Food-grade polystyrene is specifically manufactured to meet safety standards for direct contact with food, ensuring it is free from harmful chemicals and contaminants that could migrate into consumables. Industrial-grade polystyrene, on the other hand, is designed for non-food applications, offering strength and durability without the stringent purity requirements necessary for food safety. Choosing food-grade polystyrene is essential for packaging and containers to guarantee consumer health and regulatory compliance.
Table of Comparison
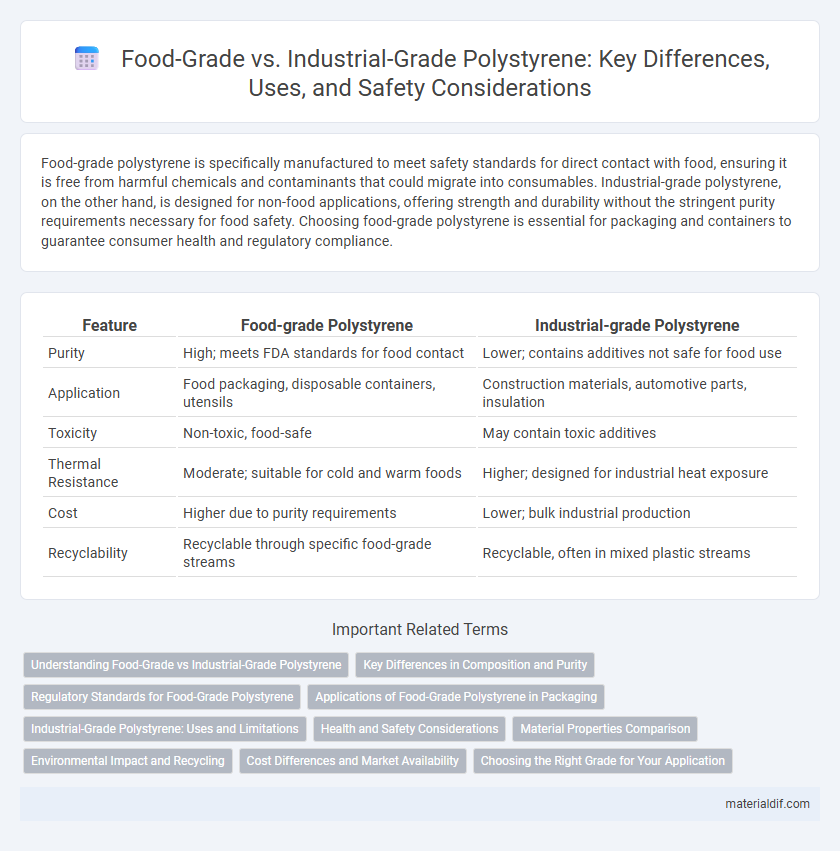
| Feature | Food-grade Polystyrene | Industrial-grade Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High; meets FDA standards for food contact | Lower; contains additives not safe for food use |
| Application | Food packaging, disposable containers, utensils | Construction materials, automotive parts, insulation |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, food-safe | May contain toxic additives |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate; suitable for cold and warm foods | Higher; designed for industrial heat exposure |
| Cost | Higher due to purity requirements | Lower; bulk industrial production |
| Recyclability | Recyclable through specific food-grade streams | Recyclable, often in mixed plastic streams |
Understanding Food-Grade vs Industrial-Grade Polystyrene
Food-grade polystyrene is formulated to meet stringent safety standards set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA, ensuring non-toxicity and preventing contamination in food packaging applications. Industrial-grade polystyrene, in contrast, is designed primarily for durability and cost-efficiency in manufacturing processes, lacking the strict purity and safety requirements necessary for direct food contact. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate polystyrene grade based on application, especially when food safety and regulatory compliance are priorities.
Key Differences in Composition and Purity
Food-grade polystyrene is manufactured with stringent purity standards, ensuring absence of harmful additives, heavy metals, and contaminants to make it safe for direct food contact. Industrial-grade polystyrene contains higher levels of residual monomers and may include plasticizers or flame retardants unsuitable for food applications. The molecular weight distribution and polymer chain integrity in food-grade polystyrene are optimized to prevent leaching and maintain biocompatibility, contrasting with the less controlled composition of industrial-grade variants.
