Recycling polystyrene significantly reduces environmental impact by converting waste into reusable materials, thus conserving resources and minimizing landfill space. In contrast, landfilling polystyrene leads to long-term environmental issues, as this material is non-biodegradable and can persist for hundreds of years. Efficient recycling of polystyrene helps reduce pollution, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and supports sustainable waste management practices.
Table of Comparison
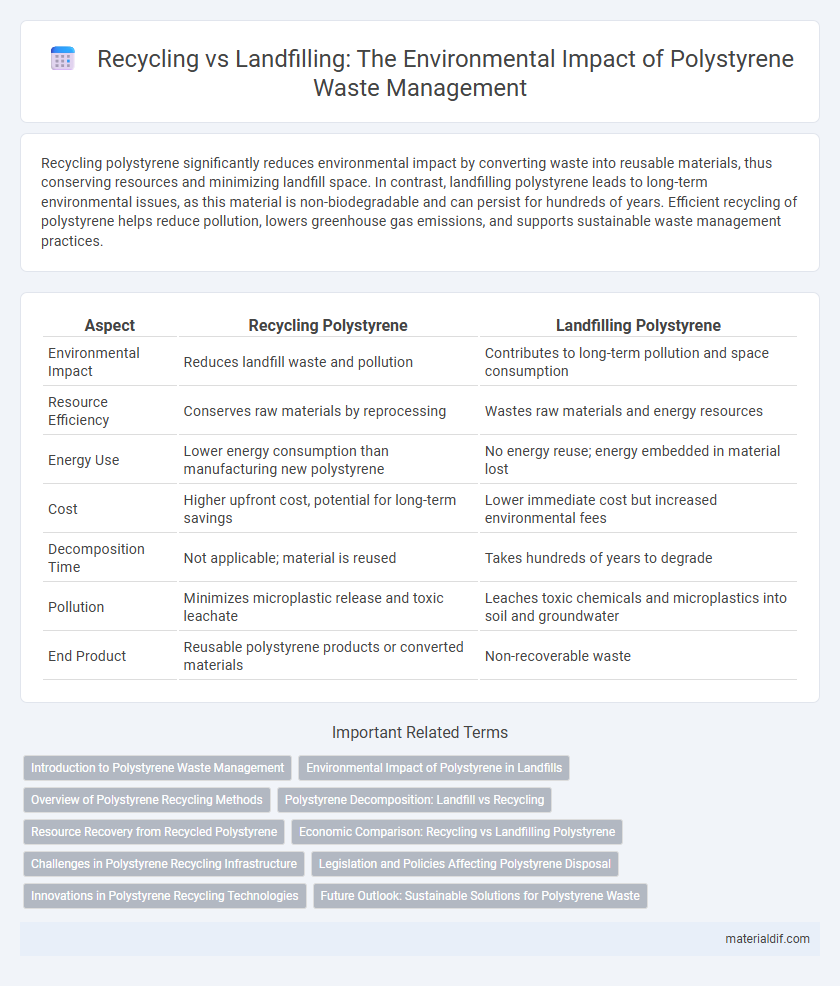
| Aspect | Recycling Polystyrene | Landfilling Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste and pollution | Contributes to long-term pollution and space consumption |
| Resource Efficiency | Conserves raw materials by reprocessing | Wastes raw materials and energy resources |
| Energy Use | Lower energy consumption than manufacturing new polystyrene | No energy reuse; energy embedded in material lost |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, potential for long-term savings | Lower immediate cost but increased environmental fees |
| Decomposition Time | Not applicable; material is reused | Takes hundreds of years to degrade |
| Pollution | Minimizes microplastic release and toxic leachate | Leaches toxic chemicals and microplastics into soil and groundwater |
| End Product | Reusable polystyrene products or converted materials | Non-recoverable waste |
Introduction to Polystyrene Waste Management
Polystyrene waste management presents significant environmental challenges due to its large volume and low biodegradability. Recycling polystyrene reduces landfill pressure by converting foam waste into reusable pellets for manufacturing, thereby minimizing toxic leachate and greenhouse gas emissions common in landfilling processes. Effective polystyrene recycling programs enhance resource efficiency and support sustainable waste reduction strategies compared to traditional landfilling methods.
