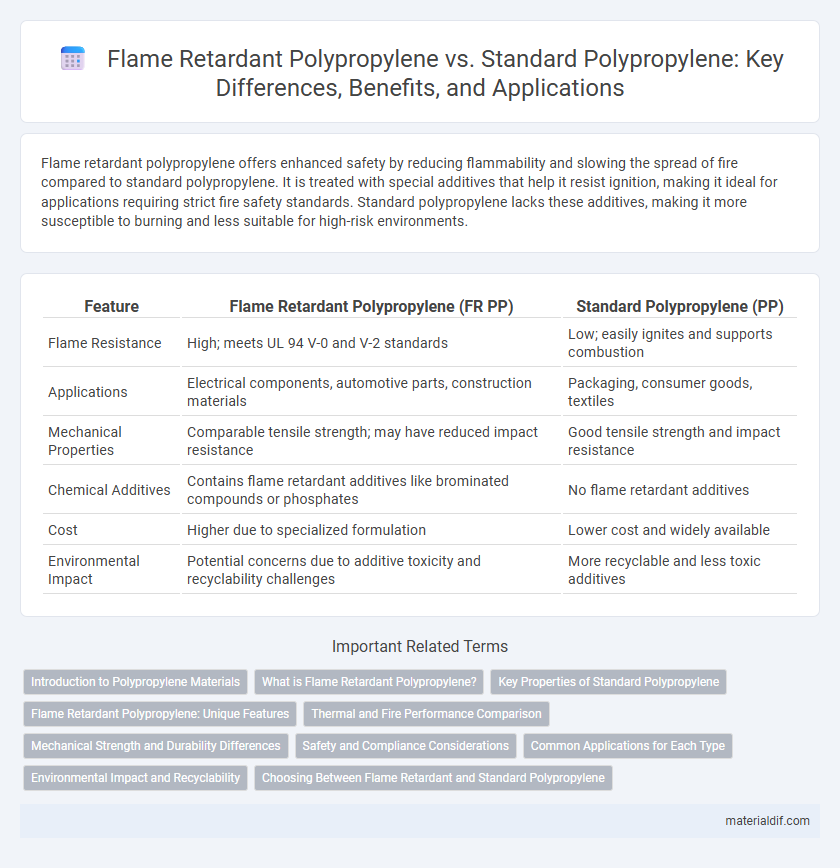
Flame retardant polypropylene offers enhanced safety by reducing flammability and slowing the spread of fire compared to standard polypropylene. It is treated with special additives that help it resist ignition, making it ideal for applications requiring strict fire safety standards. Standard polypropylene lacks these additives, making it more susceptible to burning and less suitable for high-risk environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flame Retardant Polypropylene (FR PP) | Standard Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Resistance | High; meets UL 94 V-0 and V-2 standards | Low; easily ignites and supports combustion |
| Applications | Electrical components, automotive parts, construction materials | Packaging, consumer goods, textiles |
| Mechanical Properties | Comparable tensile strength; may have reduced impact resistance | Good tensile strength and impact resistance |
| Chemical Additives | Contains flame retardant additives like brominated compounds or phosphates | No flame retardant additives |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized formulation | Lower cost and widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Potential concerns due to additive toxicity and recyclability challenges | More recyclable and less toxic additives |
Introduction to Polypropylene Materials
Flame retardant polypropylene is engineered with additives that enhance its resistance to ignition and flame spread, making it suitable for applications requiring increased fire safety. Standard polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, low density, and versatility but lacks inherent flame retardant properties. Selecting between flame retardant and standard polypropylene depends on regulatory requirements and specific performance needs in industries such as automotive, electronics, and construction.
What is Flame Retardant Polypropylene?
Flame retardant polypropylene is a modified form of standard polypropylene that contains additives or treatments designed to inhibit or resist the spread of fire. These flame retardant additives improve the polymer's ability to self-extinguish, reducing flammability and enhancing safety in various applications such as electronics, automotive parts, and construction materials. Unlike standard polypropylene, which is highly flammable and can ignite easily, flame retardant polypropylene meets stringent fire safety standards for use in environments requiring enhanced fire resistance.