Regulatory Standards for Food-Grade Polystyrene
Food-grade polystyrene complies with strict regulatory standards set by agencies such as the FDA and EFSA, ensuring it is free from harmful contaminants and safe for direct food contact. This grade undergoes rigorous testing for migration limits of residual monomers and additives to prevent chemical leaching into food products. Industrial-grade polystyrene lacks these certifications and is typically used for applications where direct food contact is not required, prioritizing cost and mechanical properties over safety compliance.
Applications of Food-Grade Polystyrene in Packaging
Food-grade polystyrene is primarily used in packaging applications such as disposable food containers, foam trays, and clamshell packaging due to its safety compliance with FDA regulations for direct food contact. Its lightweight, moisture-resistant, and insulating properties make it ideal for preserving freshness and protecting perishable items during transportation. Industrial-grade polystyrene, by contrast, is utilized for non-food applications like insulation panels and automotive parts, lacking the necessary certifications for food safety.
Industrial-Grade Polystyrene: Uses and Limitations
Industrial-grade polystyrene is widely utilized in manufacturing applications such as automotive parts, electrical housings, and packaging materials due to its rigidity and cost-effectiveness. Its limitations include lower purity levels and the presence of additives that make it unsuitable for direct food contact, differentiating it from food-grade polystyrene which meets strict safety and hygiene standards. The industrial variant's chemical stability and insulating properties make it ideal for non-food applications, but regulatory restrictions prevent its use in consumable products.
Health and Safety Considerations
Food-grade polystyrene is specifically formulated to meet stringent health and safety regulations, ensuring it is free from harmful additives and contaminants, making it safe for direct contact with food. Industrial-grade polystyrene, in contrast, often contains additives or processing agents that can pose health risks if ingested, rendering it unsuitable for food applications. Proper labeling and certification of food-grade polystyrene are critical to prevent chemical leaching and protect consumer health.
Material Properties Comparison
Food-grade polystyrene is manufactured under strict regulatory standards to ensure non-toxicity, high purity, and suitability for direct food contact, featuring enhanced clarity, low residual monomer levels, and resistance to oil and fats. Industrial-grade polystyrene, by contrast, prioritizes mechanical strength and thermal stability, often containing additives that improve durability but may pose contamination risks if used for food applications. The molecular weight distribution and impact resistance differ significantly, with food-grade variants optimized for safety and cleanliness rather than heavy-duty industrial performance.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Food-grade polystyrene is designed to meet strict safety standards for direct food contact and typically contains fewer additives, making it more suitable for recycling and less harmful to the environment compared to industrial-grade polystyrene. Industrial-grade polystyrene often includes additional chemicals and reinforcements that complicate recycling processes and increase environmental pollution risks when improperly disposed of. Recycling programs prioritize food-grade polystyrene due to its higher purity and reduced contamination, contributing to more efficient material recovery and lower environmental impact.
Cost Differences and Market Availability
Food-grade polystyrene is produced under strict regulatory standards, ensuring safety and purity for packaging edible items, which results in higher production costs compared to industrial-grade polystyrene. Industrial-grade polystyrene, utilized for applications such as insulation and manufacturing components, is more widely available and less expensive due to fewer processing requirements and less stringent quality controls. Market availability of food-grade polystyrene is generally limited to suppliers specializing in food packaging, whereas industrial-grade polystyrene benefits from broader distribution channels and a larger volume market.
Choosing the Right Grade for Your Application
Food-grade polystyrene meets strict FDA regulations for safe contact with food and beverages, ensuring non-toxicity and resistance to contamination. Industrial-grade polystyrene offers enhanced mechanical properties and durability, suited for applications like packaging, insulation, and automotive parts where food safety is not a concern. Selecting the appropriate grade depends on whether the end product requires compliance with food safety standards or emphasizes structural strength and cost-effectiveness in non-food industries.
Food-grade Polystyrene vs Industrial-grade Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com