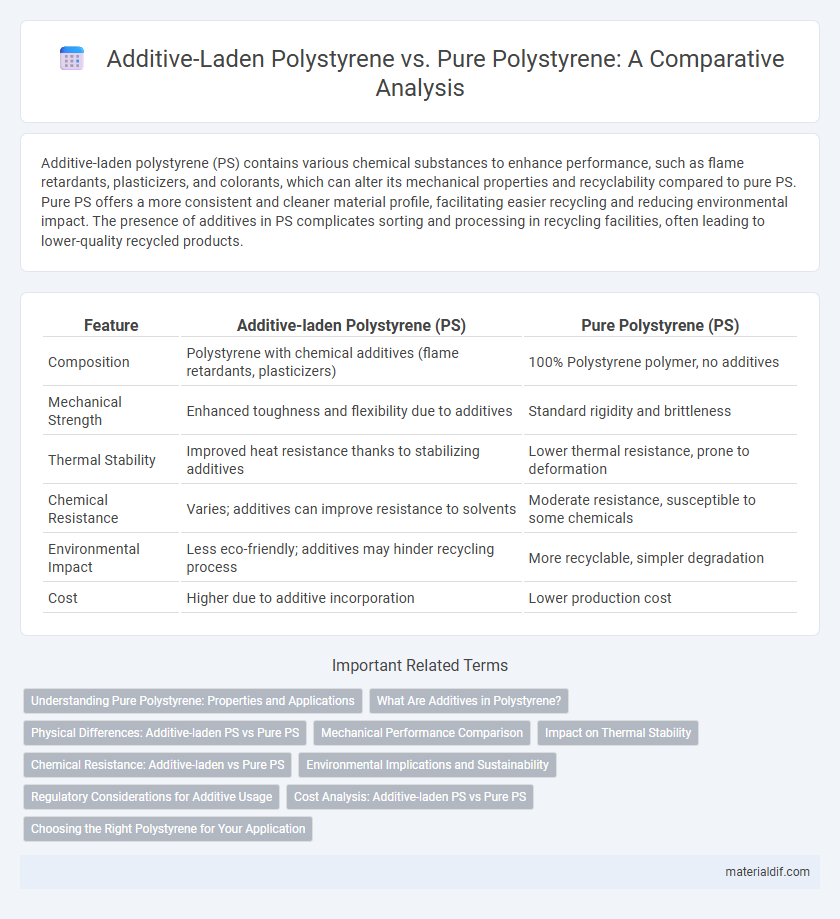
Additive-laden polystyrene (PS) contains various chemical substances to enhance performance, such as flame retardants, plasticizers, and colorants, which can alter its mechanical properties and recyclability compared to pure PS. Pure PS offers a more consistent and cleaner material profile, facilitating easier recycling and reducing environmental impact. The presence of additives in PS complicates sorting and processing in recycling facilities, often leading to lower-quality recycled products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Additive-laden Polystyrene (PS) | Pure Polystyrene (PS) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polystyrene with chemical additives (flame retardants, plasticizers) | 100% Polystyrene polymer, no additives |
| Mechanical Strength | Enhanced toughness and flexibility due to additives | Standard rigidity and brittleness |
| Thermal Stability | Improved heat resistance thanks to stabilizing additives | Lower thermal resistance, prone to deformation |
| Chemical Resistance | Varies; additives can improve resistance to solvents | Moderate resistance, susceptible to some chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Less eco-friendly; additives may hinder recycling process | More recyclable, simpler degradation |
| Cost | Higher due to additive incorporation | Lower production cost |
Understanding Pure Polystyrene: Properties and Applications
Pure polystyrene is a versatile thermoplastic known for its rigidity, clarity, and excellent insulating properties, making it ideal for applications such as packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation panels. Unlike additive-laden polystyrene, which may contain flame retardants, plasticizers, or colorants that alter its mechanical and thermal characteristics, pure polystyrene retains consistent chemical stability and recyclability. Its transparency and ease of molding enable its widespread use in consumer products requiring lightweight, durable, and cost-effective materials.
What Are Additives in Polystyrene?
