HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) offers superior impact resistance and durability compared to GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene), making it ideal for applications requiring toughness and flexibility. GPPS provides excellent clarity and smooth surface finish but is more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. Choosing between HIPS and GPPS depends on the balance between strength and appearance needed for specific pet product applications.
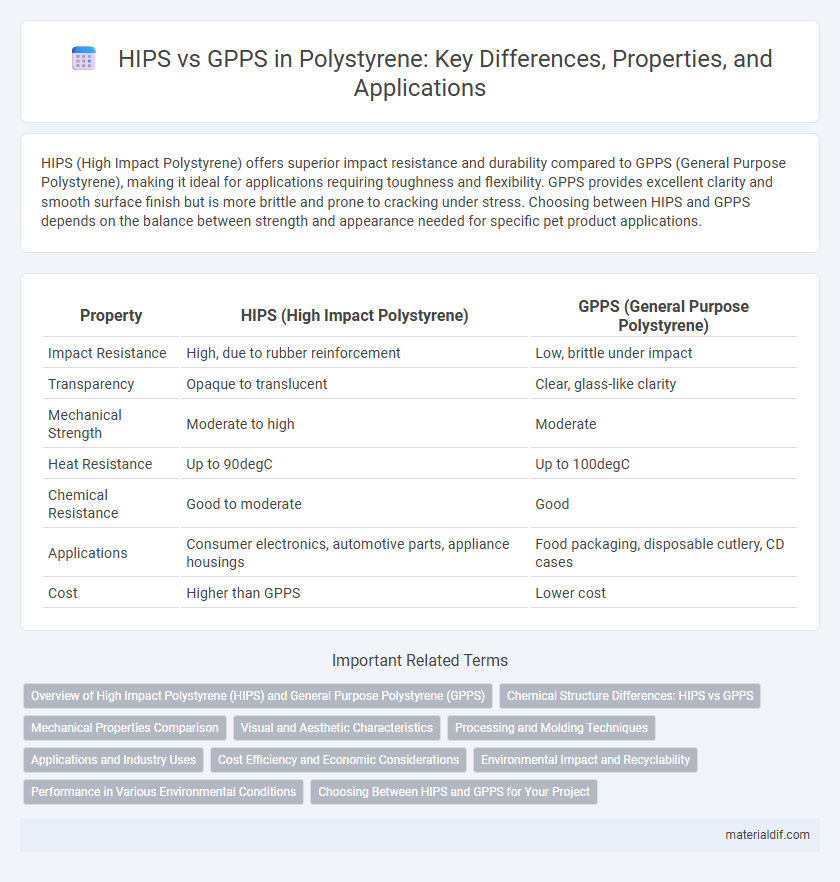
Table of Comparison
| Property | HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) | GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High, due to rubber reinforcement | Low, brittle under impact |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Clear, glass-like clarity |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 90degC | Up to 100degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good to moderate | Good |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, automotive parts, appliance housings | Food packaging, disposable cutlery, CD cases |
| Cost | Higher than GPPS | Lower cost |
Overview of High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS)
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is a rubber-modified version of General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) designed to enhance impact resistance and toughness, making it ideal for applications requiring durability such as packaging, appliance housings, and automotive parts. GPPS, known for its clarity and rigidity, is widely used in food containers, disposable cutlery, and transparent housings, where dimensional stability and aesthetic appearance are crucial. The main difference lies in HIPS's improved mechanical properties due to the incorporation of polybutadiene rubber, offering better shock absorption compared to the brittle nature of GPPS.
Chemical Structure Differences: HIPS vs GPPS
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) differs from General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) primarily in its chemical structure due to the inclusion of polybutadiene rubber, which forms a dispersed phase within the polystyrene matrix, enhancing its impact resistance. GPPS consists of a homogenous polystyrene polymer chain with a rigid, brittle molecular arrangement, whereas HIPS features a two-phase system with rubber domains that absorb and dissipate energy upon impact. The presence of these rubber particles in HIPS alters its morphology and mechanical properties without significantly changing the fundamental styrene monomer units compared to the pure GPPS structure.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) exhibits superior impact resistance and toughness compared to General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS), making it suitable for applications requiring enhanced durability. GPPS offers higher rigidity and clarity but is more brittle under mechanical stress, limiting its use in impact-sensitive environments. The mechanical strength of HIPS results from its elastomer-modified composition, providing better energy absorption and flexibility than the amorphous and more rigid GPPS.
Visual and Aesthetic Characteristics
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) offers enhanced visual appeal with improved impact resistance and a slightly matte finish, making it ideal for products requiring durability and a refined look. GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) provides superior clarity and gloss, resulting in a highly transparent and shiny surface preferred for display applications and packaging where aesthetic vibrancy is key. The choice between HIPS and GPPS balances the need for toughness versus optical clarity depending on the visual and aesthetic requirements of the final product.
Processing and Molding Techniques
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) offers superior impact resistance and is commonly processed using injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming, facilitating complex shapes with enhanced durability. GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) provides excellent clarity and rigidity, making it suitable for injection molding and sheet forming, although it is more brittle compared to HIPS. Processing temperatures for HIPS typically range from 200degC to 260degC, while GPPS processes effectively at slightly lower temperatures, around 190degC to 250degC.
Applications and Industry Uses
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and appliance housings due to its enhanced impact resistance and toughness. General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) is preferred for applications requiring clarity and rigidity, such as food containers, laboratory ware, and display cases. Industries like consumer goods, electronics, and healthcare rely heavily on HIPS for durability and GPPS for optical clarity and ease of processing.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) typically offers better cost efficiency than GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) due to its enhanced durability reducing replacement and maintenance expenses in applications like packaging and automotive parts. GPPS, while generally cheaper upfront, can lead to higher long-term costs because of its brittleness and lower impact resistance, making it less suitable for demanding environments. Evaluating the total lifecycle cost, including material performance and application requirements, is essential for optimal economic considerations between HIPS and GPPS.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) exhibits better mechanical properties than General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS), but both contribute significantly to plastic waste due to their non-biodegradable nature. Recycling processes for HIPS are more established because of its widespread use in packaging and consumer goods, allowing higher recovery rates compared to GPPS, which is less commonly recycled. However, both types present challenges in environmental impact due to their persistence in landfills and limited biodegradability, highlighting the need for improved recycling technologies and sustainable alternatives.
Performance in Various Environmental Conditions
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) demonstrates superior resistance to impact and stress cracking compared to General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS), especially in low-temperature environments, making it more suitable for demanding conditions. GPPS offers greater clarity and stiffness but tends to become brittle under cold or high humidity settings, limiting its application in harsh environments. The enhanced durability of HIPS under fluctuating temperatures and mechanical stress provides an advantage for product longevity and reliability in diverse environmental conditions.
Choosing Between HIPS and GPPS for Your Project
Choosing between High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) depends on project requirements such as impact resistance and surface finish. HIPS offers greater toughness and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced mechanical strength, while GPPS provides a clearer, more rigid option suited for aesthetic and precision parts. Evaluating factors like environmental stress, transparency needs, and cost efficiency ensures optimal material selection for your specific use case.
HIPS vs GPPS Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com