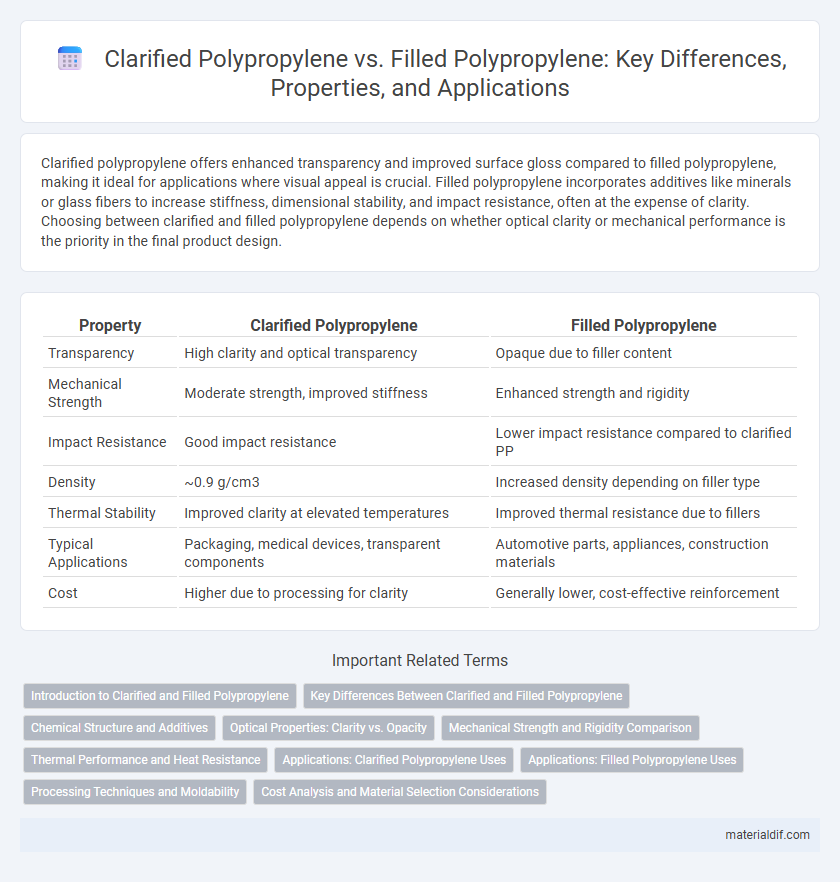
Clarified polypropylene offers enhanced transparency and improved surface gloss compared to filled polypropylene, making it ideal for applications where visual appeal is crucial. Filled polypropylene incorporates additives like minerals or glass fibers to increase stiffness, dimensional stability, and impact resistance, often at the expense of clarity. Choosing between clarified and filled polypropylene depends on whether optical clarity or mechanical performance is the priority in the final product design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Clarified Polypropylene | Filled Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High clarity and optical transparency | Opaque due to filler content |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate strength, improved stiffness | Enhanced strength and rigidity |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance | Lower impact resistance compared to clarified PP |
| Density | ~0.9 g/cm3 | Increased density depending on filler type |
| Thermal Stability | Improved clarity at elevated temperatures | Improved thermal resistance due to fillers |
| Typical Applications | Packaging, medical devices, transparent components | Automotive parts, appliances, construction materials |
| Cost | Higher due to processing for clarity | Generally lower, cost-effective reinforcement |
Introduction to Clarified and Filled Polypropylene
Clarified polypropylene offers enhanced transparency and improved aesthetic appeal due to the addition of clarifying agents that reduce the polymer's crystallinity. Filled polypropylene incorporates mineral fillers such as talc, calcium carbonate, or glass fibers, which significantly increase stiffness, thermal stability, and dimensional stability. Selection between clarified and filled polypropylene depends on end-use requirements like optical clarity versus mechanical strength.
Key Differences Between Clarified and Filled Polypropylene
Clarified polypropylene typically contains nucleating agents that enhance transparency and increase stiffness, making it ideal for applications requiring optical clarity and improved mechanical properties. Filled polypropylene incorporates additives like talc, calcium carbonate, or glass fibers to boost rigidity, heat resistance, and impact strength, often resulting in a more opaque material. The key differences lie in their visual appearance, mechanical enhancements, and targeted application uses, with clarified grades favored for aesthetic appeal and filled grades chosen for structural reinforcement.
