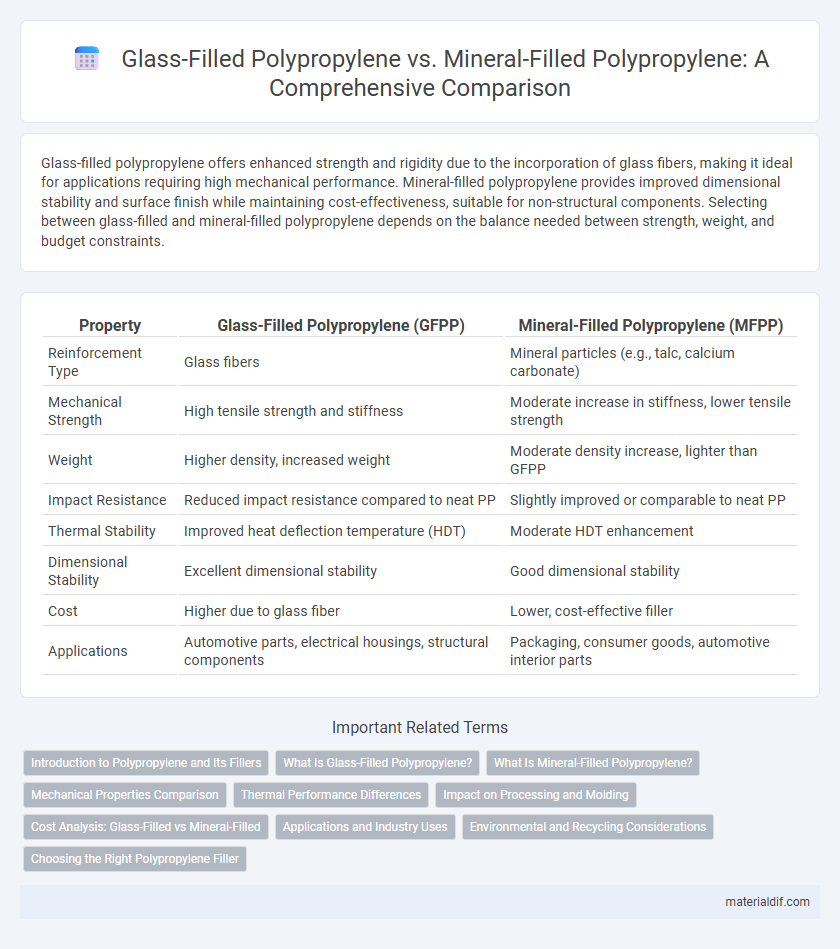
Glass-filled polypropylene offers enhanced strength and rigidity due to the incorporation of glass fibers, making it ideal for applications requiring high mechanical performance. Mineral-filled polypropylene provides improved dimensional stability and surface finish while maintaining cost-effectiveness, suitable for non-structural components. Selecting between glass-filled and mineral-filled polypropylene depends on the balance needed between strength, weight, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass-Filled Polypropylene (GFPP) | Mineral-Filled Polypropylene (MFPP) |
|---|---|---|
| Reinforcement Type | Glass fibers | Mineral particles (e.g., talc, calcium carbonate) |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate increase in stiffness, lower tensile strength |
| Weight | Higher density, increased weight | Moderate density increase, lighter than GFPP |
| Impact Resistance | Reduced impact resistance compared to neat PP | Slightly improved or comparable to neat PP |
| Thermal Stability | Improved heat deflection temperature (HDT) | Moderate HDT enhancement |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent dimensional stability | Good dimensional stability |
| Cost | Higher due to glass fiber | Lower, cost-effective filler |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electrical housings, structural components | Packaging, consumer goods, automotive interior parts |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Its Fillers
Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in automotive, packaging, and consumer goods due to its excellent chemical resistance and mechanical properties. Incorporating fillers such as glass fibers or mineral compounds enhances polypropylene's strength, stiffness, and thermal stability for demanding applications. Glass-filled polypropylene provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, while mineral-filled polypropylene offers improved dimensional stability and cost-effectiveness.
