Polypropylene fiber offers superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to polypropylene pellets, making it ideal for textile and reinforcement applications. While polypropylene pellets serve as the raw material for molding and extrusion processes, fibers provide enhanced durability and resistance to wear in finished products. Selecting between polypropylene fiber and pellet depends on the desired end-use properties, such as mechanical performance and manufacturing method.
Table of Comparison
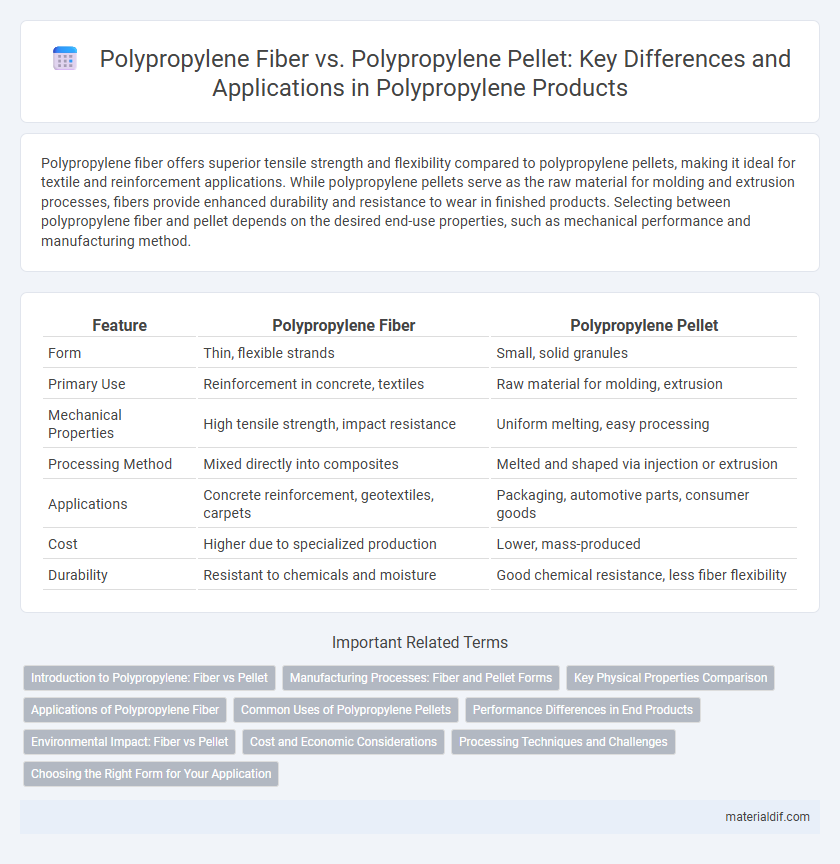
| Feature | Polypropylene Fiber | Polypropylene Pellet |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Thin, flexible strands | Small, solid granules |
| Primary Use | Reinforcement in concrete, textiles | Raw material for molding, extrusion |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength, impact resistance | Uniform melting, easy processing |
| Processing Method | Mixed directly into composites | Melted and shaped via injection or extrusion |
| Applications | Concrete reinforcement, geotextiles, carpets | Packaging, automotive parts, consumer goods |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized production | Lower, mass-produced |
| Durability | Resistant to chemicals and moisture | Good chemical resistance, less fiber flexibility |
Introduction to Polypropylene: Fiber vs Pellet
Polypropylene fiber and polypropylene pellet represent two primary forms of polypropylene used in diverse industrial applications. Polypropylene fiber offers enhanced tensile strength, flexibility, and is widely used in textiles, geotextiles, and reinforcement materials due to its fibrous structure. In contrast, polypropylene pellets serve as the raw material in injection molding and extrusion processes, providing ease of handling and versatility for manufacturing various plastic products.
