PP homopolymer features higher rigidity and melting point, making it ideal for applications requiring stiffness and heat resistance. PP block copolymer offers improved impact resistance and flexibility due to its unique block structure, enhancing toughness in low-temperature environments. Selecting between these polymers depends on balancing mechanical strength and flexibility for specific polypropylene PET uses.
Table of Comparison
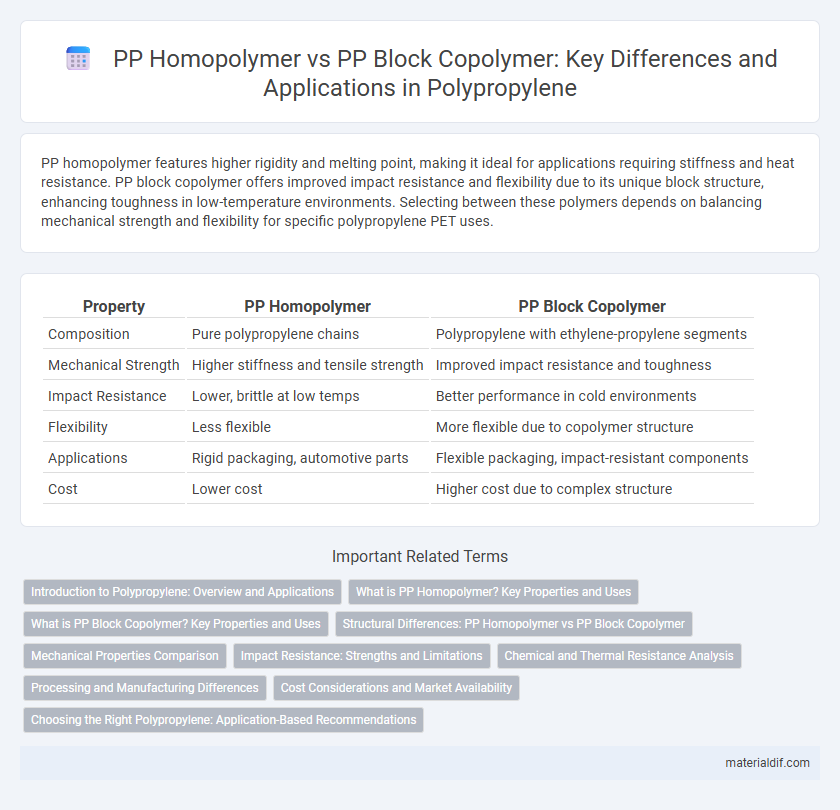
| Property | PP Homopolymer | PP Block Copolymer |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure polypropylene chains | Polypropylene with ethylene-propylene segments |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher stiffness and tensile strength | Improved impact resistance and toughness |
| Impact Resistance | Lower, brittle at low temps | Better performance in cold environments |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible due to copolymer structure |
| Applications | Rigid packaging, automotive parts | Flexible packaging, impact-resistant components |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to complex structure |
Introduction to Polypropylene: Overview and Applications
Polypropylene homopolymer (PPH) consists of only propylene monomers, offering high stiffness, excellent chemical resistance, and good weldability, making it ideal for rigid packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods. PP block copolymer (PPBC) incorporates small amounts of ethylene blocks within the propylene chain, providing enhanced impact resistance and flexibility suitable for automotive bumpers, housewares, and industrial components. The distinct molecular structures of PPH and PPBC dictate their mechanical properties and application versatility across packaging, automotive, and consumer sectors.
What is PP Homopolymer? Key Properties and Uses
PP homopolymer consists of a polymer chain made solely from propylene monomers, characterized by high crystallinity and stiffness, resulting in excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Its key properties include high melting point (around 160degC), rigidity, good fatigue resistance, and transparency, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and clarity. Common uses of PP homopolymer include packaging films, plastic containers, automotive components, and household goods due to its balance of strength and versatility.
What is PP Block Copolymer? Key Properties and Uses
PP block copolymer is a type of polypropylene created by polymerizing propylene with small amounts of ethylene, resulting in distinct blocks of polymer chains that enhance impact strength and flexibility. This structure gives PP block copolymer superior toughness and clarity compared to PP homopolymer, making it ideal for applications requiring higher impact resistance, such as automotive parts, packaging films, and consumer goods. Its balanced stiffness and improved stress crack resistance expand its usability in demanding environments where durability and performance are critical.
Structural Differences: PP Homopolymer vs PP Block Copolymer
PP Homopolymer consists of a uniform, repeating propylene monomer unit resulting in a highly crystalline structure with increased rigidity and tensile strength. PP Block Copolymer contains alternating blocks of propylene and ethylene-propylene segments, creating a semi-crystalline material that balances rigidity with improved impact resistance and flexibility. This structural variation leads to distinct mechanical properties, with homopolymers favoring stiffness and block copolymers offering enhanced toughness and versatility in diverse applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
PP homopolymer exhibits higher tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for rigid applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. PP block copolymer offers enhanced impact resistance and flexibility due to its ethylene-propylene rubber segments, suitable for products needing toughness at low temperatures. The mechanical property differences influence their selection in automotive parts, packaging, and consumer goods based on performance requirements.
Impact Resistance: Strengths and Limitations
PP homopolymer offers high rigidity and tensile strength but has lower impact resistance, making it prone to cracking under sudden stress. PP block copolymer enhances impact resistance significantly due to its rubbery elastomeric phase, providing better toughness and durability in low-temperature applications. However, PP block copolymers may exhibit slightly reduced stiffness compared to homopolymers, which can limit their use in applications requiring maximum structural rigidity.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance Analysis
PP homopolymer exhibits superior thermal resistance with a melting point around 160-170degC, maintaining structural integrity under prolonged heat exposure, while PP block copolymer offers enhanced impact strength but slightly reduced thermal stability. Chemically, PP homopolymer is more resistant to solvents and acids due to its uniform polymer chain structure, whereas PP block copolymer's segmented chains introduce sites more susceptible to oxidative degradation. Analysis shows that for applications demanding high chemical inertness and thermal endurance, PP homopolymer is preferred, while PP block copolymer balances toughness with moderate resistance.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
PP Homopolymer offers superior stiffness and higher melting point, which facilitates easier molding and higher temperature resistance during processing. PP Block Copolymer, containing elastomeric blocks, enhances impact strength and flexibility but requires controlled processing conditions to maintain phase distribution and avoid shear degradation. Manufacturing of PP Homopolymer typically involves single-site or Ziegler-Natta catalysts for uniform isotactic chains, while PP Block Copolymer production employs specialized catalysts enabling sequential polymerization of hard and soft segments, impacting extrusion and injection molding parameters.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
PP homopolymer offers lower production costs due to its simpler polymerization process, making it more economical for large-scale manufacturing and widely available in the global market. PP block copolymer, with its enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, incurs higher costs from more complex synthesis methods and specialized catalysts, resulting in more limited but growing availability in niche applications. Market demand trends indicate PP homopolymer dominates commodity sectors, while PP block copolymer gains traction in automotive and packaging industries requiring improved mechanical properties.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene: Application-Based Recommendations
PP Homopolymer offers higher rigidity and tensile strength, making it ideal for automotive parts, packaging films, and household goods that require durability. PP Block Copolymer provides enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, suited for applications like living hinges, pipes, and packaging that demand toughness at low temperatures. Selecting the right polypropylene hinges on the specific mechanical properties needed for the end-use, with homopolymers excelling in stiffness and block copolymers favored for impact-sensitive environments.
PP Homopolymer vs PP Block Copolymer Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com