FDA-grade polypropylene meets strict regulatory standards for food safety, ensuring it is non-toxic and suitable for direct food contact applications. Industrial-grade polypropylene, while durable and cost-effective, lacks the certification required for food-related use and may contain additives unsafe for ingestion. Choosing FDA-grade polypropylene is essential for packaging and products that require compliance with health and safety regulations.
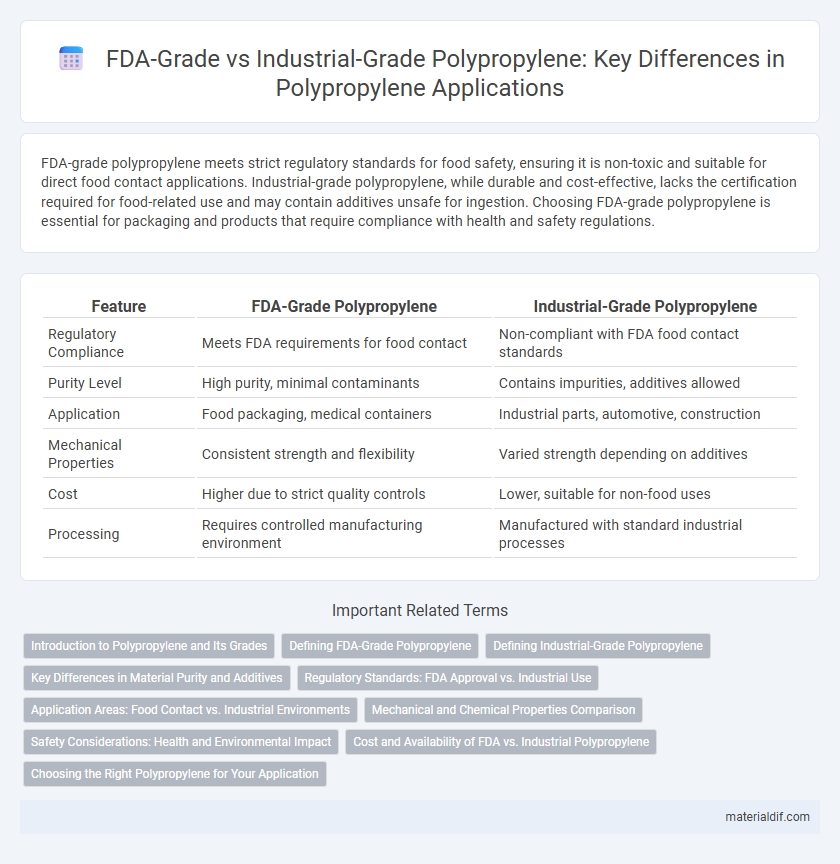
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FDA-Grade Polypropylene | Industrial-Grade Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets FDA requirements for food contact | Non-compliant with FDA food contact standards |
| Purity Level | High purity, minimal contaminants | Contains impurities, additives allowed |
| Application | Food packaging, medical containers | Industrial parts, automotive, construction |
| Mechanical Properties | Consistent strength and flexibility | Varied strength depending on additives |
| Cost | Higher due to strict quality controls | Lower, suitable for non-food uses |
| Processing | Requires controlled manufacturing environment | Manufactured with standard industrial processes |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Its Grades
Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to its chemical resistance and durability. FDA-grade polypropylene meets stringent regulations for food contact applications, ensuring non-toxicity and high purity, while industrial-grade polypropylene is tailored for non-food industries with varied performance specifications. Differences in additive content, processing standards, and certification distinguish these grades, making FDA-grade ideal for medical, food packaging, and pharmaceutical uses.
Defining FDA-Grade Polypropylene
FDA-grade polypropylene is specifically formulated to meet stringent Food and Drug Administration requirements for safety, purity, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for direct food contact and medical applications. This grade undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it is free from harmful contaminants and maintains stability under high temperatures and sterilization processes. Unlike industrial-grade polypropylene, which is designed primarily for structural and packaging uses without stringent purity standards, FDA-grade polypropylene guarantees compliance with regulatory standards essential for consumer health protection.
