Polypropylene sheet offers greater thickness and rigidity compared to polypropylene film, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and structural support. Polypropylene film is thinner, more flexible, and commonly used for packaging, lamination, and protective overlays. Choosing between the two depends on the intended use, with sheets preferred for sturdiness and films for lightweight, flexible solutions.
Table of Comparison
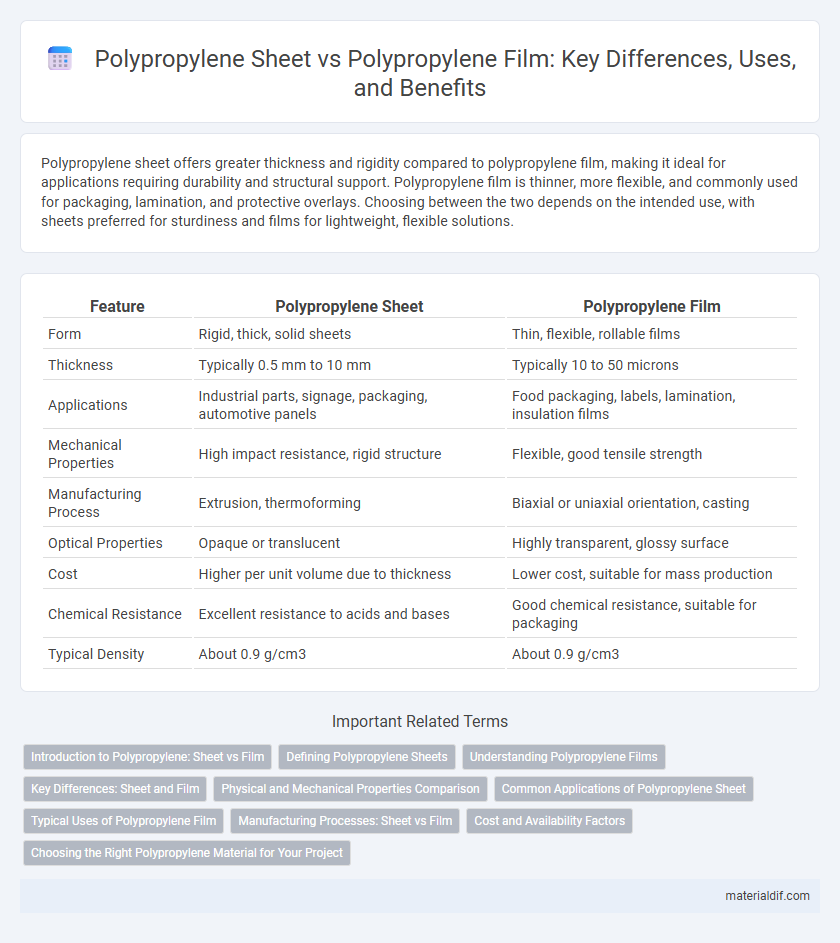
| Feature | Polypropylene Sheet | Polypropylene Film |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Rigid, thick, solid sheets | Thin, flexible, rollable films |
| Thickness | Typically 0.5 mm to 10 mm | Typically 10 to 50 microns |
| Applications | Industrial parts, signage, packaging, automotive panels | Food packaging, labels, lamination, insulation films |
| Mechanical Properties | High impact resistance, rigid structure | Flexible, good tensile strength |
| Manufacturing Process | Extrusion, thermoforming | Biaxial or uniaxial orientation, casting |
| Optical Properties | Opaque or translucent | Highly transparent, glossy surface |
| Cost | Higher per unit volume due to thickness | Lower cost, suitable for mass production |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and bases | Good chemical resistance, suitable for packaging |
| Typical Density | About 0.9 g/cm3 | About 0.9 g/cm3 |
Introduction to Polypropylene: Sheet vs Film
Polypropylene sheets are rigid, thick, and commonly used for structural applications such as signage, packaging trays, and automotive parts due to their high impact resistance and durability. Polypropylene films are thin, flexible, and widely utilized in packaging, labeling, and lamination where clarity, moisture barrier properties, and lightweight characteristics are essential. Both forms leverage polypropylene's chemical resistance and thermal stability but cater to distinct industries based on their physical attributes and mechanical performance.
