Thermoformed polystyrene offers thinner, more flexible sheets ideal for packaging and disposable containers, while injection molded polystyrene provides denser, more rigid parts suitable for durable goods and precision components. Thermoforming involves heating a plastic sheet and shaping it over a mold, creating lightweight and cost-effective products with rapid turnaround. Injection molding injects molten polystyrene into a mold cavity, producing complex geometries with uniform strength and high structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
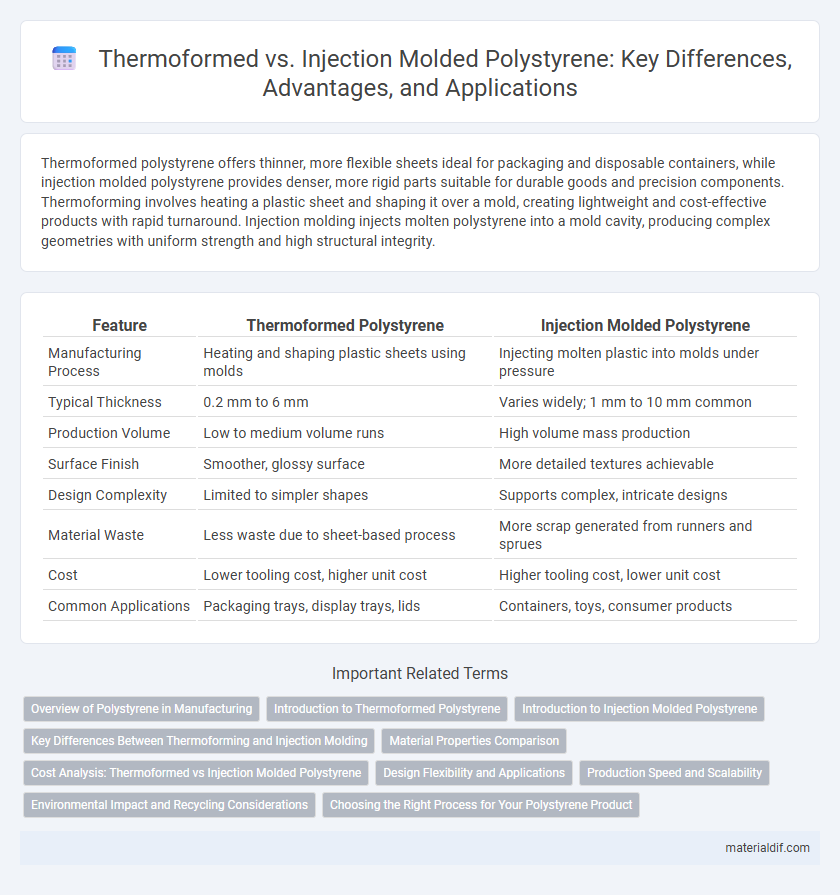
| Feature | Thermoformed Polystyrene | Injection Molded Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Heating and shaping plastic sheets using molds | Injecting molten plastic into molds under pressure |
| Typical Thickness | 0.2 mm to 6 mm | Varies widely; 1 mm to 10 mm common |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume runs | High volume mass production |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, glossy surface | More detailed textures achievable |
| Design Complexity | Limited to simpler shapes | Supports complex, intricate designs |
| Material Waste | Less waste due to sheet-based process | More scrap generated from runners and sprues |
| Cost | Lower tooling cost, higher unit cost | Higher tooling cost, lower unit cost |
| Common Applications | Packaging trays, display trays, lids | Containers, toys, consumer products |
Overview of Polystyrene in Manufacturing
Thermoformed polystyrene offers flexibility in producing large, thin-walled parts by heating and shaping sheets, making it ideal for packaging and displays. Injection molded polystyrene provides high precision and complex geometries with rapid cycle times, suited for detailed components and mass production. Both methods utilize polystyrene's lightweight, rigidity, and cost-effectiveness, impacting choices based on design complexity and production volume.
