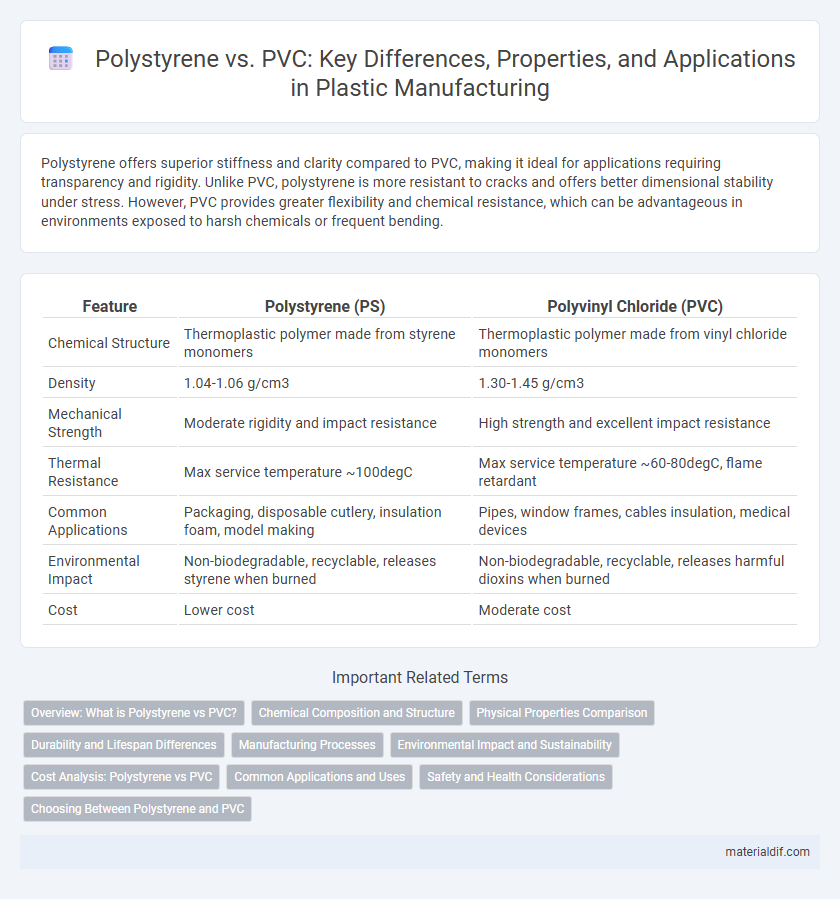
Polystyrene offers superior stiffness and clarity compared to PVC, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and rigidity. Unlike PVC, polystyrene is more resistant to cracks and offers better dimensional stability under stress. However, PVC provides greater flexibility and chemical resistance, which can be advantageous in environments exposed to harsh chemicals or frequent bending.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polystyrene (PS) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Thermoplastic polymer made from styrene monomers | Thermoplastic polymer made from vinyl chloride monomers |
| Density | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 | 1.30-1.45 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate rigidity and impact resistance | High strength and excellent impact resistance |
| Thermal Resistance | Max service temperature ~100degC | Max service temperature ~60-80degC, flame retardant |
| Common Applications | Packaging, disposable cutlery, insulation foam, model making | Pipes, window frames, cables insulation, medical devices |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable, releases styrene when burned | Non-biodegradable, recyclable, releases harmful dioxins when burned |
| Cost | Lower cost | Moderate cost |
Overview: What is Polystyrene vs PVC?