Defining Polypropylene Sheets
Polypropylene sheets are rigid, thick plastic panels primarily used in industrial applications for their durability, chemical resistance, and impact strength. Unlike polypropylene film, which is thin and flexible for packaging and lamination, polypropylene sheets provide structural support in manufacturing, signage, and automotive components. These sheets typically range from 0.5mm to several millimeters in thickness, offering superior stability and dimensional strength.
Understanding Polypropylene Films
Polypropylene films are thin, flexible sheets known for their excellent clarity, moisture resistance, and tensile strength, making them ideal for packaging, labeling, and lamination applications. In contrast, polypropylene sheets are thicker, rigid, and used primarily in industrial and structural applications where durability and impact resistance are required. Understanding the distinct properties of polypropylene films, including their barrier capabilities and surface finish, is crucial for selecting the right material in consumer goods and protective packaging solutions.
Key Differences: Sheet and Film
Polypropylene sheet offers rigid, thick material ideal for structural applications, while polypropylene film provides thin, flexible layers suitable for packaging and lamination. The sheet form demonstrates higher impact resistance and dimensional stability compared to the film, which excels in transparency and moisture barrier properties. Manufacturing processes like extrusion differ, with sheets produced through thermoforming and films created via biaxial orientation for enhanced strength.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene sheets exhibit higher rigidity and impact resistance compared to polypropylene films, making them ideal for structural applications requiring durability. In contrast, polypropylene films offer greater flexibility, superior elongation at break, and enhanced clarity, which suit packaging and wrapping purposes. The tensile strength of sheets typically surpasses that of films, while films provide better moisture barrier properties due to their thinner, more uniform composition.
Common Applications of Polypropylene Sheet
Polypropylene sheets are widely utilized in automotive components, packaging, and stationery due to their rigidity and impact resistance. These sheets serve as durable materials for chemical tanks, reusable containers, and industrial parts that require toughness and chemical inertness. Unlike polypropylene film, which is valued for flexibility and transparency, polypropylene sheets are preferred in applications demanding structural strength and dimensional stability.
Typical Uses of Polypropylene Film
Polypropylene film is commonly used for flexible packaging, labels, and lamination due to its clarity, moisture resistance, and excellent barrier properties against gases. It finds applications in food wrapping, stationery products, and medical packaging where durability and transparency are critical. In contrast, polypropylene sheets are preferred for rigid, molded applications such as automotive components, signage, and reusable containers.
Manufacturing Processes: Sheet vs Film
Polypropylene sheets are typically produced through an extrusion process where melted polymer is forced through a flat die and then cooled, resulting in a thick, rigid form ideal for structural applications. In contrast, polypropylene film manufacturing involves a biaxial stretching process after extrusion, which enhances flexibility, clarity, and tensile strength, making it suitable for packaging and lamination. The difference in these manufacturing processes significantly affects the physical properties and end-use applications of polypropylene products.
Cost and Availability Factors
Polypropylene sheets typically cost more than polypropylene films due to their thicker gauge and enhanced durability, which require more raw material and processing. Polypropylene films are widely available in various thicknesses and widths, making them more accessible and cost-effective for packaging and labeling applications. The sheet form's limited suppliers and specialized production processes can affect availability and lead times in certain markets.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene Material for Your Project
Polypropylene sheets offer superior rigidity and impact resistance ideal for structural or heavy-duty applications, while polypropylene films provide flexibility and excellent moisture barriers suited for packaging and labeling. Selecting the right polypropylene material depends on factors like required thickness, durability, transparency, and chemical resistance specific to your project's needs. Consider mechanical properties, temperature tolerance, and surface finish to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness in your application.
Polypropylene Sheet vs Polypropylene Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com