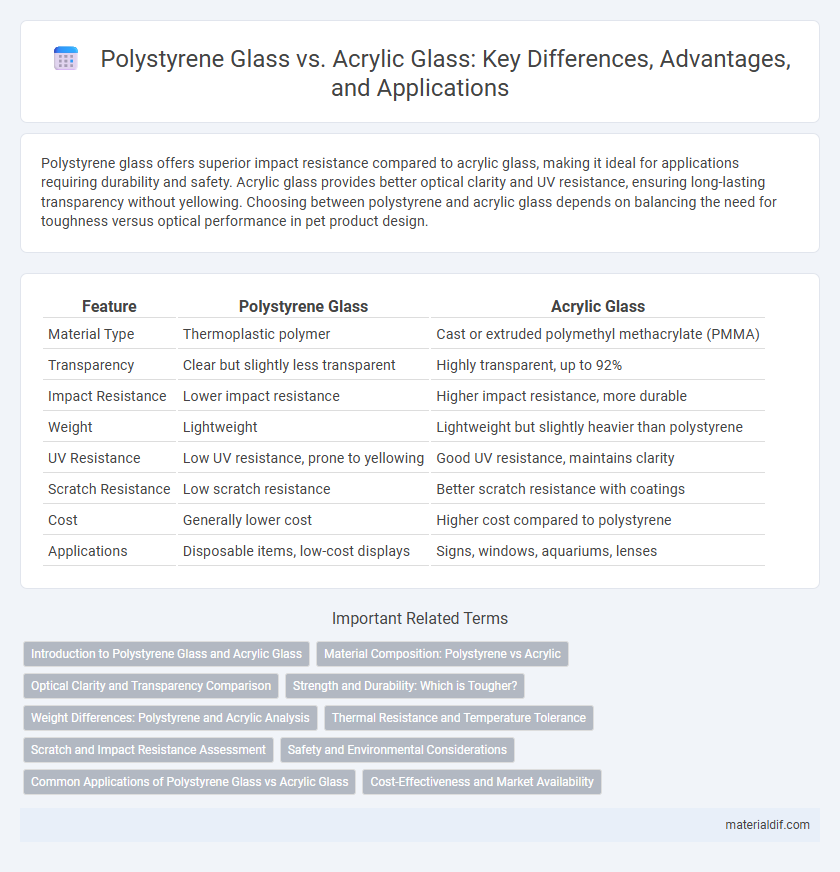
Polystyrene glass offers superior impact resistance compared to acrylic glass, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and safety. Acrylic glass provides better optical clarity and UV resistance, ensuring long-lasting transparency without yellowing. Choosing between polystyrene and acrylic glass depends on balancing the need for toughness versus optical performance in pet product design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polystyrene Glass | Acrylic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Cast or extruded polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) |
| Transparency | Clear but slightly less transparent | Highly transparent, up to 92% |
| Impact Resistance | Lower impact resistance | Higher impact resistance, more durable |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but slightly heavier than polystyrene |
| UV Resistance | Low UV resistance, prone to yellowing | Good UV resistance, maintains clarity |
| Scratch Resistance | Low scratch resistance | Better scratch resistance with coatings |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost compared to polystyrene |
| Applications | Disposable items, low-cost displays | Signs, windows, aquariums, lenses |
Introduction to Polystyrene Glass and Acrylic Glass
Polystyrene glass, a lightweight and cost-effective thermoplastic, offers good impact resistance and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for budget-conscious applications requiring clarity. Acrylic glass, also known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), provides superior optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, favored in high-performance glazing and display uses. Both materials serve as versatile alternatives to traditional glass, differing primarily in durability, transparency, and environmental resilience.
