Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives offer significant environmental benefits by decomposing naturally, unlike conventional polystyrene, which persists in landfills and oceans for centuries. These eco-friendly materials reduce plastic pollution and can be produced from renewable resources, promoting sustainability. Consumer demand and regulatory pressures are accelerating the adoption of biodegradable options to replace traditional polystyrene in packaging and single-use products.
Table of Comparison
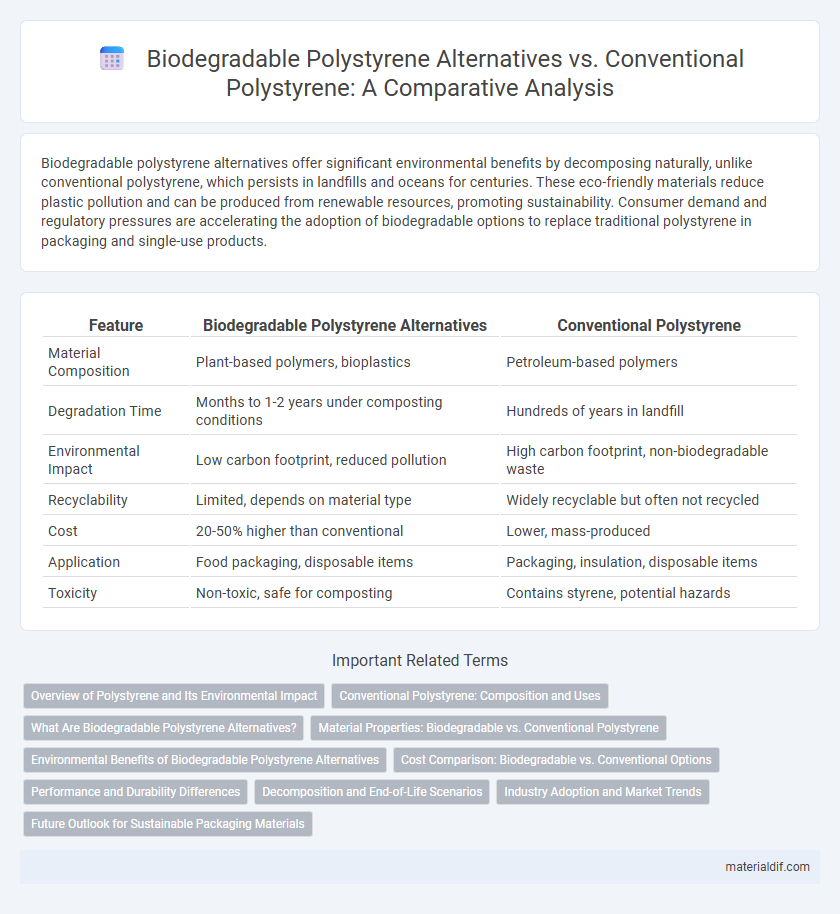
| Feature | Biodegradable Polystyrene Alternatives | Conventional Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Plant-based polymers, bioplastics | Petroleum-based polymers |
| Degradation Time | Months to 1-2 years under composting conditions | Hundreds of years in landfill |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, reduced pollution | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable waste |
| Recyclability | Limited, depends on material type | Widely recyclable but often not recycled |
| Cost | 20-50% higher than conventional | Lower, mass-produced |
| Application | Food packaging, disposable items | Packaging, insulation, disposable items |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, safe for composting | Contains styrene, potential hazards |
Overview of Polystyrene and Its Environmental Impact
Polystyrene, a widely used synthetic polymer, is prized for its lightweight and insulating properties but poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability and persistence in ecosystems. Conventional polystyrene waste accumulates in landfills and oceans, contributing to long-term pollution and harm to marine life through microplastic formation. Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives are engineered to break down more rapidly, reducing environmental impact by minimizing plastic accumulation and promoting sustainability in packaging and insulation applications.
