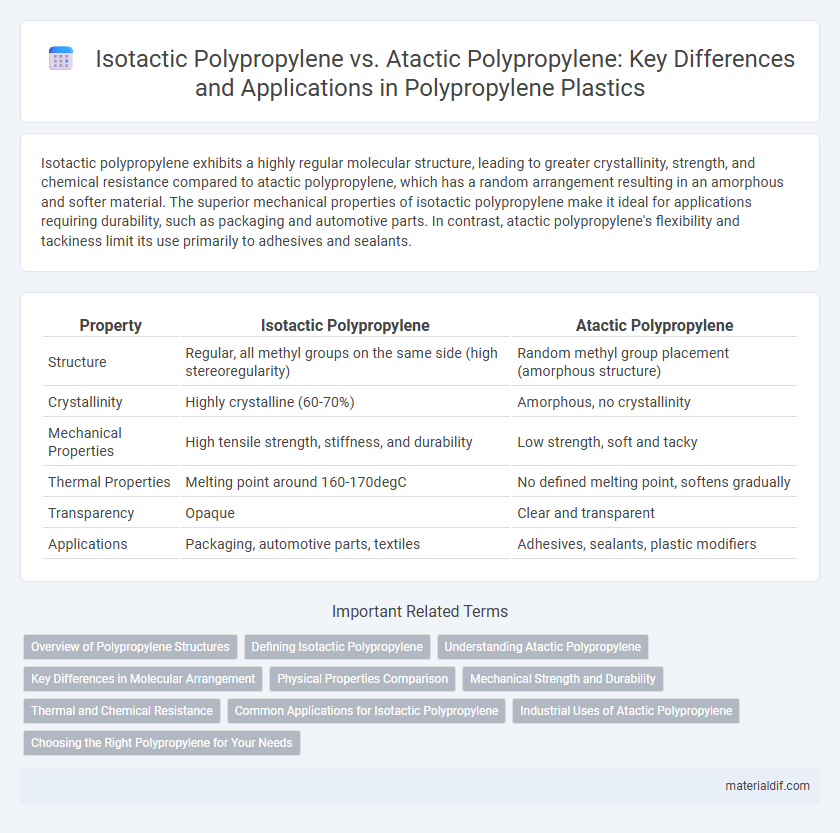
Isotactic polypropylene exhibits a highly regular molecular structure, leading to greater crystallinity, strength, and chemical resistance compared to atactic polypropylene, which has a random arrangement resulting in an amorphous and softer material. The superior mechanical properties of isotactic polypropylene make it ideal for applications requiring durability, such as packaging and automotive parts. In contrast, atactic polypropylene's flexibility and tackiness limit its use primarily to adhesives and sealants.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Isotactic Polypropylene | Atactic Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Regular, all methyl groups on the same side (high stereoregularity) | Random methyl group placement (amorphous structure) |
| Crystallinity | Highly crystalline (60-70%) | Amorphous, no crystallinity |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength, stiffness, and durability | Low strength, soft and tacky |
| Thermal Properties | Melting point around 160-170degC | No defined melting point, softens gradually |
| Transparency | Opaque | Clear and transparent |
| Applications | Packaging, automotive parts, textiles | Adhesives, sealants, plastic modifiers |
Overview of Polypropylene Structures
Isotactic polypropylene features a regular arrangement of methyl groups on the same side of the polymer chain, resulting in a highly crystalline structure with enhanced strength and thermal resistance. Atactic polypropylene has randomly arranged methyl groups, leading to an amorphous, non-crystalline form with lower density and reduced mechanical properties. The structural difference directly impacts polypropylene's application range, making isotactic polypropylene suitable for molded products and fibers, while atactic polypropylene is typically used in adhesives and coatings.
