Polystyrene sheets provide a rigid, flat surface ideal for insulation, crafting, and structural applications, offering consistency in thickness and easy cutting. Polystyrene pellets, on the other hand, are small, lightweight, and flexible, commonly used for packaging, stuffing, and as a molding base. Choosing between sheets and pellets depends on the project's need for shape stability versus cushioning and adaptability.
Table of Comparison
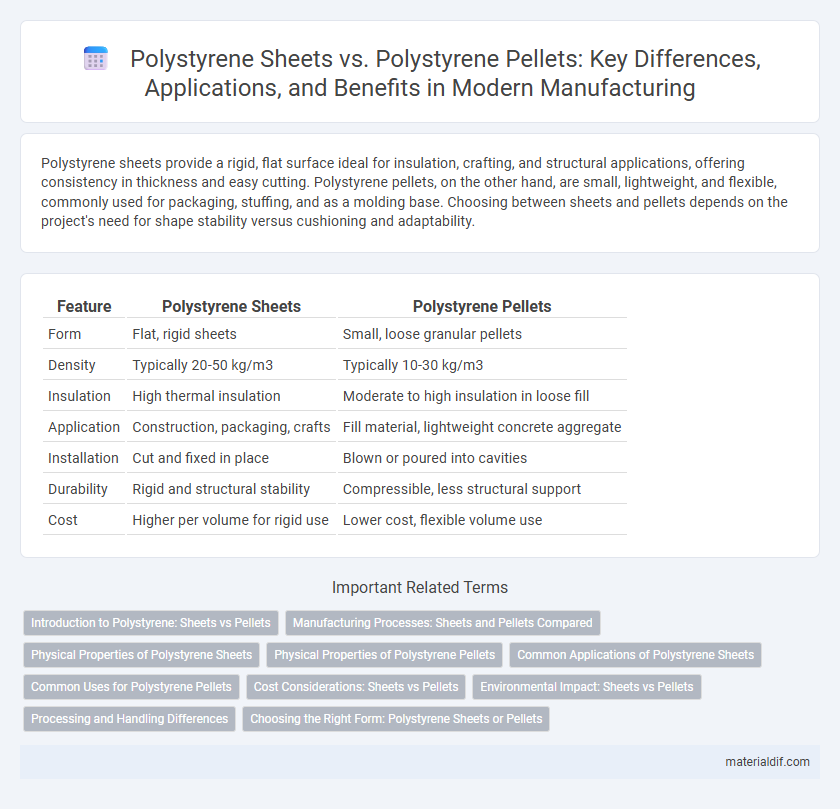
| Feature | Polystyrene Sheets | Polystyrene Pellets |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Flat, rigid sheets | Small, loose granular pellets |
| Density | Typically 20-50 kg/m3 | Typically 10-30 kg/m3 |
| Insulation | High thermal insulation | Moderate to high insulation in loose fill |
| Application | Construction, packaging, crafts | Fill material, lightweight concrete aggregate |
| Installation | Cut and fixed in place | Blown or poured into cavities |
| Durability | Rigid and structural stability | Compressible, less structural support |
| Cost | Higher per volume for rigid use | Lower cost, flexible volume use |
Introduction to Polystyrene: Sheets vs Pellets
Polystyrene sheets offer rigidity and ease of fabrication for applications such as signage, model making, and packaging, while polystyrene pellets serve as a versatile raw material for molding and extrusion processes in manufacturing. The sheets provide uniform thickness and structural stability, making them ideal for flat surfaces and insulation panels. In contrast, pellets allow for customization in shape and density through melting and molding, supporting diverse industrial uses including automotive parts and disposable containers.
Manufacturing Processes: Sheets and Pellets Compared
Polystyrene sheets are produced through an extrusion process where molten polystyrene is forced through a flat die and cooled into continuous, uniform sheets, enabling precise thickness control and smooth surfaces. Polystyrene pellets, on the other hand, are created by pelletizing molten polystyrene into small, uniform bead-like granules used as raw material for various molding and extrusion applications. The manufacturing process of sheets emphasizes dimensional stability and surface quality, while pellets focus on versatility and ease of transport for downstream fabrication.
Physical Properties of Polystyrene Sheets
Polystyrene sheets exhibit a rigid, smooth surface with consistent thickness, offering excellent dimensional stability and high impact resistance compared to polystyrene pellets. These sheets provide superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making them ideal for construction and packaging applications. Unlike pellets, which are granular and used primarily for molding, polystyrene sheets enable precise fabrication and cutting for detailed design work.
Physical Properties of Polystyrene Pellets
Polystyrene pellets exhibit distinct physical properties including uniform size, high durability, and excellent flowability, making them ideal for various manufacturing processes such as injection molding and extrusion. These pellets typically have a low density around 1.04 g/cm3, good thermal resistance up to 100degC, and high clarity in the resulting products. Compared to polystyrene sheets, pellets offer greater versatility in shaping and customization due to their granular form and consistent melting behavior.
Common Applications of Polystyrene Sheets
Polystyrene sheets are widely used in insulation for walls, ceilings, and roofs due to their excellent thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties. They serve as durable substrates in model making, signage, and packaging, offering a rigid, lightweight, and easily cut material. In contrast, polystyrene pellets are primarily utilized in foam manufacturing and injection molding processes for creating lightweight, insulated packaging and container products.
Common Uses for Polystyrene Pellets
Polystyrene pellets are widely used in packaging applications, providing lightweight cushioning and shock absorption for fragile items during shipping. They serve as raw material for injection molding and extrusion processes to create various consumer products like disposable cups, food containers, and insulation panels. Their versatility and ease of molding make them ideal for industrial manufacturing and crafting detailed plastic components.
Cost Considerations: Sheets vs Pellets
Polystyrene sheets typically incur higher upfront costs due to manufacturing processes and material density, making them more expensive per unit area compared to polystyrene pellets. Pellets offer a cost-effective solution for bulk applications, as they are easier to transport, store, and melt down for molding or insulation purposes. Budget planning for projects requiring polystyrene should account for the different cost structures of sheets versus pellets, where pellets generally provide better scalability and lower raw material expenses.
Environmental Impact: Sheets vs Pellets
Polystyrene sheets generate less airborne particulate pollution during manufacturing compared to pellets, which can release microplastic particles into ecosystems when not disposed of properly. Sheets tend to have higher recyclability rates due to their uniform structure, whereas pellets pose greater risks of environmental contamination through spillage and fragmentation. The long degradation period of both forms contributes to persistent environmental challenges, but improved handling of sheets reduces direct soil and water pollution.
Processing and Handling Differences
Polystyrene sheets offer ease of cutting, shaping, and thermoforming, making them ideal for applications requiring precise dimensions and structural rigidity, while polystyrene pellets require melting and molding processes such as injection molding or extrusion for product formation. Handling polystyrene sheets involves minimal equipment, typically involving saws or heat guns, whereas pellets demand specialized machinery to control temperature and pressure during melting to achieve uniform shapes. The processing time for sheets is generally faster due to their ready-to-use form, whereas pellets require longer preparation and cooling cycles to solidify final products.
Choosing the Right Form: Polystyrene Sheets or Pellets
Polystyrene sheets offer rigidity and are ideal for applications requiring structural support or insulation, while polystyrene pellets provide versatility in molding and packaging due to their lightweight and shock-absorbing properties. Selecting the right form depends on the project's requirements for durability, shape complexity, and thermal insulation. Understanding these functional differences ensures optimal material performance in construction, packaging, or manufacturing processes.
Polystyrene Sheets vs Polystyrene Pellets Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com