Polypropylene flame retardant grade offers enhanced fire resistance by incorporating additives that significantly reduce flammability compared to polypropylene standard grade. This modification ensures improved safety in applications requiring strict compliance with fire safety regulations without compromising mechanical properties. Standard grade polypropylene, while cost-effective and versatile, lacks these fire-retardant enhancements, making it less suitable for environments with stringent fire hazards.
Table of Comparison
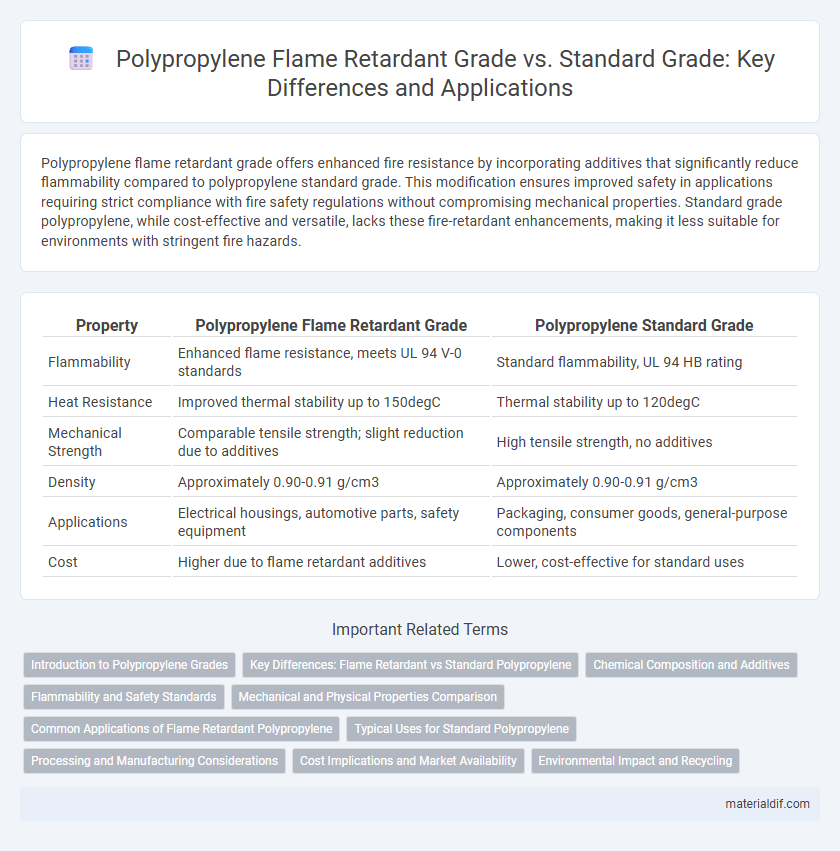
| Property | Polypropylene Flame Retardant Grade | Polypropylene Standard Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Flammability | Enhanced flame resistance, meets UL 94 V-0 standards | Standard flammability, UL 94 HB rating |
| Heat Resistance | Improved thermal stability up to 150degC | Thermal stability up to 120degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Comparable tensile strength; slight reduction due to additives | High tensile strength, no additives |
| Density | Approximately 0.90-0.91 g/cm3 | Approximately 0.90-0.91 g/cm3 |
| Applications | Electrical housings, automotive parts, safety equipment | Packaging, consumer goods, general-purpose components |
| Cost | Higher due to flame retardant additives | Lower, cost-effective for standard uses |
Introduction to Polypropylene Grades
Polypropylene flame retardant grade is specially formulated with additives that enhance its resistance to ignition and reduce flame propagation, making it suitable for applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. In contrast, polypropylene standard grade offers excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance but lacks inherent flame retardancy, limiting its use in environments with fire hazards. Selecting the appropriate grade depends on balancing performance requirements such as durability, safety compliance, and cost-effectiveness for specific industrial applications.
