Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) offers fine filtration capabilities due to its microfibrous structure, making it ideal for applications requiring high filtration efficiency and barrier properties. Spun-bonded PP features a continuous fiber web, providing superior strength, durability, and breathability, suitable for durable medical masks and protective clothing. Understanding the differences between melt-blown and spun-bonded PP helps manufacturers select the right material for specific industrial and healthcare needs.
Table of Comparison
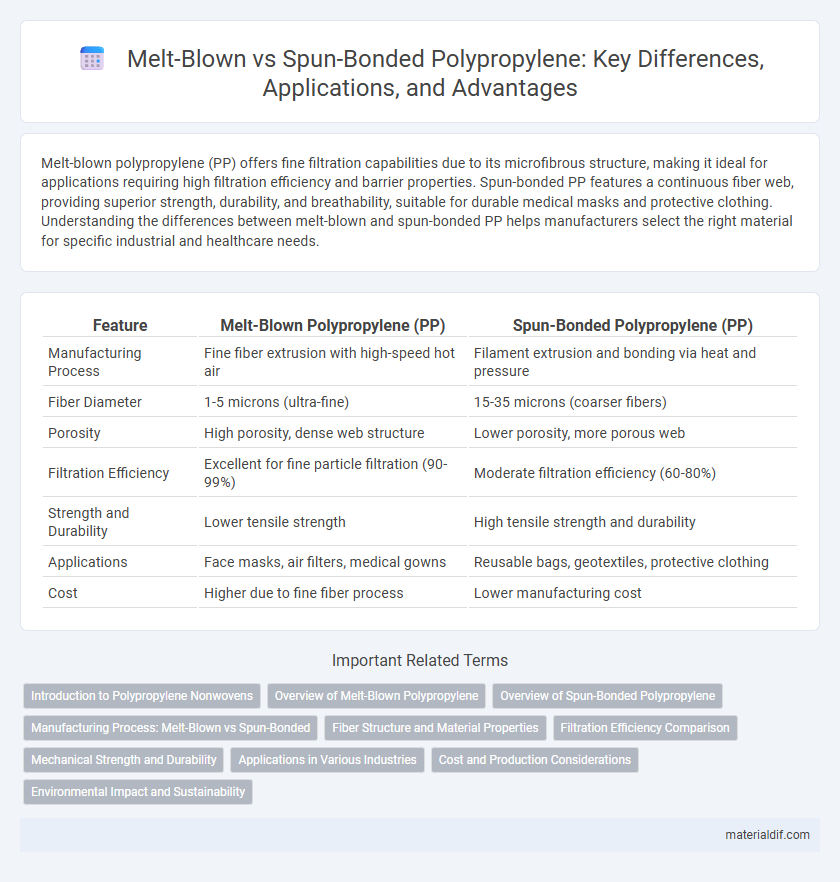
| Feature | Melt-Blown Polypropylene (PP) | Spun-Bonded Polypropylene (PP) |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Fine fiber extrusion with high-speed hot air | Filament extrusion and bonding via heat and pressure |
| Fiber Diameter | 1-5 microns (ultra-fine) | 15-35 microns (coarser fibers) |
| Porosity | High porosity, dense web structure | Lower porosity, more porous web |
| Filtration Efficiency | Excellent for fine particle filtration (90-99%) | Moderate filtration efficiency (60-80%) |
| Strength and Durability | Lower tensile strength | High tensile strength and durability |
| Applications | Face masks, air filters, medical gowns | Reusable bags, geotextiles, protective clothing |
| Cost | Higher due to fine fiber process | Lower manufacturing cost |
Introduction to Polypropylene Nonwovens
Polypropylene nonwovens are widely used in filtration, medical, and hygiene applications due to their lightweight and durable properties. Melt-blown PP features fine fibers with a high surface area, offering superior filtration efficiency, while spun-bonded PP consists of continuous filaments that provide strength and breathability. These complementary technologies enable versatile polypropylene nonwoven fabrics tailored for specific performance requirements in various industries.