Additives in polystyrene are chemical compounds incorporated during manufacturing to enhance properties such as flexibility, UV resistance, flame retardancy, and color. Common additives include plasticizers, stabilizers, antioxidants, and flame retardants, which modify the physical and chemical behavior of the polymer. Additive-laden PS typically exhibits improved performance characteristics compared to pure polystyrene, which lacks these enhancements and often shows greater brittleness and lower durability.
Physical Differences: Additive-laden PS vs Pure PS
Additive-laden polystyrene (PS) exhibits enhanced mechanical properties such as increased impact resistance and improved thermal stability compared to pure PS, which is more brittle and prone to deformation under stress. The presence of plasticizers, flame retardants, and UV stabilizers in additive-laden PS alters its density and reduces its glass transition temperature. Pure PS maintains higher optical clarity and rigidity but lacks the durability and flexibility imparted by these additives.
Mechanical Performance Comparison
Additive-laden polystyrene (PS) shows enhanced mechanical properties compared to pure PS, with improved impact resistance and tensile strength due to the incorporation of plasticizers, fillers, or reinforcements. Pure PS tends to be brittle and exhibits lower elongation at break, while additives increase flexibility and durability under stress. These mechanical enhancements make additive-laden PS more suitable for applications requiring toughness and resilience, such as packaging and automotive components.
Impact on Thermal Stability
Additive-laden polystyrene (PS) typically exhibits enhanced thermal stability compared to pure PS due to the presence of flame retardants, plasticizers, and UV stabilizers that delay decomposition and reduce heat release rates. Pure polystyrene degrades at lower temperatures, generally starting around 270degC, whereas additives can increase the onset of thermal degradation to above 300degC. The choice and concentration of additives directly influence the char formation and volatile emission, significantly improving fire resistance and thermal performance of the polymer.
Chemical Resistance: Additive-laden vs Pure PS
Additive-laden polystyrene often exhibits enhanced chemical resistance compared to pure polystyrene due to the incorporation of stabilizers, antioxidants, and plasticizers that mitigate degradation from solvents and environmental factors. Pure PS is more prone to swelling, cracking, or dissolving when exposed to strong solvents like acetone, benzene, or toluene. The additives improve durability and extend the material's usability in chemically aggressive environments.
Environmental Implications and Sustainability
Additive-laden polystyrene contains flame retardants, plasticizers, and colorants that complicate recycling processes and increase toxic leachate risks during decomposition, posing greater environmental hazards compared to pure polystyrene. Pure PS, being chemically simpler, offers enhanced recyclability and reduced pollutant output, contributing to improved sustainability outcomes. Selecting pure polystyrene in manufacturing and packaging reduces ecological impact by facilitating closed-loop recycling and minimizing hazardous waste accumulation.
Regulatory Considerations for Additive Usage
Regulatory considerations for additive-laden polystyrene (PS) focus on stringent safety and environmental impact assessments to ensure compliance with agencies such as the FDA and EPA. Pure PS typically faces fewer regulatory hurdles due to the absence of chemicals that can leach or degrade, whereas additives like flame retardants, plasticizers, and colorants must meet specific migration limits and toxicity standards. Compliance with REACH in Europe and TSCA in the United States drives manufacturers to rigorously evaluate additive formulations to guarantee product safety and regulatory acceptance.
Cost Analysis: Additive-laden PS vs Pure PS
Additive-laden polystyrene incurs higher production costs due to the expense of specialty additives like flame retardants, plasticizers, and colorants compared to pure polystyrene. These additives increase material complexity and can raise recycling and disposal expenses by impacting processability and contaminant levels. Conversely, pure polystyrene offers lower raw material costs and simpler processing, but lacks enhanced properties that additives provide, affecting performance in specialized applications.
Choosing the Right Polystyrene for Your Application
Additive-laden polystyrene offers enhanced properties such as increased impact resistance, UV stability, and flame retardancy compared to pure polystyrene, making it suitable for demanding applications like automotive parts and electronic housings. Pure polystyrene provides excellent clarity, rigidity, and ease of processing, ideal for packaging, disposable cutlery, and laboratory equipment where purity and transparency are critical. Selecting the right polystyrene depends on balancing mechanical performance, environmental exposure, and regulatory requirements specific to the intended use.
Additive-laden PS vs Pure PS Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com