Key Differences: Flame Retardant vs Standard Polypropylene
Polypropylene flame retardant grades are engineered with additives like halogen-free flame retardants or mineral fillers, enhancing fire resistance and reducing flammability in applications requiring safety compliance. In contrast, standard polypropylene grades offer higher clarity, better processability, and cost-effectiveness but lack inherent fire-resistant properties, making them suitable for general-purpose uses. The key differences lie in their thermal stability, ignition resistance, and compliance with fire safety standards, impacting material choice in automotive, electrical, and construction industries.
Chemical Composition and Additives
Polypropylene Flame Retardant Grade contains specific halogen-free or halogen-based flame retardant additives such as aluminum trihydrate, antimony trioxide, or phosphorous compounds to enhance its fire resistance properties. In contrast, Polypropylene Standard Grade primarily consists of the base polymer without these specialized additives, focusing on general-purpose mechanical and thermal properties. The chemical composition differences significantly impact the thermal decomposition behavior and flame propagation characteristics between the two grades.
Flammability and Safety Standards
Polypropylene flame retardant grade is specially formulated to meet stringent fire safety standards, significantly reducing flammability and enhancing self-extinguishing properties compared to standard grade. This type maintains structural integrity under high heat, complying with UL 94 V-0 or similar certifications, essential for electrical and automotive applications. Standard grade polypropylene lacks these additives and thus exhibits higher ignition risks, making it less suitable for environments demanding rigorous fire resistance and safety compliance.
Mechanical and Physical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene Flame Retardant Grade exhibits enhanced thermal stability and improved fire resistance compared to Standard Grade, making it suitable for applications requiring stringent safety standards. Mechanical properties of Flame Retardant Grade show slightly reduced tensile strength and impact resistance due to additive incorporation, while maintaining comparable stiffness and density. Physical properties such as melting point remain similar between both grades, but Flame Retardant Grade offers superior flame retardance without significantly compromising durability.
Common Applications of Flame Retardant Polypropylene
Flame retardant polypropylene is engineered to meet fire safety standards, making it ideal for electrical housing, automotive components, and construction materials where flame resistance is critical. Common applications include circuit breaker casings, appliance parts, and cable insulation, benefiting from enhanced thermal stability and reduced flammability. This grade's specialized additives ensure compliance with UL 94 V-0 and other fire-retardant certifications, unlike standard polypropylene used in everyday packaging and consumer goods.
Typical Uses for Standard Polypropylene
Standard polypropylene is widely used in packaging, automotive components, and household goods due to its excellent chemical resistance and mechanical properties. It serves in applications such as containers, bottle caps, and interior car parts where basic durability and lightweight features are essential. Unlike flame retardant grades, standard polypropylene is not formulated for enhanced fire resistance, limiting its use in safety-critical environments.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Polypropylene flame retardant grade requires specialized processing parameters, such as higher melting temperatures and controlled cooling rates, to maintain flame retardant properties without compromising mechanical strength. Manufacturing considerations include the integration of flame retardant additives that can affect melt flow index and may necessitate equipment adjustments to prevent degradation or excessive wear. In contrast, standard polypropylene grade offers easier processability with lower thermal sensitivity, enabling faster cycle times and reduced tooling wear in conventional molding processes.
Cost Implications and Market Availability
Polypropylene flame retardant grade typically incurs higher production costs due to the incorporation of specialized additives that enhance fire resistance, leading to increased raw material expenses compared to standard grade polypropylene. Market availability of flame retardant polypropylene is comparatively limited, with suppliers focusing on niche industries such as electronics and automotive sectors where fire safety standards are stringent, whereas standard polypropylene enjoys widespread availability across diverse applications including packaging and textiles. Price-sensitive markets often favor standard grade polypropylene, while flame retardant variants command premium pricing driven by regulatory compliance and performance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Polypropylene flame retardant grades contain additives that can complicate recycling processes and may release harmful substances during incineration, increasing environmental impact compared to standard grades. Standard polypropylene grades are more environmentally friendly due to their higher recyclability and lower potential for toxic emissions. Selecting standard grades over flame retardant variants supports circular economy goals and reduces ecological footprint in plastic waste management.
Polypropylene Flame Retardant Grade vs Polypropylene Standard Grade Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com