Transparent polystyrene offers high clarity and excellent light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility and aesthetic appeal. Opaque polystyrene provides enhanced strength and UV resistance, suitable for products that need durability and protection from light exposure. Selecting between transparent and opaque polystyrene depends on balancing transparency needs with mechanical and environmental performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
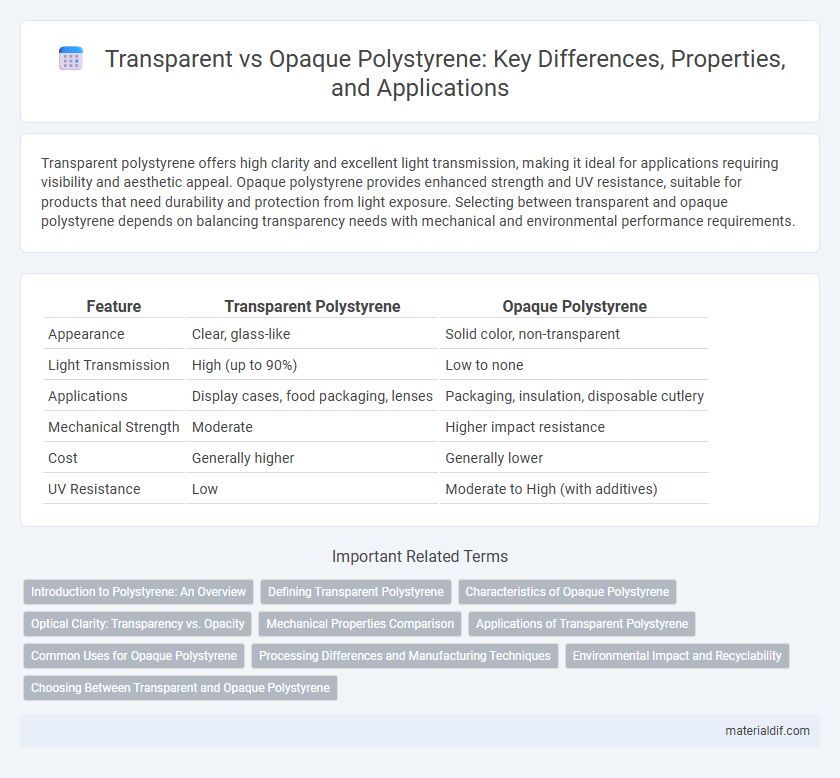
| Feature | Transparent Polystyrene | Opaque Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, glass-like | Solid color, non-transparent |
| Light Transmission | High (up to 90%) | Low to none |
| Applications | Display cases, food packaging, lenses | Packaging, insulation, disposable cutlery |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | Higher impact resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| UV Resistance | Low | Moderate to High (with additives) |
Introduction to Polystyrene: An Overview
Polystyrene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, insulation, and consumer goods, available in both transparent and opaque forms. Transparent polystyrene, known for its clarity and rigidity, is ideal for applications requiring visibility and aesthetic appeal, such as food containers and display cases. Opaque polystyrene, often blended with additives for enhanced durability and color, is commonly used in applications like household items and automotive components where strength and opacity are essential.
Defining Transparent Polystyrene
Transparent polystyrene is a clear, lightweight thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent clarity and glossy finish, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility and aesthetic appeal. Unlike opaque polystyrene, which is typically modified with additives or pigments to block light, transparent polystyrene maintains high optical transparency and is commonly used in packaging, display cases, and laboratory ware. Its chemical composition and amorphous structure contribute to its distinctive transparency, enabling effective light transmission without significant distortion.
Characteristics of Opaque Polystyrene
Opaque polystyrene exhibits a milky white appearance due to the inclusion of mineral fillers or pigments that scatter light, increasing its opacity. It offers enhanced impact resistance and structural strength compared to transparent polystyrene, making it suitable for applications requiring durability such as food packaging and disposable containers. The denser molecular structure of opaque polystyrene also improves its thermal insulation properties and resistance to chemical degradation.
Optical Clarity: Transparency vs. Opacity
Transparent polystyrene offers superior optical clarity, allowing light to pass through with minimal distortion, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility such as food packaging and display cases. Opaque polystyrene, on the other hand, scatters light due to its additive composition, providing a matte appearance and enhanced UV protection suitable for insulation panels and automotive parts. The molecular structure and degree of polymer crystallinity directly influence the material's transparency, with amorphous regions enabling transparency and crystalline regions causing opacity.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Transparent polystyrene exhibits higher tensile strength and better impact resistance compared to opaque polystyrene, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and clarity. Opaque polystyrene, typically reinforced with fillers and additives, shows enhanced stiffness and improved cryogenic toughness but lower elongation at break. Both types offer distinct mechanical property profiles that influence their use in packaging, consumer goods, and insulation materials.
Applications of Transparent Polystyrene
Transparent polystyrene is widely used in packaging applications such as clear food containers, display cases, and protective covers due to its excellent clarity and ability to showcase products effectively. Its optical transparency makes it ideal for medical device components and laboratory equipment where visibility of contents or processes is essential. Unlike opaque polystyrene, transparent grades enhance aesthetic appeal and functional visibility, driving demand in retail and healthcare industries.
Common Uses for Opaque Polystyrene
Opaque polystyrene is widely used in packaging materials, disposable cutlery, and CD cases due to its excellent rigidity and impact resistance. Its ability to be easily molded makes it ideal for producing household items, toys, and refrigerator liners. These applications benefit from opaque polystyrene's durability and cost-effectiveness compared to transparent variants.
Processing Differences and Manufacturing Techniques
Transparent polystyrene is produced using suspension polymerization with strict control over polymer chain length to achieve clarity, while opaque polystyrene relies on bulk polymerization and often incorporates additives to enhance opacity. Injection molding and extrusion techniques vary, as transparent grades require slower cooling rates and precision in maintaining polymer homogeneity to prevent cloudiness. Manufacturing transparent polystyrene demands clean environments and refined processing parameters to avoid crystallization, whereas opaque variants allow for more flexible processing conditions due to their inherent light-scattering properties.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Transparent polystyrene (PS) generally exhibits higher recyclability due to its purity and fewer additives compared to opaque polystyrene, which contains pigments and fillers that complicate recycling processes. The environmental impact of opaque polystyrene is often greater because these additives can release harmful substances during degradation and limit the material's recyclability. Transparent PS offers a more sustainable option, facilitating closed-loop recycling systems and reducing waste in plastic recycling streams.
Choosing Between Transparent and Opaque Polystyrene
Choosing between transparent and opaque polystyrene depends on the application requirements such as visibility and aesthetic appeal. Transparent polystyrene offers high clarity and is ideal for display packaging and optical uses, while opaque polystyrene provides better UV resistance and is preferred for applications needing light diffusion or concealment. Factors like impact resistance, cost, and processing methods also influence the selection between these two types of polystyrene.
Transparent Polystyrene vs Opaque Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com