What Is Glass-Filled Polypropylene?
Glass-filled polypropylene is a composite material reinforced with glass fibers that enhance its mechanical strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to standard polypropylene. This type of polypropylene exhibits improved resistance to impact, fatigue, and heat, making it ideal for automotive parts, electrical components, and industrial applications. The glass fibers typically constitute 10-40% of the material by weight, significantly boosting structural performance while maintaining lightweight properties.
What Is Mineral-Filled Polypropylene?
Mineral-filled polypropylene is a composite material where inorganic materials such as calcium carbonate, talc, or mica are added to enhance the polymer's mechanical properties. This type of polypropylene offers improved stiffness, dimensional stability, and heat resistance while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Unlike glass-filled polypropylene, mineral-filled variants typically provide better surface finish and impact resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Glass-filled polypropylene offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to mineral-filled polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring high mechanical durability. The glass fibers significantly enhance impact resistance and dimensional stability, whereas mineral fillers primarily improve rigidity but to a lesser extent. Mineral-filled polypropylene provides better wear resistance and cost efficiency, but glass-filled variants dominate in mechanical performance demanding environments.
Thermal Performance Differences
Glass-filled polypropylene exhibits superior thermal stability and heat deflection temperature compared to mineral-filled polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring sustained performance under elevated temperatures. The glass fibers enhance thermal conductivity and reduce thermal expansion, providing better dimensional stability in high-heat environments. Mineral-filled polypropylene, while generally offering improved stiffness, has lower heat resistance and is less effective in maintaining mechanical integrity during prolonged thermal exposure.
Impact on Processing and Molding
Glass-filled polypropylene enhances stiffness and heat resistance but increases melt viscosity, requiring higher injection pressures and temperatures during molding. Mineral-filled polypropylene offers improved dimensional stability and cost efficiency with lower viscosity, enabling easier processing and faster cycle times. The choice between glass and mineral fillers directly impacts mold flow behavior, processing window, and the final component's mechanical properties.
Cost Analysis: Glass-Filled vs Mineral-Filled
Glass-filled polypropylene typically incurs higher material costs due to the expense of glass fibers, impacting overall production budgets more than mineral-filled variants. Mineral-filled polypropylene offers a cost advantage by using less expensive fillers such as talc or calcium carbonate, reducing raw material expenses and enabling more economical manufacturing. Despite these differences, selecting between glass-filled and mineral-filled polypropylene requires balancing cost considerations with performance requirements like strength and stiffness.
Applications and Industry Uses
Glass-filled polypropylene is widely used in automotive parts, electrical housings, and industrial equipment due to its enhanced strength, stiffness, and heat resistance. Mineral-filled polypropylene finds applications in consumer goods, packaging, and construction materials where improved rigidity and dimensional stability are required without significantly increasing weight. Both materials serve critical roles in industries demanding cost-effective, durable thermoplastics with tailored mechanical properties.
Environmental and Recycling Considerations
Glass-filled polypropylene offers enhanced strength and durability but poses more challenges in recycling due to the abrasive nature of glass fibers and potential wear on processing equipment. Mineral-filled polypropylene, containing additives like talc or calcium carbonate, generally provides easier recyclability and lower environmental impact by reducing energy consumption during processing. Choosing mineral-filled polypropylene supports improved sustainability by facilitating material recovery and reducing landfill waste.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene Filler
Glass-filled polypropylene offers enhanced tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for applications requiring superior mechanical performance and durability. Mineral-filled polypropylene provides improved dimensional stability and heat resistance while being more cost-effective, suitable for non-structural components. Selecting the right polypropylene filler depends on balancing mechanical requirements, thermal properties, and budget constraints to optimize product performance.
Glass-Filled Polypropylene vs Mineral-Filled Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com