Introduction to Thermoformed Polystyrene
Thermoformed polystyrene is produced by heating polystyrene sheets until pliable, then shaping them over molds using vacuum or pressure. This process is ideal for creating lightweight, rigid packaging and disposable trays with consistent wall thickness and smooth surfaces. Unlike injection molding, thermoforming offers faster production cycles and lower tooling costs, making it suitable for medium to large part sizes.
Introduction to Injection Molded Polystyrene
Injection molded polystyrene offers precise dimensional accuracy and high production efficiency, making it ideal for complex and detailed components. This process involves injecting molten polystyrene into a mold cavity, allowing for rapid cooling and solidification that ensures consistent part quality. Its superior surface finish and ability to produce large volumes at lower cycle times differentiate it from thermoformed polystyrene products.
Key Differences Between Thermoforming and Injection Molding
Thermoformed polystyrene involves heating plastic sheets until pliable and then shaping them using molds, ideal for producing large, thin-walled parts with lower tooling costs. Injection molded polystyrene requires melting plastic pellets and injecting them into precision molds, enabling complex geometries, high dimensional accuracy, and faster production rates. Key differences include material waste (thermoforming generates less scrap), mold complexity, surface finish quality, and suitability for high-volume versus custom or intricate components.
Material Properties Comparison
Thermoformed polystyrene typically offers greater flexibility and lower material density, making it ideal for lightweight packaging and disposable containers, whereas injection molded polystyrene provides superior rigidity, higher impact resistance, and enhanced dimensional stability suitable for complex, durable parts. Injection molding achieves finer surface detail and tighter tolerances due to high-pressure processing, while thermoforming is better for cost-effective, large-area components with moderate mechanical strength. Both methods utilize the same base polymer, but processing techniques significantly influence properties like tensile strength, heat resistance, and elongation at break.
Cost Analysis: Thermoformed vs Injection Molded Polystyrene
Thermoformed polystyrene typically incurs lower initial tooling costs compared to injection molded polystyrene, making it cost-effective for small to medium production runs. Injection molding requires higher upfront investment in molds but offers lower per-unit costs and faster cycle times for large-scale manufacturing. The overall cost efficiency depends on production volume, with thermoforming favored for short runs and injection molding benefiting high-volume applications due to economies of scale.
Design Flexibility and Applications
Thermoformed polystyrene offers greater design flexibility for creating large, lightweight, and custom-shaped parts, making it ideal for packaging trays, display cases, and automotive interior panels. Injection molded polystyrene excels in producing highly detailed, complex geometries with tight tolerances, commonly used in consumer goods, electronics housings, and medical devices. Both methods cater to different application needs based on design complexity, production volume, and part durability requirements.
Production Speed and Scalability
Thermoformed polystyrene offers faster production speeds due to its ability to quickly shape sheets into custom forms, making it ideal for lower volume runs and prototype development. Injection molded polystyrene supports high scalability by producing complex parts with consistent quality in large volumes, driven by automated cycles that reduce per-unit time. Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial setup time against long-term production demands and cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Considerations
Thermoformed polystyrene typically generates less waste during production compared to injection molded polystyrene, which involves higher material usage and energy consumption. Both forms are recyclable; however, thermoformed polystyrene is often easier to recycle due to its thinner gauge and less complex structure, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Proper recycling facilities and separation processes are crucial to effectively reclaim polystyrene materials and reduce their environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Polystyrene Product
Thermoformed polystyrene offers cost-effective production for large, thin-walled parts with moderate strength requirements, making it ideal for packaging and disposable items. Injection molded polystyrene provides high precision, complex geometries, and superior mechanical properties, suitable for durable consumer products and detailed components. Selecting the right process depends on factors like product complexity, volume, desired strength, and budget constraints to optimize performance and manufacturing efficiency.
Thermoformed Polystyrene vs Injection Molded Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com