Key Properties of Standard Polypropylene
Standard polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, low density of approximately 0.9 g/cm3, and a melting point around 160degC, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. It features good impact resistance, high tensile strength averaging 30-40 MPa, and excellent electrical insulating properties, but lacks inherent flame retardancy. These characteristics make standard polypropylene ideal for packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods where flame retardant properties are not critical.
Flame Retardant Polypropylene: Unique Features
Flame Retardant Polypropylene (FRPP) incorporates specialized additives that significantly enhance its resistance to ignition and reduce flame spread compared to standard polypropylene. Its unique features include improved thermal stability, self-extinguishing properties, and compliance with rigorous fire safety standards such as UL 94 V-0. These characteristics make FRPP ideal for applications in electronics, automotive components, and construction materials where fire safety is critical.
Thermal and Fire Performance Comparison
Flame retardant polypropylene exhibits enhanced thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity at higher temperatures compared to standard polypropylene, which tends to soften and degrade more rapidly under heat exposure. The incorporation of flame retardant additives significantly reduces flammability, achieving lower heat release rates and inhibiting ignition, whereas standard polypropylene is highly flammable and sustains combustion. Consequently, flame retardant polypropylene meets stringent fire safety standards, making it suitable for applications requiring improved fire resistance and thermal endurance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Differences
Flame retardant polypropylene incorporates additives like halogen-free compounds or phosphorus-based agents that enhance fire resistance while slightly reducing mechanical strength compared to standard polypropylene. Standard polypropylene generally exhibits higher tensile strength and impact resistance due to its unmodified polymer matrix, making it more suitable for applications demanding superior durability. The incorporation of flame retardants can alter polymer crystallinity and molecular interactions, resulting in changes to long-term durability and performance under mechanical stress.
Safety and Compliance Considerations
Flame retardant polypropylene is engineered with additives that enhance its resistance to ignition, significantly improving safety in applications subject to fire hazards. This specialized variant meets rigorous industry standards such as UL 94 V-0, ensuring compliance with fire safety regulations across automotive, electrical, and construction sectors. Standard polypropylene, while offering excellent chemical resistance and mechanical properties, lacks inherent flame retardancy, making it less suitable for environments where fire safety certification is mandatory.
Common Applications for Each Type
Flame retardant polypropylene is widely used in electrical enclosures, automotive components, and construction materials where fire resistance is critical to safety standards. Standard polypropylene finds extensive application in packaging, consumer goods, textiles, and automotive parts that do not require enhanced fire protection. The choice between these types depends on regulatory compliance, performance requirements, and specific industry safety demands.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Flame retardant polypropylene often contains additives such as halogenated compounds or phosphorus-based chemicals that can hinder recycling processes and increase environmental toxicity compared to standard polypropylene, which is more easily recyclable and has a lower ecological footprint. The presence of flame retardants may lead to the release of hazardous substances during incineration or degradation, posing greater risks to air quality and soil health. Standard polypropylene's simpler polymer structure facilitates mechanical recycling and reduces the generation of harmful byproducts, making it more environmentally sustainable in circular economy applications.
Choosing Between Flame Retardant and Standard Polypropylene
Flame retardant polypropylene incorporates specialized additives like halogenated compounds or intumescent agents that significantly enhance its resistance to ignition and flame spread compared to standard polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring strict fire safety standards. Standard polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, low density, and good mechanical properties at a lower cost but lacks inherent flame retardancy, limiting its use in environments with stringent fire regulations. Selection between flame retardant and standard polypropylene depends on specific industry requirements such as electrical insulation, automotive components, or consumer goods where fire safety risks must be balanced against performance and budget considerations.
Flame Retardant Polypropylene vs Standard Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com