Polypropylene Raffia Yarn is known for its flat, ribbon-like structure, making it ideal for packaging, weaving, and sack production due to its high tensile strength and resistance to tearing. In contrast, Polypropylene Multifilament Yarn consists of multiple continuous filaments twisted together, offering superior flexibility and durability suited for textile applications like ropes and fishing nets. Both yarn types provide excellent chemical resistance and moisture-wicking properties, but their distinct physical characteristics determine their best uses in various industrial sectors.
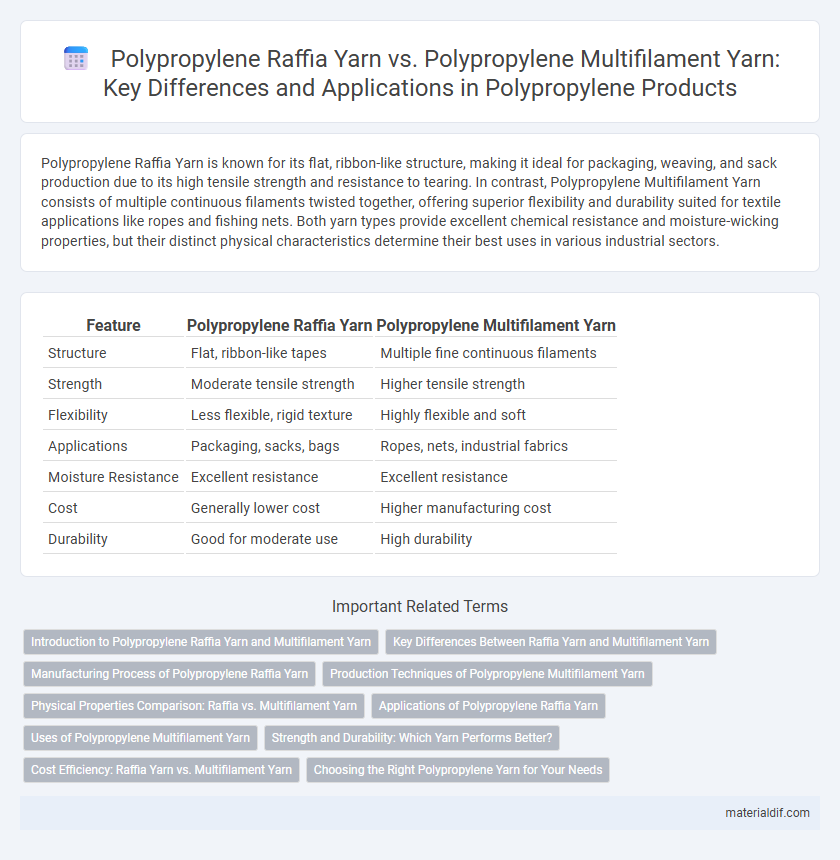
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene Raffia Yarn | Polypropylene Multifilament Yarn |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flat, ribbon-like tapes | Multiple fine continuous filaments |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, rigid texture | Highly flexible and soft |
| Applications | Packaging, sacks, bags | Ropes, nets, industrial fabrics |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent resistance | Excellent resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Durability | Good for moderate use | High durability |
Introduction to Polypropylene Raffia Yarn and Multifilament Yarn
Polypropylene Raffia Yarn is known for its flat, ribbon-like structure primarily used in packaging and agriculture due to its high tensile strength and lightweight properties. Polypropylene Multifilament Yarn consists of numerous fine filaments twisted together, offering enhanced flexibility and durability suited for textiles and industrial applications. Both yarn types leverage polypropylene's resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation, optimizing performance across diverse uses.
Key Differences Between Raffia Yarn and Multifilament Yarn
Polypropylene raffia yarn is characterized by its flat, ribbon-like structure, making it ideal for weaving applications such as sacks and mats, whereas polypropylene multifilament yarn consists of numerous fine continuous filaments twisted together, providing superior strength and flexibility for textiles and industrial uses. Raffia yarn offers excellent moisture resistance and rigidity, suitable for packaging, while multifilament yarn delivers enhanced tensile strength and durability, favored in high-performance fabrics and ropes. The production process also differs, with raffia yarn created through slit film extrusion and multifilament yarn produced by spinning individual filaments followed by texturizing or twisting.