Material Composition: Polystyrene vs Acrylic
Polystyrene glass is composed of polystyrene polymers, offering a lightweight, rigid material with moderate impact resistance, while acrylic glass, made from polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), provides superior clarity and higher resistance to UV light and weathering. Polystyrene's chemical structure results in lower tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to acrylic, making it more suitable for short-term applications or indoor use. Acrylic glass's material composition enhances durability and clarity, often preferred for outdoor displays and applications requiring long-lasting optical performance.
Optical Clarity and Transparency Comparison
Polystyrene glass offers excellent optical clarity with a light transmittance of around 92%, making it suitable for display cases and packaging. Acrylic glass surpasses polystyrene with superior transparency, boasting a light transmittance of approximately 93-98%, and exhibits better resistance to yellowing and UV degradation. This enhanced clarity and durability make acrylic the preferred choice for applications requiring long-term optical performance.
Strength and Durability: Which is Tougher?
Polystyrene glass offers moderate strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for lightweight applications but less durable under heavy stress compared to acrylic glass. Acrylic glass exhibits superior toughness and enhanced durability with high resistance to cracking and weathering, ideal for demanding environments requiring long-lasting clarity. When comparing strength and durability, acrylic glass outperforms polystyrene glass in toughness, maintaining structural integrity over extended use.
Weight Differences: Polystyrene and Acrylic Analysis
Polystyrene glass weighs significantly less than acrylic glass, with polystyrene density around 1.05 g/cm3 compared to acrylic's 1.18 g/cm3, making polystyrene a lighter alternative for weight-sensitive applications. This weight difference translates to easier handling and reduced transportation costs in industries such as signage and display manufacturing. The lower density of polystyrene also impacts its mechanical properties, often making acrylic preferable when higher strength-to-weight ratio is required despite the additional weight.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Polystyrene glass exhibits lower thermal resistance compared to acrylic glass, with a maximum temperature tolerance around 80degC, making it less suitable for high-heat applications. Acrylic glass, also known as PMMA, withstands higher temperatures up to approximately 160degC, offering superior thermal stability and resistance to deformation under heat. This makes acrylic glass preferable over polystyrene for applications requiring greater temperature tolerance and durability under thermal stress.
Scratch and Impact Resistance Assessment
Polystyrene glass exhibits superior scratch resistance compared to acrylic glass, making it more suitable for applications where surface durability is critical. However, acrylic glass outperforms polystyrene glass in impact resistance, providing better resistance to cracking and shattering under stress. Evaluating both materials for scratch and impact resistance is essential to determine the optimal choice for protective glazing and display applications.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Polystyrene glass, also known as PS, is more brittle and prone to cracking compared to acrylic glass, which offers superior impact resistance and durability, enhancing safety in various applications. Environmentally, polystyrene is less recyclable and takes longer to degrade, contributing to persistent plastic pollution, whereas acrylic glass, although also a plastic, can be recycled more effectively and has a longer lifespan, reducing waste generation. Both materials pose challenges in terms of chemical leaching and environmental impact, but acrylic glass's enhanced recyclability offers a slight advantage in sustainability efforts.
Common Applications of Polystyrene Glass vs Acrylic Glass
Polystyrene glass is commonly used in disposable cutlery, food packaging, and CD cases due to its cost-effectiveness and rigidity, while acrylic glass is favored for display cases, signage, and aquariums because of its superior optical clarity and impact resistance. Polystyrene's ease of molding supports its application in promotional items and containers, whereas acrylic glass's weather resistance makes it ideal for outdoor applications such as skylights and storefront windows. Both materials serve diverse purposes, but acrylic glass is preferred where durability and transparency are critical, contrasting with polystyrene's widespread use in single-use or less demanding products.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polystyrene glass is significantly more cost-effective than acrylic glass, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious projects and high-volume production. Its widespread market availability ensures easy sourcing and quick turnaround times compared to acrylic glass, which tends to be pricier and less readily accessible. Polystyrene's affordability and strong supply chain position it as a pragmatic alternative in applications requiring transparent materials.
Polystyrene Glass vs Acrylic Glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com