Overview of Melt-Blown Polypropylene
Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) is a nonwoven fabric characterized by its fine fiber diameter and high filtration efficiency, commonly used in applications such as face masks, air, and liquid filtration. Its manufacturing process involves extruding molten polymer through small nozzles with high-velocity air, creating fibers that form a dense web with excellent barrier properties. Compared to spun-bonded PP, melt-blown PP offers superior particle filtration and softness but lower tensile strength and durability.
Overview of Spun-Bonded Polypropylene
Spun-bonded polypropylene (PP) is a nonwoven fabric produced by extruding molten polypropylene through spinnerets to form continuous filaments, which are then laid down randomly and bonded thermally. This process results in a durable, breathable, and lightweight material with high tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications such as medical masks, geotextiles, and hygiene products. Compared to melt-blown PP, spun-bonded PP offers greater mechanical strength and bulk production capability, supporting large-scale manufacturing with cost efficiency.
Manufacturing Process: Melt-Blown vs Spun-Bonded
Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) is produced by extruding molten polymer through fine nozzles with high-velocity blowing gas, creating microfibers with a nonwoven, fine mesh structure ideal for filtration and medical applications. Spun-bonded PP involves extruding continuous filaments spun and laid randomly to form a strong, durable fabric commonly used in hygiene products and geotextiles. The melt-blown process results in finer fibers with higher surface area, while spun-bonded produces thicker, more robust fibers with superior tensile strength.
Fiber Structure and Material Properties
Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) features ultrafine fibers with diameters typically ranging from 1 to 5 microns, resulting in a dense, nonwoven fabric with high filtration efficiency and excellent barrier properties. Spun-bonded PP, in contrast, has continuous fibers with larger diameters around 15 to 35 microns, providing enhanced mechanical strength, durability, and breathability. The fiber structure in melt-blown PP favors applications requiring fine particle filtration, while spun-bonded PP excels in uses demanding tear resistance and dimensional stability.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) exhibits superior filtration efficiency compared to spun-bonded PP due to its fine fiber diameter and high surface area, enabling it to capture smaller particulate matter effectively. The microstructure of melt-blown PP creates a dense web of fibers ideal for high-performance applications such as medical masks and air filters. In contrast, spun-bonded PP fibers are coarser, providing strength and durability but lower filtration efficiency for fine particles.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Melt-blown polypropylene exhibits fine fiber structures that provide high filtration efficiency but generally lower mechanical strength and durability compared to spun-bonded polypropylene. Spun-bonded polypropylene features continuous filament fibers that deliver superior tensile strength and enhanced durability, making it ideal for applications requiring robust material performance. The mechanical strength of spun-bonded PP supports repeated use and resistance to wear, while melt-blown PP tends to be more fragile and suited for single-use products.
Applications in Various Industries
Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) excels in filtration applications across medical masks, air filters, and liquid barriers due to its fine fiber structure and high filtration efficiency. Spun-bonded PP offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for hygiene products, geotextiles, agriculture covers, and reusable bags. Both materials serve distinct roles in industries like healthcare, construction, and agriculture, leveraging their unique properties for specialized applications.
Cost and Production Considerations
Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) offers fine fiber diameters ideal for high-efficiency filtration but comes with higher production costs due to complex equipment and energy-intensive processes. Spun-bonded PP provides a more cost-effective solution with faster production speeds and greater material strength, making it suitable for applications requiring durability over fine filtration. Manufacturers must balance budget constraints and product performance when choosing between the economical, high-throughput spun-bonded PP and the premium, filtration-focused melt-blown PP.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Melt-blown polypropylene (PP) offers superior filtration efficiency but requires higher energy consumption during production, resulting in a larger carbon footprint compared to spun-bonded PP. Spun-bonded polypropylene exhibits lower environmental impact due to its energy-efficient manufacturing process and enhanced recyclability, promoting sustainable applications in textile and packaging industries. Both materials are recyclable, yet spun-bonded PP's durability extends product lifespan, ultimately reducing waste generation and supporting circular economy initiatives.
Melt-Blown PP vs Spun-Bonded PP Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com