Manufacturing Process of Polypropylene Raffia Yarn
Polypropylene raffia yarn is produced through a unique process involving the extrusion of molten polypropylene into flat tapes that are then slit into narrow ribbons before being stretched to enhance strength and flexibility. This manufacturing technique contrasts with polypropylene multifilament yarn, which is created by extruding continuous filaments and twisting them into yarn. The flat, ribbon-like structure of raffia yarn provides superior stiffness and durability, making it ideal for applications like woven sacks and industrial packaging.
Production Techniques of Polypropylene Multifilament Yarn
Polypropylene multifilament yarn is produced using a melt spinning process where molten polypropylene is extruded through spinnerets to form multiple continuous filaments, which are then drawn to align molecular chains and enhance tensile strength. This production technique results in yarns with high strength, durability, and uniformity, making them suitable for industrial applications such as geotextiles and industrial sewing threads. In contrast, polypropylene raffia yarn is typically manufactured through a slit-film process, which yields flat, wide tapes rather than continuous filaments.
Physical Properties Comparison: Raffia vs. Multifilament Yarn
Polypropylene Raffia yarn features a coarser texture and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications, while Multifilament yarn offers a finer, smoother finish with greater flexibility and elongation. Raffia yarn exhibits lower elongation at break, providing rigid structure, whereas Multifilament yarn's enhanced elasticity contributes to superior abrasion resistance and flexibility. Both yarn types maintain excellent chemical and moisture resistance but differ significantly in physical durability and application suitability due to these contrasting mechanical properties.
Applications of Polypropylene Raffia Yarn
Polypropylene Raffia Yarn is primarily used in packaging, agriculture, and construction sectors due to its high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to moisture. It is commonly utilized in the production of woven sacks, bags, and geotextiles that require cost-effective and lightweight material solutions. Unlike Polypropylene Multifilament Yarn, which is preferred for textiles and industrial fabrics demanding finer finishes, Raffia Yarn excels in heavy-duty applications needing robust and coarse structure.
Uses of Polypropylene Multifilament Yarn
Polypropylene multifilament yarn is extensively used in industrial applications such as geotextiles, agricultural nets, and packaging materials due to its high tensile strength and durability. Its fine filaments provide excellent flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for weaving robust fabrics in upholstery and automotive interiors. Unlike raffia yarn, multifilament yarn offers superior performance in textile production where consistent quality and strength are critical.
Strength and Durability: Which Yarn Performs Better?
Polypropylene multifilament yarn typically exhibits higher tensile strength and superior durability compared to polypropylene raffia yarn due to its finer filaments and enhanced bonding structure. The multifilament yarn's increased resistance to abrasion and environmental stress makes it ideal for applications requiring long-term performance and mechanical robustness. Polypropylene raffia yarn, while strong, generally offers less durability under heavy strain or prolonged exposure to harsh conditions.
Cost Efficiency: Raffia Yarn vs. Multifilament Yarn
Polypropylene raffia yarn offers higher cost efficiency compared to polypropylene multifilament yarn due to its simpler manufacturing process and lower raw material consumption. Raffia yarn is ideal for packaging and agricultural applications where durability at a minimal cost is crucial, whereas multifilament yarn commands a premium for enhanced strength and flexibility in textile and industrial uses. Choosing raffia yarn reduces overall production costs without significantly compromising performance in cost-sensitive markets.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene Yarn for Your Needs
Polypropylene raffia yarn offers excellent durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging, agricultural bags, and heavy-duty wrapping applications. In contrast, polypropylene multifilament yarn provides higher tensile strength, flexibility, and softness, suitable for textiles, geotextiles, and industrial sewing threads. Selecting the right polypropylene yarn depends on balancing factors such as strength requirements, exposure conditions, and desired texture for optimal performance.
Polypropylene Raffia Yarn vs Polypropylene Multifilament Yarn Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com