Defining Industrial-Grade Polypropylene
Industrial-grade polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer primarily used in manufacturing, packaging, and automotive components due to its toughness, chemical resistance, and high melting point. Unlike FDA-grade polypropylene, it is not formulated to meet stringent food safety standards, making it unsuitable for direct food contact applications. Industrial-grade polypropylene often contains additives or fillers optimized for enhanced mechanical properties rather than compliance with health and safety regulations.
Key Differences in Material Purity and Additives
FDA-grade polypropylene meets stringent purity standards with minimal additives to ensure safety in food and medical applications, while industrial-grade polypropylene often contains higher levels of fillers, stabilizers, and processing aids that may introduce impurities. Material purity in FDA-grade polypropylene is tightly controlled to prevent contamination, making it suitable for direct contact with consumables. Industrial-grade polypropylene prioritizes mechanical properties and cost-efficiency over purity, resulting in a broader range of additive compositions.
Regulatory Standards: FDA Approval vs. Industrial Use
FDA-grade polypropylene meets strict regulatory standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, ensuring it is safe for direct contact with food, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices. Industrial-grade polypropylene does not require FDA approval and is primarily designed for applications where human contact is minimal, focusing on mechanical properties and cost efficiency. The distinction between these grades lies in compliance with health and safety regulations, making FDA-approved polypropylene essential for regulated industries.
Application Areas: Food Contact vs. Industrial Environments
FDA-grade polypropylene meets stringent regulatory standards for safe food contact and is widely used in packaging, containers, and medical devices due to its chemical resistance and non-toxicity. Industrial-grade polypropylene is designed for durability and performance in harsh environments, making it suitable for automotive parts, construction materials, and machinery components. The primary distinction lies in FDA-grade's compliance with food safety regulations versus industrial-grade's emphasis on mechanical strength and chemical resistance for non-food applications.
Mechanical and Chemical Properties Comparison
FDA-grade polypropylene exhibits superior chemical resistance and higher purity levels compared to industrial-grade polypropylene, making it suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications. Mechanically, FDA-grade polypropylene maintains better tensile strength and impact resistance under regulatory compliance requirements, ensuring safety and durability. Industrial-grade polypropylene often contains additives that enhance flexibility or processing ease but may compromise chemical inertness and mechanical consistency in sensitive environments.
Safety Considerations: Health and Environmental Impact
FDA-grade polypropylene meets stringent safety standards for direct food contact, ensuring non-toxicity and minimizing chemical leaching risks, thereby protecting consumer health. Industrial-grade polypropylene lacks these certifications and may contain additives or contaminants unsuitable for food or medical applications, posing potential health hazards. From an environmental perspective, FDA-grade polypropylene typically undergoes more rigorous quality controls to reduce harmful emissions and facilitate safer recycling processes.
Cost and Availability of FDA vs. Industrial Polypropylene
FDA-grade polypropylene typically incurs higher costs due to stringent manufacturing standards and certification processes ensuring safety for food and medical applications. Industrial-grade polypropylene offers broader availability and lower prices as it meets less rigorous specifications, making it suitable for general packaging and automotive parts. The price variance reflects not only production complexity but also the limited supply chain dedicated to FDA-compliant materials.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene for Your Application
FDA-grade polypropylene meets stringent regulatory requirements for food and medical use, ensuring it is free from harmful contaminants and safe for direct contact with consumables. Industrial-grade polypropylene offers enhanced mechanical properties for durability and chemical resistance, making it ideal for structural or automotive components. Selecting the right polypropylene depends on application-specific factors such as regulatory compliance, exposure conditions, and mechanical demands.
FDA-Grade Polypropylene vs Industrial-Grade Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com