Conventional Polystyrene: Composition and Uses
Conventional polystyrene is a synthetic aromatic polymer derived from the polymerization of styrene monomers, primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon chain. Its rigid, lightweight, and insulating properties make it widely used in packaging, disposable cutlery, insulation materials, and consumer electronics. Despite its versatility and low cost, conventional polystyrene poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and persistence in landfills and marine ecosystems.
What Are Biodegradable Polystyrene Alternatives?
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives are materials designed to mimic the properties of conventional polystyrene while breaking down more rapidly in natural environments through microbial activity. These alternatives often consist of biopolymers such as polylactic acid (PLA), starch-based composites, or cellulose derivatives that offer reduced environmental impact compared to traditional petroleum-based polystyrene. Their development targets minimizing plastic pollution by providing sustainable packaging and insulation solutions with improved end-of-life biodegradability.
Material Properties: Biodegradable vs. Conventional Polystyrene
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives offer enhanced environmental compatibility due to their ability to decompose naturally under specific conditions, whereas conventional polystyrene is highly resistant to biodegradation, leading to persistent environmental pollution. Material properties of biodegradable variants often include comparable thermal insulation and lightweight characteristics, but with reduced durability and shorter lifespan compared to conventional polystyrene. Innovations in biodegradable polymers aim to balance mechanical strength and biodegradability, addressing limitations in conventional polystyrene's environmental footprint.
Environmental Benefits of Biodegradable Polystyrene Alternatives
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives significantly reduce environmental impact by decomposing naturally within months, unlike conventional polystyrene which persists for centuries in landfills. These alternatives, often derived from plant-based materials like cornstarch or cellulose, minimize toxic emissions and microplastic pollution linked to traditional polystyrene waste. Implementing biodegradable options enhances soil health and marine ecosystems by preventing long-term contamination and promoting sustainable waste management practices.
Cost Comparison: Biodegradable vs. Conventional Options
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives often incur higher production costs due to specialized raw materials and manufacturing processes, resulting in price points 20-40% above conventional polystyrene. Conventional polystyrene benefits from established supply chains and economies of scale, making it significantly more economical for mass production and widespread commercial use. Despite higher costs, biodegradable options offer long-term environmental savings by reducing landfill impact and complying with increasing regulatory pressures on plastic waste.
Performance and Durability Differences
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives exhibit lower durability and thermal resistance compared to conventional polystyrene, impacting their suitability for long-term applications. Conventional polystyrene provides superior structural strength and moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging and insulation tasks. Innovations in biodegradable formulations aim to enhance performance metrics, yet they currently lag behind in mechanical robustness and lifespan.
Decomposition and End-of-Life Scenarios
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives decompose significantly faster than conventional polystyrene, breaking down within months to a few years under composting conditions compared to the centuries-long persistence of traditional polystyrene in landfills. End-of-life scenarios for biodegradable options include industrial composting and enhanced microbial degradation, which reduce environmental impact by minimizing plastic pollution and microplastic formation. Conventional polystyrene primarily undergoes mechanical recycling or landfill disposal, where it resists degradation, contributing to long-term environmental contamination.
Industry Adoption and Market Trends
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives are gaining traction in packaging and consumer goods sectors due to increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products. Industry adoption is accelerating with major manufacturers investing in bio-based resins and compostable foam materials to reduce reliance on conventional polystyrene derived from petrochemicals. Market trends indicate a steady rise in the global biodegradable polystyrene substitutes market, projected to grow at a CAGR of over 8% through 2030, driven by innovation in polymer technology and expanding regulatory support.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Packaging Materials
Biodegradable polystyrene alternatives, derived from renewable resources like plant-based polymers and starch composites, are rapidly gaining attention for reducing plastic waste and environmental impact. Innovations in bio-based additives and microbial degradation technologies enhance the performance and decomposition rate of these sustainable materials compared to conventional polystyrene, which persists in landfills for centuries. The future outlook for sustainable packaging emphasizes scalable production, cost-effectiveness, and regulatory support to accelerate the transition toward eco-friendly polystyrene substitutes in the global packaging industry.
Biodegradable Polystyrene Alternatives vs Conventional Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com