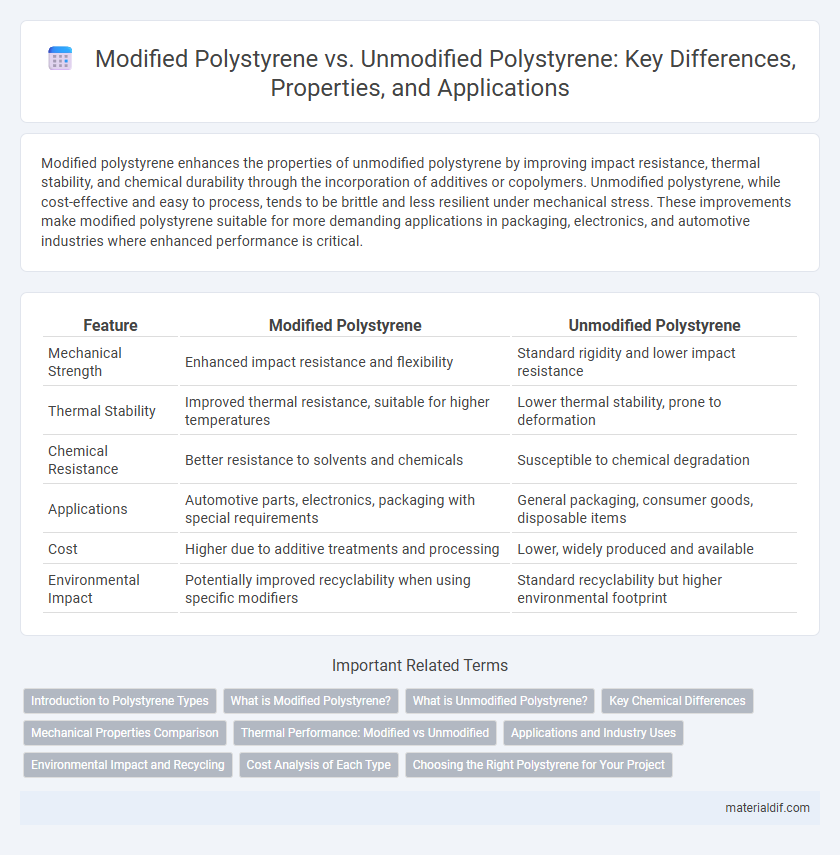
Modified polystyrene enhances the properties of unmodified polystyrene by improving impact resistance, thermal stability, and chemical durability through the incorporation of additives or copolymers. Unmodified polystyrene, while cost-effective and easy to process, tends to be brittle and less resilient under mechanical stress. These improvements make modified polystyrene suitable for more demanding applications in packaging, electronics, and automotive industries where enhanced performance is critical.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modified Polystyrene | Unmodified Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Enhanced impact resistance and flexibility | Standard rigidity and lower impact resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Improved thermal resistance, suitable for higher temperatures | Lower thermal stability, prone to deformation |
| Chemical Resistance | Better resistance to solvents and chemicals | Susceptible to chemical degradation |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, packaging with special requirements | General packaging, consumer goods, disposable items |
| Cost | Higher due to additive treatments and processing | Lower, widely produced and available |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially improved recyclability when using specific modifiers | Standard recyclability but higher environmental footprint |
Introduction to Polystyrene Types
Modified polystyrene incorporates additives or copolymers to enhance impact resistance, thermal stability, and chemical durability compared to unmodified polystyrene, which is rigid and brittle in its basic form. Unmodified polystyrene is widely used for disposable cutlery, CD cases, and insulation due to its clarity and ease of molding, whereas modified variants like high-impact polystyrene (HIPS) serve applications requiring greater toughness, such as in automotive parts and appliance housings. These modifications enable tailored physical properties, expanding polystyrene's functionality across various industrial sectors.
What is Modified Polystyrene?
