Medical grade polypropylene offers enhanced purity and biocompatibility, making it suitable for sensitive healthcare applications compared to general purpose polypropylene. It undergoes stringent quality control and meets regulatory standards to ensure safety in medical use. General purpose polypropylene, while versatile and cost-effective, lacks the specialized properties required for critical medical environments.
Table of Comparison
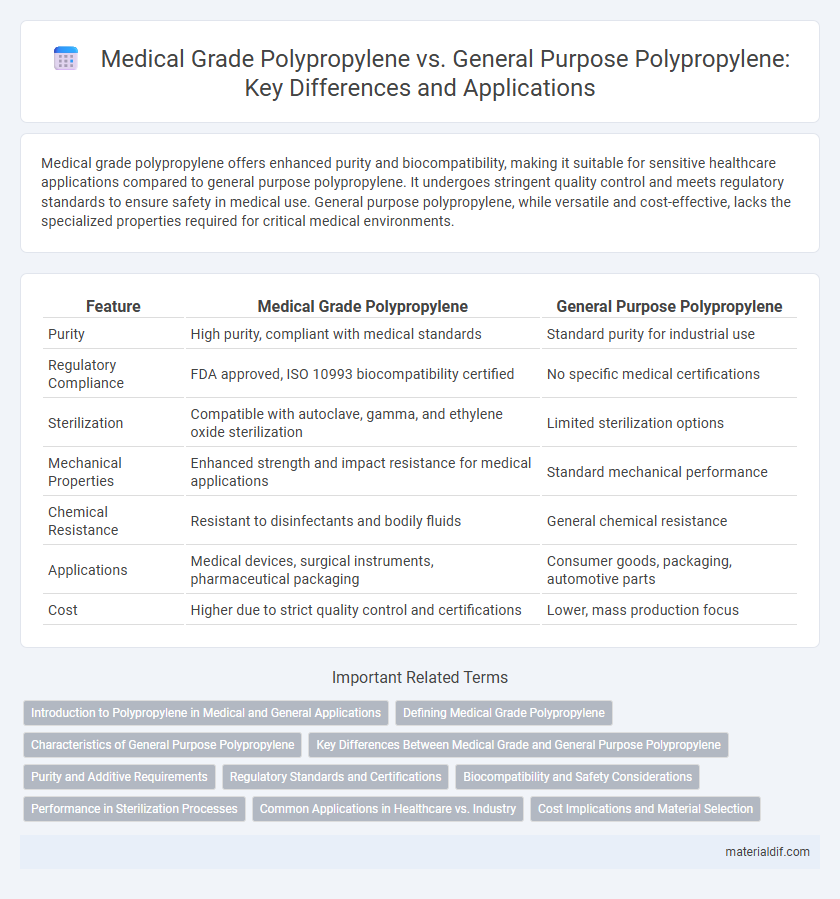
| Feature | Medical Grade Polypropylene | General Purpose Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High purity, compliant with medical standards | Standard purity for industrial use |
| Regulatory Compliance | FDA approved, ISO 10993 biocompatibility certified | No specific medical certifications |
| Sterilization | Compatible with autoclave, gamma, and ethylene oxide sterilization | Limited sterilization options |
| Mechanical Properties | Enhanced strength and impact resistance for medical applications | Standard mechanical performance |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to disinfectants and bodily fluids | General chemical resistance |
| Applications | Medical devices, surgical instruments, pharmaceutical packaging | Consumer goods, packaging, automotive parts |
| Cost | Higher due to strict quality control and certifications | Lower, mass production focus |
Introduction to Polypropylene in Medical and General Applications
Medical grade polypropylene is specifically engineered to meet stringent regulatory standards for biocompatibility, sterilization resistance, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for medical devices, pharmaceutical packaging, and surgical instruments. General purpose polypropylene, valued for its versatility and cost-effectiveness, is widely used in consumer goods, automotive parts, and packaging materials where strict medical-grade requirements are not necessary. The molecular structure and additive composition of medical-grade polypropylene ensure enhanced purity and performance under sterilization conditions, distinguishing it from the general purpose variant in critical healthcare applications.
