combine different properties such as enhanced strength, barrier resistance, and improved thermal insulation compared to monolayer PS sheets. Monolayer PS sheets are single-layer, uniform materials commonly used for basic packaging and display applications due to their lightweight and clarity. The multilayer design optimizes performance for specialized uses in food packaging, electronics, and automotive industries by addressing specific functional requirements while maintaining the inherent characteristics of polystyrene.
What Are Monolayer PS Sheets?
Monolayer PS sheets consist of a single homogeneous layer of polystyrene, offering uniform properties such as clarity, rigidity, and ease of thermoforming. These sheets are widely used in packaging, displays, and model making due to their consistent thickness and straightforward manufacturing process. Unlike multilayer PS sheets, they lack additional barrier or functional layers, which limits their application where enhanced mechanical or barrier performance is required.
Defining Multilayer PS Sheets
Multilayer polystyrene (PS) sheets consist of multiple layers of PS material laminated together to enhance mechanical properties, thermal insulation, and chemical resistance compared to monolayer PS sheets. These multilayer structures improve impact strength and dimensional stability, making them suitable for packaging, construction, and automotive applications. The distinct layers can be engineered with varying densities and molecular weights to optimize performance characteristics not achievable by single-layer PS sheets.
Manufacturing Processes: Monolayer vs Multilayer PS Sheets
Monolayer PS sheets are produced through a single extrusion or casting process, resulting in a uniform structure with consistent physical properties. Multilayer PS sheets undergo co-extrusion, combining different polymer layers to enhance mechanical strength, barrier performance, and thermal stability. The multilayer manufacturing process enables the customization of sheet properties by varying layer composition and thickness, which is not achievable with monolayer sheets.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Multilayer polystyrene (PS) sheets exhibit enhanced mechanical properties compared to monolayer PS sheets, including improved impact resistance, tensile strength, and dimensional stability. The layered structure in multilayer PS sheets provides better stress distribution and resistance to cracking under mechanical load. Monolayer PS sheets generally show uniform but lower strength characteristics due to the absence of reinforcing interfaces.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance Differences
Multilayer polystyrene (PS) sheets exhibit enhanced thermal resistance compared to monolayer PS sheets due to multiple specialized layers that improve heat insulation and reduce thermal degradation. Chemically, multilayer PS sheets offer superior resistance by incorporating barrier layers that protect against solvents and corrosive substances, whereas monolayer sheets are more susceptible to chemical permeation and damage. This structural complexity makes multilayer PS sheets preferable for applications requiring robust thermal stability and chemical protection.
Applications of Monolayer PS Sheets
Monolayer PS sheets are widely used in packaging applications due to their clarity, rigidity, and ease of thermoforming, making them ideal for food containers, trays, and blister packs. Their single-layer structure allows efficient recycling and lower production costs compared to multilayer PS sheets. These sheets also find applications in signage and display materials where lightweight and cost-effectiveness are critical.
Key Uses of Multilayer PS Sheets
Multilayer PS sheets are extensively used in food packaging due to their enhanced barrier properties, improving shelf life by protecting contents from moisture, oxygen, and contaminants. Their superior mechanical strength and thermal insulation make them ideal for applications such as trays, clamshell containers, and blisters in pharmaceutical packaging. These sheets also offer improved printability and aesthetic appeal, supporting brand differentiation in consumer goods.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Considerations
Multilayer PS sheets complicate recycling processes due to the difficulty in separating layers, often resulting in lower recycling rates and increased environmental burden compared to monolayer PS sheets, which are more easily processed in standard recycling streams. Monolayer PS sheets contribute less to landfill accumulation and facilitate circular economy practices by enabling higher material recovery and reuse. Environmental impact assessments highlight that multilayer configurations, although beneficial for product performance, pose significant challenges in waste management and reduce overall sustainability of polystyrene-based packaging.
Choosing Between Multilayer and Monolayer PS Sheets
Multilayer PS sheets offer enhanced barrier properties, improved mechanical strength, and better thermal stability compared to monolayer PS sheets, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and extended shelf life. Monolayer PS sheets, being simpler and more cost-effective, suit applications where basic insulation or packaging protection is sufficient without the need for advanced performance features. Selecting between multilayer and monolayer PS sheets depends on specific requirements such as product sensitivity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints in packaging or construction projects.
Multilayer PS sheets vs Monolayer PS sheets Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com