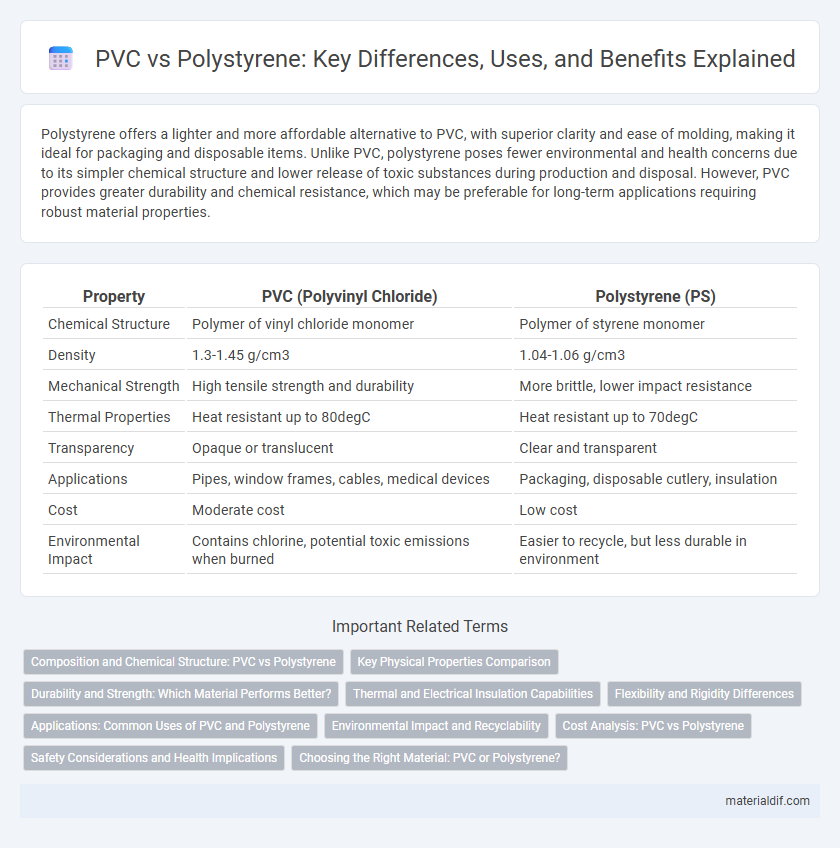
Polystyrene offers a lighter and more affordable alternative to PVC, with superior clarity and ease of molding, making it ideal for packaging and disposable items. Unlike PVC, polystyrene poses fewer environmental and health concerns due to its simpler chemical structure and lower release of toxic substances during production and disposal. However, PVC provides greater durability and chemical resistance, which may be preferable for long-term applications requiring robust material properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Polymer of vinyl chloride monomer | Polymer of styrene monomer |
| Density | 1.3-1.45 g/cm3 | 1.04-1.06 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | More brittle, lower impact resistance |
| Thermal Properties | Heat resistant up to 80degC | Heat resistant up to 70degC |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Applications | Pipes, window frames, cables, medical devices | Packaging, disposable cutlery, insulation |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Low cost |
| Environmental Impact | Contains chlorine, potential toxic emissions when burned | Easier to recycle, but less durable in environment |
Composition and Chemical Structure: PVC vs Polystyrene
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a polymer composed of repeating vinyl chloride units featuring a carbon-carbon backbone with chlorine atoms attached, contributing to its rigidity and chemical resistance. Polystyrene consists of styrene monomers forming a hydrocarbon chain with phenyl side groups, which impart rigidity and transparency. The presence of chlorine in PVC's structure differentiates it chemically from polystyrene's purely hydrocarbon composition, influencing their thermal properties and applications.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polystyrene exhibits lower density, around 1.05 g/cm3, compared to PVC's 1.38 g/cm3, making it lighter and more suitable for applications requiring less weight. Polystyrene has a higher rigidity and brittleness, with a tensile strength of approximately 50 MPa, whereas PVC offers greater flexibility and impact resistance, with tensile strength near 55 MPa. Thermal properties show polystyrene's lower heat distortion temperature at about 95degC, contrasting with PVC's higher resistance up to 80-85degC when plasticized, influencing their suitability in heat-exposed environments.
Durability and Strength: Which Material Performs Better?
Polystyrene offers rigid structure but lacks the impact resistance that PVC provides, making PVC more durable for applications requiring toughness. PVC's greater tensile strength and flexibility contribute to its superior performance under stress and environmental exposure. For long-term durability and strength, PVC typically outperforms polystyrene in most practical uses.
Thermal and Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polystyrene offers superior thermal insulation compared to PVC, with a lower thermal conductivity typically around 0.033-0.040 W/m*K, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient temperature control. In electrical insulation, polystyrene exhibits excellent dielectric properties, including a high dielectric strength of approximately 18-21 kV/mm, surpassing the insulation capabilities of PVC. These characteristics make polystyrene a preferred choice in electronics and building insulation where both thermal and electrical resistances are critical.
Flexibility and Rigidity Differences
Polystyrene exhibits higher rigidity compared to PVC, making it ideal for applications requiring structural stability and brittleness resistance. PVC offers greater flexibility and impact resistance, which suits products needing durability and bending capability, such as pipes and cables. The inherent differences in polymer chain structure result in polystyrene's stiffness versus PVC's elastomeric properties.
Applications: Common Uses of PVC and Polystyrene
PVC is widely used in construction for pipes, window frames, and electrical cable insulation due to its durability and chemical resistance. Polystyrene finds common applications in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation materials because of its lightweight and excellent thermal insulation properties. Both polymers serve distinct markets, with PVC favored for structural uses and polystyrene preferred for lightweight, protective, and insulating functions.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene produces fewer toxic emissions during manufacturing compared to PVC, which releases hazardous dioxins and chlorine compounds, posing greater environmental risks. Polystyrene's recyclability is limited due to its lightweight structure and contamination issues, while PVC offers more established recycling streams but creates harmful byproducts if not processed correctly. Choosing polystyrene or PVC significantly affects environmental sustainability, with both requiring improved recycling technologies to reduce landfill burden and pollution.
Cost Analysis: PVC vs Polystyrene
PVC generally offers a lower initial material cost compared to polystyrene, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale construction and manufacturing projects. Polystyrene, while typically more expensive upfront, provides better thermal insulation properties which can reduce long-term energy expenses and offset higher initial costs. When evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and energy savings, polystyrene often delivers superior value despite its higher material price.
Safety Considerations and Health Implications
Polystyrene and PVC differ significantly in safety considerations and health implications; polystyrene is generally considered safer for consumer products as it does not release harmful chlorine-based compounds when burned, unlike PVC which emits toxic dioxins and hydrochloric acid. Polystyrene's low chemical reactivity reduces risks of exposure to hazardous substances, whereas PVC's production and disposal involve potential carcinogens and respiratory irritants impacting both environmental and human health. Regulatory agencies often favor polystyrene in food packaging and medical uses due to its inertness and lower toxicity profile compared to PVC.
Choosing the Right Material: PVC or Polystyrene?
Polystyrene offers excellent clarity and rigidity, making it ideal for packaging and disposable consumer products, while PVC provides superior chemical resistance and durability for construction and piping applications. PVC's resistance to environmental stress and weathering surpasses that of polystyrene, which tends to be more brittle and less UV stable. Selecting between PVC and polystyrene depends on the required mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and end-use application to ensure optimal performance.
PVC vs Polystyrene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com