Defining Isotactic Polypropylene
Isotactic polypropylene is a highly crystalline polymer characterized by uniform stereochemistry, with all methyl groups aligned on the same side of the polymer chain, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength and thermal resistance. This regular arrangement facilitates tighter molecular packing, leading to higher density and improved clarity compared to atactic polypropylene, which has random methyl group placement and amorphous structure. Industrial applications of isotactic polypropylene include packaging films, automotive parts, and medical devices, where durability and chemical resistance are critical.
Understanding Atactic Polypropylene
Atactic polypropylene consists of randomly arranged methyl groups along the polymer chain, resulting in an amorphous structure with low crystallinity and reduced mechanical strength compared to isotactic polypropylene. This irregular stereochemistry leads to its tacky, flexible nature and enhances its solubility in organic solvents. Applications of atactic polypropylene primarily involve adhesives, coatings, and as an impact modifier in polymer blends due to its adhesive properties and low melting point.
Key Differences in Molecular Arrangement
Isotactic polypropylene features a regular, repeating arrangement of methyl groups all aligned on the same side of the polymer chain, resulting in a highly crystalline structure. Atactic polypropylene has a random placement of methyl groups along the chain, producing an amorphous and non-crystalline material. This fundamental difference in molecular stereochemistry directly affects their physical properties, with isotactic being rigid and strong, while atactic is flexible and tacky.
Physical Properties Comparison
Isotactic polypropylene exhibits high crystallinity, resulting in greater tensile strength, stiffness, and melting point compared to atactic polypropylene, which is largely amorphous and softer. The regular arrangement of methyl groups in isotactic polypropylene leads to better chemical resistance and higher thermal stability, whereas atactic polypropylene has lower density and flexibility due to its irregular molecular structure. These contrasting physical properties make isotactic polypropylene suitable for rigid packaging and automotive parts, while atactic polypropylene finds applications in adhesives and sealants.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Isotactic polypropylene exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to atactic polypropylene due to its highly crystalline structure, which enhances stiffness and resistance to wear. The regular arrangement of methyl groups in isotactic polypropylene allows for tighter molecular packing, resulting in higher tensile strength and improved impact resistance. In contrast, atactic polypropylene, with its amorphous nature and irregular molecular arrangement, demonstrates lower mechanical integrity and reduced long-term durability under stress.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Isotactic polypropylene exhibits superior thermal resistance, with a melting point around 160-170degC, making it ideal for applications demanding high heat tolerance. Its highly crystalline structure contributes to excellent chemical resistance against acids, bases, and organic solvents. In contrast, atactic polypropylene is amorphous, resulting in lower thermal stability and weaker chemical resistance, limiting its use in environments exposed to heat and aggressive chemicals.
Common Applications for Isotactic Polypropylene
Isotactic polypropylene is widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to its high crystallinity, strength, and thermal resistance. Common applications include rigid containers, automotive bumpers, and household appliances where durability and chemical resistance are essential. In contrast, atactic polypropylene, characterized by its amorphous and rubbery nature, is primarily used as a tackifier or in adhesive formulations.
Industrial Uses of Atactic Polypropylene
Atactic polypropylene (APP), characterized by its amorphous and non-crystalline structure, is primarily used in adhesive formulations and as a tackifier in rubber compounding due to its excellent adhesive properties and compatibility with various polymers. Industrially, APP serves as a modifier in bitumen for roofing membranes and road paving, improving flexibility and weather resistance. Unlike isotactic polypropylene, APP lacks significant mechanical strength but excels in applications requiring tackiness and binding capabilities.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene for Your Needs
Isotactic polypropylene features a highly regular molecular structure, resulting in superior crystallinity, strength, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability like packaging and automotive parts. Atactic polypropylene, with its irregular polymer chain arrangement, exhibits amorphous properties, softness, and tackiness, suitable for adhesives and sealants where flexibility is essential. Selecting the right polypropylene depends on factors such as mechanical performance, thermal stability, and end-use environment, guiding the choice between isotactic's rigidity and atactic's pliability.
Isotactic Polypropylene vs Atactic Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com