Modified polystyrene refers to polystyrene that has been chemically or physically altered to improve its properties such as impact resistance, thermal stability, or surface adhesion, compared to unmodified polystyrene. Common modifications include copolymerization with rubber or other monomers, grafting, or blending with additives to enhance flexibility, durability, and application range. These enhancements enable modified polystyrene to be used in more demanding applications like automotive parts, protective packaging, and consumer electronics.
What is Unmodified Polystyrene?
Unmodified polystyrene is a thermoplastic polymer derived from the styrene monomer, characterized by its rigid structure, transparency, and brittleness. It lacks any chemical or physical modifications that enhance its properties, resulting in limited impact resistance and low heat tolerance. This basic form is primarily used in applications such as disposable cutlery, CD cases, and insulation materials where cost-effectiveness and ease of processing are prioritized over mechanical strength.
Key Chemical Differences
Modified polystyrene incorporates additives or copolymers that alter its molecular structure, enhancing properties such as impact resistance, thermal stability, and chemical durability compared to unmodified polystyrene. Unmodified polystyrene consists primarily of polystyrene chains with a rigid, brittle nature due to its linear polymeric structure without functionalized groups or plasticizers. The introduction of rubber copolymers or chemical modifiers creates a more flexible, tougher polymer matrix in modified polystyrene, while unmodified polystyrene remains a homopolymer with limited mechanical performance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Modified polystyrene exhibits enhanced mechanical properties compared to unmodified polystyrene, including increased impact resistance and improved tensile strength. Additives such as rubber or fiber reinforcements in modified polystyrene contribute to greater toughness and flexibility, reducing brittleness typical of unmodified variants. As a result, modified polystyrene is preferred in applications requiring durability and resistance to mechanical stress.
Thermal Performance: Modified vs Unmodified
Modified polystyrene exhibits enhanced thermal performance compared to unmodified polystyrene, featuring improved insulation properties and higher heat resistance. Chemical additives or copolymerization techniques alter the polymer structure, reducing thermal conductivity and increasing stability under elevated temperatures. These modifications make it suitable for applications requiring superior thermal management, such as in building insulation and electronic packaging.
Applications and Industry Uses
Modified polystyrene exhibits enhanced thermal stability, impact resistance, and chemical durability compared to unmodified polystyrene, making it suitable for automotive components, electrical housings, and medical devices. Unmodified polystyrene's rigidity and low cost favor its widespread use in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation materials. Industries such as electronics, healthcare, and construction often choose modified polystyrene for high-performance applications, while food packaging and consumer goods primarily rely on unmodified variants for economical solutions.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Modified polystyrene often contains additives or copolymers that enhance its properties but can complicate recycling processes and reduce material purity. Unmodified polystyrene, being a more homogeneous polymer, is easier to recycle and typically generates less environmental waste during processing. Environmental impact assessments show that modified variants tend to have higher energy demands and potential toxicity concerns due to additives, whereas unmodified polystyrene offers more straightforward end-of-life management and lower ecological risk.
Cost Analysis of Each Type
Modified polystyrene typically incurs higher production costs due to the incorporation of additives or blending agents that enhance properties like impact resistance or thermal stability, leading to increased raw material and processing expenses. Unmodified polystyrene has lower manufacturing costs, making it a more economical option for applications where standard mechanical and thermal properties are sufficient. The cost difference between modified and unmodified polystyrene directly affects product pricing, with modified variants offering performance benefits at a premium price point.
Choosing the Right Polystyrene for Your Project
Modified polystyrene offers enhanced properties such as increased impact resistance, improved thermal stability, and better chemical resistance compared to unmodified polystyrene, making it ideal for demanding applications like automotive parts and packaging. Unmodified polystyrene provides excellent clarity and ease of processing, suitable for applications requiring lightweight and cost-effective materials such as disposable cutlery and CD cases. Selecting the right polystyrene depends on project-specific requirements regarding strength, durability, and visual appearance to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Modified polystyrene vs Unmodified polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com