Chemical Structure and Additives
Clarified polypropylene contains no fillers and utilizes nucleating agents to enhance clarity by promoting uniform polymer crystallization, resulting in improved transparency and mechanical properties. Filled polypropylene incorporates additives like talc, glass fibers, or calcium carbonate, which alter the polymer's chemical structure by increasing rigidity and dimensional stability but reduce clarity due to light scattering. The choice between clarified and filled polypropylene depends on the desired balance of optical properties and mechanical performance dictated by the type and concentration of additives affecting polymer morphology.
Optical Properties: Clarity vs. Opacity
Clarified polypropylene offers superior optical clarity with high light transmission and minimal haze, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency such as packaging and medical devices. Filled polypropylene, enhanced with additives like glass or calcium carbonate, exhibits increased opacity and improved mechanical strength but sacrifices clarity. The choice between clarified and filled polypropylene depends on whether optical transparency or opacity and reinforcement are prioritized in the end-use.
Mechanical Strength and Rigidity Comparison
Clarified polypropylene exhibits enhanced transparency and moderate mechanical strength, making it suitable for applications requiring visual appeal alongside durability. Filled polypropylene, typically reinforced with glass fibers or mineral fillers, offers significantly higher mechanical strength and rigidity, improving impact resistance and structural stability. The choice depends on whether the priority is optical clarity or superior mechanical performance in demanding environments.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Clarified polypropylene exhibits improved thermal performance due to its enhanced clarity and reduced crystallinity, which allows for better light transmission and heat dissipation. Filled polypropylene, reinforced with materials such as talc or glass fibers, offers superior heat resistance and dimensional stability under high-temperature conditions. Both types are selected based on specific application requirements, with clarified polypropylene favored for optical and aesthetic purposes, while filled polypropylene is preferred for mechanical strength and thermal durability.
Applications: Clarified Polypropylene Uses
Clarified polypropylene is widely used in packaging applications requiring high transparency, such as food containers, medical packaging, and consumer goods, due to its excellent optical clarity and chemical resistance. It is favored for manufacturing clear films, lids, and containers where product visibility is crucial. In contrast to filled polypropylene, which enhances mechanical properties and heat resistance, clarified polypropylene emphasizes aesthetic appeal and transparency for packaging solutions.
Applications: Filled Polypropylene Uses
Filled polypropylene is extensively used in automotive components, offering enhanced rigidity and thermal stability for parts such as dashboards, bumpers, and under-the-hood applications. Its improved mechanical properties make it ideal for construction materials, including pipes, fittings, and protective coatings, where resistance to wear and impact is critical. Additionally, filled polypropylene finds applications in electrical housings and consumer goods, providing durability and dimensional stability in demanding environments.
Processing Techniques and Moldability
Clarified polypropylene undergoes advanced nucleating agent addition during processing, enhancing optical clarity and improving flow characteristics, which facilitates intricate mold designs with precise surface finishes. Filled polypropylene incorporates reinforcing fillers like glass fibers or talc, increasing stiffness and dimensional stability but requiring adjusted molding parameters due to higher viscosity and potential wear on molds. Both materials demand tailored injection molding techniques, with clarified polypropylene favoring faster cycle times and filled polypropylene necessitating higher injection pressures and mold temperature control for optimal moldability.
Cost Analysis and Material Selection Considerations
Clarified polypropylene typically incurs higher production costs due to the use of nucleating agents that improve transparency and stiffness, while filled polypropylene reduces material costs by incorporating affordable fillers like talc or calcium carbonate to enhance mechanical properties. Material selection depends on balancing cost, optical clarity, and mechanical performance requirements; applications demanding aesthetic appeal and rigidity often favor clarified polypropylene, whereas cost-sensitive uses with less emphasis on transparency tend to choose filled polypropylene. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, including processing complexity and end-use specifications, is critical in selecting between clarified and filled polypropylene for manufacturing.
Clarified Polypropylene vs Filled Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com