Environmental Impact of Polystyrene in Landfills
Polystyrene in landfills poses significant environmental risks due to its non-biodegradable nature, leading to persistent pollution and leachate contamination of soil and groundwater. Recycling polystyrene reduces the volume of landfill waste and lowers greenhouse gas emissions by diverting it from incineration or decomposition processes. Sustainable management of polystyrene through recycling helps mitigate long-term ecological damage and conserves fossil fuel resources.
Overview of Polystyrene Recycling Methods
Polystyrene recycling primarily involves mechanical recycling, where collected waste is cleaned, shredded, and melted into pellets for reuse in manufacturing new products such as insulation and packaging materials. Chemical recycling methods, including pyrolysis and depolymerization, break polystyrene down into its original monomers for repolymerization, offering potential for closed-loop recycling and reducing environmental impact compared to landfilling. These recycling processes help mitigate landfilling issues, such as long degradation times and space consumption, making polystyrene recycling a more sustainable waste management approach.
Polystyrene Decomposition: Landfill vs Recycling
Polystyrene decomposition in landfills can take hundreds of years due to its resistance to microbial breakdown, leading to long-term environmental persistence and potential leaching of harmful chemicals. Recycling polystyrene significantly reduces its environmental impact by converting waste into reusable materials, decreasing landfill volume and conserving resources. Mechanical and chemical recycling methods enable the transformation of polystyrene into new products, minimizing degradation time and supporting sustainable waste management.
Resource Recovery from Recycled Polystyrene
Recycling polystyrene significantly enhances resource recovery by converting waste into valuable raw materials, reducing the demand for virgin petrochemicals. Mechanical and chemical recycling methods enable the production of new polystyrene products with comparable quality, minimizing environmental impact and landfill volume. Landfilling polystyrene leads to persistent waste accumulation due to its non-biodegradable nature, missing opportunities for energy savings and carbon footprint reduction achieved through recycling processes.
Economic Comparison: Recycling vs Landfilling Polystyrene
Recycling polystyrene typically reduces disposal costs by converting waste into valuable raw materials, generating economic benefits through material recovery and reduced landfill fees. Landfilling polystyrene incurs ongoing expenses related to space usage, environmental compliance, and potential future remediation costs, making it less economically sustainable. Investment in recycling infrastructure presents higher initial costs but results in long-term savings and resource efficiency compared to continuous landfilling expenditures.
Challenges in Polystyrene Recycling Infrastructure
Recycling polystyrene faces significant challenges due to its low density and high contamination rates, which complicate collection and processing efforts. Limited recycling facilities equipped to handle polystyrene contribute to high costs and inefficient recovery rates. Landfilling polystyrene remains common despite environmental concerns, as infrastructure gaps hinder large-scale recycling adoption.
Legislation and Policies Affecting Polystyrene Disposal
Legislation on polystyrene disposal increasingly favors recycling over landfilling due to environmental concerns and resource conservation goals. Policies such as the European Union's Waste Framework Directive and various state bans on single-use polystyrene products mandate recycling and restrict landfill disposal to reduce plastic pollution. Compliance with these regulations drives manufacturers and waste management systems to adopt advanced polystyrene recycling technologies, thereby minimizing environmental impact and promoting circular economy practices.
Innovations in Polystyrene Recycling Technologies
Innovations in polystyrene recycling technologies have significantly increased the efficiency of converting waste into reusable raw materials, reducing environmental impact compared to landfilling. Advanced chemical recycling methods, such as depolymerization and pyrolysis, enable breaking down polystyrene into monomers for manufacturing new products, minimizing plastic pollution and energy consumption. These technological advancements offer scalable solutions that decrease reliance on landfills, cutting greenhouse gas emissions and conserving resources in the plastic lifecycle.
Future Outlook: Sustainable Solutions for Polystyrene Waste
Advancements in chemical recycling technologies are enhancing the recovery and reuse of polystyrene, transforming waste into valuable raw materials, thus reducing environmental impact. Innovations in biodegradable polystyrene alternatives and improved collection systems are gaining traction, signaling a shift toward circular economy models. Future strategies emphasize integrating recycling infrastructure with policy support to minimize landfilling and promote sustainable waste management for polystyrene products.
Recycling Polystyrene vs Landfilling Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com