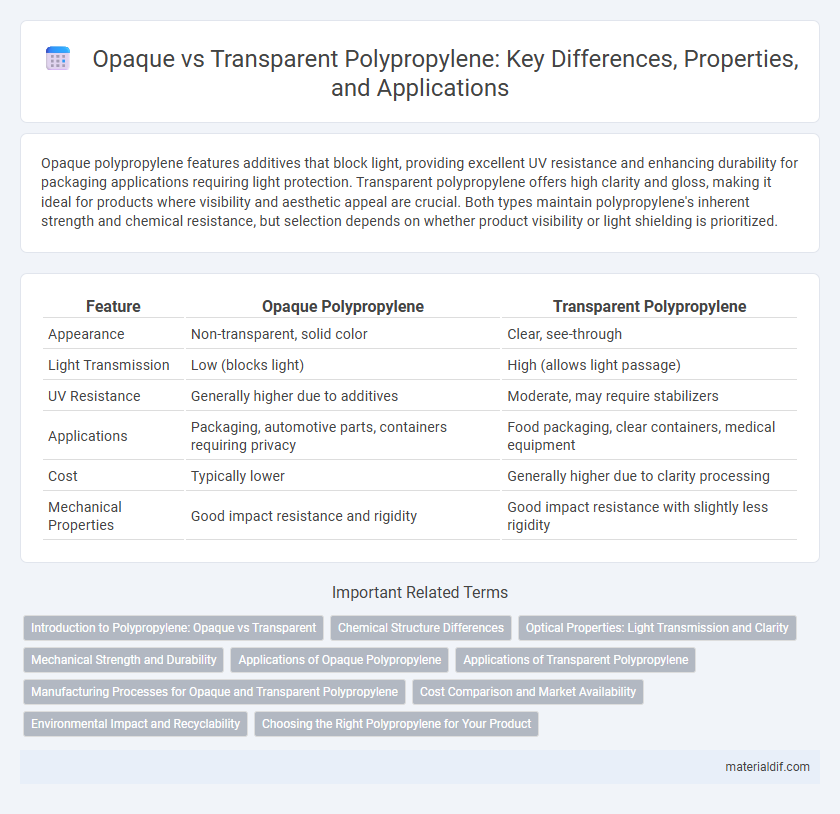
Opaque polypropylene features additives that block light, providing excellent UV resistance and enhancing durability for packaging applications requiring light protection. Transparent polypropylene offers high clarity and gloss, making it ideal for products where visibility and aesthetic appeal are crucial. Both types maintain polypropylene's inherent strength and chemical resistance, but selection depends on whether product visibility or light shielding is prioritized.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Opaque Polypropylene | Transparent Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Non-transparent, solid color | Clear, see-through |
| Light Transmission | Low (blocks light) | High (allows light passage) |
| UV Resistance | Generally higher due to additives | Moderate, may require stabilizers |
| Applications | Packaging, automotive parts, containers requiring privacy | Food packaging, clear containers, medical equipment |
| Cost | Typically lower | Generally higher due to clarity processing |
| Mechanical Properties | Good impact resistance and rigidity | Good impact resistance with slightly less rigidity |
Introduction to Polypropylene: Opaque vs Transparent
Opaque polypropylene features filler materials such as titanium dioxide that diffuse light, resulting in a solid, non-transparent appearance ideal for packaging and automotive components requiring UV resistance and durability. Transparent polypropylene, lacking these fillers, offers high clarity and gloss, making it suitable for applications like food containers where visibility of contents is essential. Both variants maintain the core properties of polypropylene, including chemical resistance, toughness, and thermal stability, with opacity primarily influenced by the presence and type of additives.
Chemical Structure Differences
Opaque polypropylene contains higher levels of isotactic crystallinity, resulting in increased light scattering and a matte appearance, whereas transparent polypropylene has a more uniform molecular chain arrangement with decreased crystallinity, allowing light to pass through with minimal distortion. The difference in tacticity and crystallite size directly influences the polymer's refractive index and opacity. Variations in polymer chain regularity and additives further modify the degree of transparency or opacity in polypropylene materials.
Optical Properties: Light Transmission and Clarity
Opaque polypropylene exhibits low light transmission due to its high pigment concentration, resulting in minimal clarity and a matte finish that effectively blocks light. Transparent polypropylene allows significant light transmission, offering superior clarity with a glossy appearance, making it ideal for applications requiring visibility of contents. The differing optical properties stem from variations in polymer crystallinity and additive usage, directly influencing product aesthetics and functional performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Opaque polypropylene exhibits higher mechanical strength due to the presence of nucleating agents and fillers that enhance impact resistance and rigidity. Transparent polypropylene, while offering superior clarity and aesthetic appeal, typically has lower tensile strength and may be less resistant to deformation under stress. Both types maintain good durability, but opaque variants often outperform in applications requiring enhanced toughness and long-term structural integrity.
Applications of Opaque Polypropylene
Opaque polypropylene is widely used in packaging applications that require UV protection and light blocking, such as food containers, dairy product packaging, and cosmetic jars. Its ability to prevent light exposure helps extend product shelf life and maintain quality by reducing oxidation. Additionally, opaque polypropylene is favored in automotive parts, household goods, and industrial components due to its durability and resistance to environmental stress.
Applications of Transparent Polypropylene
Transparent polypropylene's exceptional clarity and high gloss make it ideal for packaging applications where product visibility is crucial, such as food containers, medical packaging, and cosmetic bottles. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals ensures product integrity while allowing consumers to inspect contents easily. Transparent polypropylene is also favored in labeling and lamination, providing a durable and attractive finish without obscuring underlying graphics.
Manufacturing Processes for Opaque and Transparent Polypropylene
Opaque polypropylene is primarily produced using nucleating agents during the polymerization process, which induce crystallization and create a dense, non-translucent structure by scattering light. Transparent polypropylene is manufactured through controlled cooling and refined catalyst systems that minimize crystallite size, allowing light to pass through with minimal scattering. The choice of polymerization catalysts, cooling rates, and additives directly impacts the polymer morphology, determining whether the final product exhibits opaque or transparent characteristics.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Opaque polypropylene typically costs less than transparent polypropylene due to simpler production processes and the use of fillers such as calcium carbonate to achieve opacity. Transparent polypropylene demands higher purity and clarity, resulting in increased material and processing expenses, limiting its affordability for certain applications. Market availability favors opaque polypropylene because of its widespread use in packaging and manufacturing, while transparent polypropylene remains more niche, found predominantly in premium packaging and consumer goods.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Opaque polypropylene contains additives that reduce light transmission, which can complicate the recycling process by contaminating clear polypropylene streams and lowering the quality of recycled material. Transparent polypropylene, being free of colorants and fillers, is easier to recycle and yields higher quality recyclates, supporting circular economy efforts. Both types are recyclable, but transparent polypropylene offers a more environmentally favorable option due to its higher recyclability and reduced impact on sorting and reprocessing efficiency.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene for Your Product
Opaque polypropylene offers superior UV resistance and better light-blocking properties, making it ideal for packaging products sensitive to light exposure. Transparent polypropylene provides excellent clarity and gloss, enhancing product visibility for retail displays and packaging consumer goods. Selecting the right polypropylene depends on balancing the need for visual appeal with functional protection based on product requirements.
Opaque Polypropylene vs Transparent Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com