Defining Medical Grade Polypropylene
Medical Grade Polypropylene is a high-purity polymer specifically engineered to meet stringent regulatory standards such as ISO 10993 and USP Class VI, ensuring biocompatibility and chemical resistance essential for medical device applications. Unlike General Purpose Polypropylene, which is designed for everyday use with varied additives, Medical Grade Polypropylene undergoes rigorous testing for cytotoxicity, sterilization compatibility, and endotoxin levels to guarantee patient safety. This specialized grade exhibits controlled molecular weight distribution and minimal extractables, making it ideal for manufacturing surgical instruments, packaging, and implants.
Characteristics of General Purpose Polypropylene
General Purpose Polypropylene (PP) exhibits high chemical resistance, good fatigue resistance, and excellent moisture resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of everyday applications such as packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods. It has a relatively low melting point around 160-170degC and offers moderate mechanical strength compared to Medical Grade Polypropylene. Unlike Medical Grade PP, it does not meet the stringent biocompatibility and sterilization requirements necessary for medical or pharmaceutical use.
Key Differences Between Medical Grade and General Purpose Polypropylene
Medical grade polypropylene features stringent purity standards and biocompatibility certifications essential for medical applications, unlike general purpose polypropylene which is designed for broad, non-critical uses with lower regulatory requirements. Medical grade polypropylene undergoes rigorous sterilization testing and offers superior resistance to gamma radiation and ethylene oxide sterilization methods, ensuring safety and performance in healthcare environments. In contrast, general purpose polypropylene prioritizes cost-efficiency and versatility, sacrificing the enhanced mechanical properties and contamination control mandatory in medical contexts.
Purity and Additive Requirements
Medical Grade Polypropylene demands higher purity levels, with stringent controls on residual monomers and catalysts to meet biocompatibility standards. It requires the absence of harmful additives such as heavy metals, plasticizers, and UV stabilizers, ensuring safe contact with human tissues and bodily fluids. In contrast, General Purpose Polypropylene contains a broader range of additives for enhanced mechanical properties and is not subject to the same rigorous purity and toxicity criteria.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Medical grade polypropylene complies with stringent regulatory standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR 820, ensuring biocompatibility and sterility for medical applications. General purpose polypropylene lacks these certifications and is typically used in packaging, automotive, and consumer goods without the need for rigorous safety validation. The presence of certifications like USP Class VI and ISO 10993 in medical grade polypropylene guarantees its suitability for in vivo and in vitro medical device manufacturing.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
Medical grade polypropylene exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to general purpose polypropylene, making it ideal for use in medical devices and implants where patient safety is critical. Its chemical purity and absence of harmful additives minimize the risk of adverse reactions, ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility testing. In contrast, general purpose polypropylene lacks these certifications and may contain fillers or stabilizers that pose potential safety concerns in medical applications.
Performance in Sterilization Processes
Medical grade polypropylene exhibits superior resistance to sterilization methods such as autoclaving, gamma radiation, and ethylene oxide compared to general purpose polypropylene. Its enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance prevent deformation and degradation during repeated sterilization cycles. This makes medical grade polypropylene the preferred material for manufacturing sterilizable medical devices and packaging.
Common Applications in Healthcare vs. Industry
Medical grade polypropylene is widely used in healthcare for manufacturing sterile medical devices, surgical instruments, and pharmaceutical packaging due to its biocompatibility and resistance to chemicals. General purpose polypropylene finds applications in industrial sectors such as automotive parts, consumer goods, and packaging where mechanical durability and cost-effectiveness are essential. The distinction lies in medical grade material meeting stringent regulatory standards for cleanliness and safety, while general purpose grades prioritize versatility and economic performance.
Cost Implications and Material Selection
Medical grade polypropylene demands higher production standards and biocompatibility certifications, significantly increasing its cost compared to general purpose polypropylene. Material selection favors medical grade polypropylene for applications requiring sterilization, chemical resistance, and regulatory compliance, despite the higher price point. General purpose polypropylene remains cost-effective for non-critical uses where stringent material properties are unnecessary.
Medical Grade Polypropylene vs General Purpose Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com