Polystyrene is a lightweight, rigid plastic made from the polymerization of styrene, commonly used in packaging, insulation, and disposable containers due to its clarity and ease of molding. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a durable and versatile plastic produced from vinyl chloride monomers, widely utilized in construction, pipes, and electrical insulation for its strength and chemical resistance. Both materials differ significantly in properties, with polystyrene offering better clarity and rigidity, while PVC provides enhanced durability and weather resistance.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polystyrene is a synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer made from the monomer styrene, characterized by a rigid, transparent structure with a repeating vinylbenzene unit. In contrast, PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is composed of vinyl chloride monomers, containing chlorine atoms that provide enhanced chemical resistance and flame retardancy. The presence of the aromatic ring in polystyrene results in higher brittleness, while the chlorine groups in PVC contribute to its durability and flexibility.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polystyrene exhibits higher rigidity and lower flexibility compared to PVC, making it ideal for applications requiring stiffness. PVC demonstrates superior impact resistance and better chemical durability, which enhances its performance in outdoor and construction uses. The thermal insulation capacity of polystyrene surpasses that of PVC, contributing to its widespread use in packaging and insulation materials.
Durability and Lifespan Differences
Polystyrene offers moderate durability with resistance to impact and moisture but tends to degrade under prolonged UV exposure, limiting its lifespan to around 5-10 years outdoors. PVC (polyvinyl chloride) boasts superior durability, exhibiting high resistance to weathering, chemicals, and UV radiation, which enables it to last 20-40 years or more in similar conditions. The enhanced stability of PVC makes it a preferred material for applications requiring long-term outdoor performance compared to polystyrene.
Manufacturing Processes
Polystyrene manufacturing involves the polymerization of styrene monomers through suspension or bulk polymerization, producing a lightweight, rigid plastic with good clarity. PVC is produced via polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers, typically using suspension, emulsion, or bulk polymerization, resulting in a versatile material with high chemical resistance and flexibility. The manufacturing of polystyrene generally requires less energy and simpler catalysts compared to PVC, which demands rigorous control to stabilize its chlorine content and maintain quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene produces less toxic byproducts during production compared to PVC, which releases harmful dioxins and chlorine compounds contributing to persistent environmental pollution. Polystyrene is less recyclable but often generates lower greenhouse gas emissions over its lifecycle, whereas PVC's durability improves reuse potential but creates challenges in disposal due to its chlorine content. Both materials raise sustainability concerns, with ongoing research focusing on biodegradable alternatives and improved recycling technologies to reduce their ecological footprint.
Cost Analysis: Polystyrene vs PVC
Polystyrene generally offers a lower initial material cost compared to PVC, making it a cost-effective option for projects with budget constraints. However, PVC often provides better long-term value due to its higher durability and resistance to environmental factors, which reduces maintenance and replacement expenses. Cost analysis should consider both upfront prices and lifecycle costs, as PVC's robustness may offset its higher initial investment over time.
Common Applications and Uses
Polystyrene is widely used in packaging, disposable cutlery, insulation, and model making due to its lightweight and impact resistance, while PVC excels in construction materials, electrical cable insulation, and piping systems because of its durability and chemical resistance. Polystyrene's rigidity makes it ideal for products like CD cases and foam cups, whereas PVC's flexibility is crucial for applications such as vinyl flooring and inflatable products. Both materials serve distinct industries based on their thermal properties and mechanical strength, influencing their specialized commercial and industrial uses.
Safety and Health Considerations
Polystyrene is generally considered safer than PVC as it does not release harmful dioxins or phthalates during use or disposal, reducing health risks linked to endocrine disruption and carcinogenic effects. PVC contains chlorine and requires additives like plasticizers, which can leach toxic chemicals such as vinyl chloride and phthalates, posing greater health hazards upon exposure. Choosing polystyrene over PVC minimizes potential exposure to hazardous compounds, promoting improved indoor air quality and safer environmental impact.
Choosing Between Polystyrene and PVC
Polystyrene offers lightweight properties and excellent clarity, making it ideal for packaging and disposable cutlery, while PVC excels in durability and chemical resistance, suited for pipes and vinyl flooring. When choosing between polystyrene and PVC, consider factors such as impact resistance, flexibility, and environmental exposure. Cost-effectiveness and recyclability also influence selection, with PVC generally providing longer service life but posing greater challenges in recycling than polystyrene.
Polystyrene vs PVC Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com