Manufacturing Processes: Fiber and Pellet Forms
Polypropylene fiber is produced through a melt-spinning process where molten polypropylene is extruded into fine filaments and then stretched to align polymer chains, enhancing tensile strength and flexibility. In contrast, polypropylene pellets are manufactured by polymerizing propylene monomers into solid granules used as raw material for various molding and extrusion processes. The fiber form emphasizes continuous filament production for textile and reinforcement applications, while pellets serve as versatile feedstock in plastic manufacturing industries.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene fiber exhibits high tensile strength, low density around 0.91 g/cm3, and excellent elongation at break, making it ideal for textile and reinforcement applications. In contrast, polypropylene pellets share similar chemical composition but offer higher thermal resistance and easier moldability due to their granular form, enabling efficient processing in injection molding and extrusion. Both forms demonstrate impressive chemical resistance and moisture wicking, yet their mechanical properties differ significantly because fibers are drawn and oriented, enhancing strength and flexibility compared to pellets.
Applications of Polypropylene Fiber
Polypropylene fiber is extensively used in construction for concrete reinforcement, enhancing durability and crack resistance through its high tensile strength and chemical stability. It is also widely applied in textiles for producing carpets, upholstery, and non-woven fabrics due to its lightweight, moisture-wicking, and abrasion-resistant properties. In contrast, polypropylene pellets primarily serve as raw materials for injection molding and extrusion in manufacturing various plastic components.
Common Uses of Polypropylene Pellets
Polypropylene pellets are primarily used as raw material in injection molding, extrusion, and blown film processes to manufacture various consumer goods, automotive components, and packaging materials. These pellets offer excellent versatility and durability, making them ideal for producing household items, containers, and fibers. In contrast, polypropylene fiber is mainly utilized in textiles, carpeting, and upholstery for its high tensile strength and resistance to moisture.
Performance Differences in End Products
Polypropylene fiber offers enhanced tensile strength and flexibility, improving durability and resistance to tearing in textiles and composites, whereas polypropylene pellets provide excellent molding versatility for injection molding and extrusion processes. End products made from polypropylene fibers typically exhibit superior impact resistance and dimensional stability, ideal for applications requiring lightweight reinforcement. In contrast, polypropylene pellets enable complex shapes with consistent mechanical properties, making them suitable for automotive parts and packaging materials.
Environmental Impact: Fiber vs Pellet
Polypropylene fibers contribute to microplastic pollution due to their propensity to shed small particles during washing, which can infiltrate aquatic ecosystems and harm marine life. In contrast, polypropylene pellets pose significant environmental risks when spilled during transport or manufacturing, as these pellet losses accumulate in soil and waterways, creating persistent plastic debris. Both forms demand improved management practices to mitigate their distinct environmental impacts associated with microplastic generation and pellet pollution.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Polypropylene fiber generally incurs higher production costs compared to polypropylene pellets due to additional manufacturing processes like spinning and drawing. Polypropylene pellets serve as a raw material for various applications, offering cost efficiency and flexibility in bulk purchasing and processing. Economic considerations favor polypropylene pellets for large-scale industrial use, while polypropylene fibers are preferred for specialized, high-value textile and composite applications despite the higher expense.
Processing Techniques and Challenges
Polypropylene fiber is produced through melt spinning, involving extrusion, cooling, and drawing processes, which require precise control of temperature and mechanical tension to ensure fiber strength and uniformity. Polypropylene pellets serve as the raw material for various molding and extrusion techniques, such as injection molding or film blowing, facing challenges like homogenous melting and preventing degradation due to overheating. Processing polypropylene fiber demands tight regulation of fiber morphology for desired textile properties, whereas pellets necessitate optimization of thermal stability and flow behavior to avoid defects during molding.
Choosing the Right Form for Your Application
Polypropylene fiber offers enhanced tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for composite reinforcements, textiles, and filtration applications. Polypropylene pellets provide versatility in injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding processes due to their ease of melting and consistent flow properties. Selecting the right polypropylene form depends on the required mechanical performance, processing method, and end-use application specificity.
Polypropylene Fiber vs Polypropylene Pellet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com