Polypropylene Homopolymer Resin offers higher stiffness, heat resistance, and clarity, making it ideal for rigid packaging and automotive parts. Polypropylene Impact Copolymer provides enhanced impact strength and improved toughness at low temperatures, suitable for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Choosing between these resins depends on specific performance needs such as rigidity versus impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
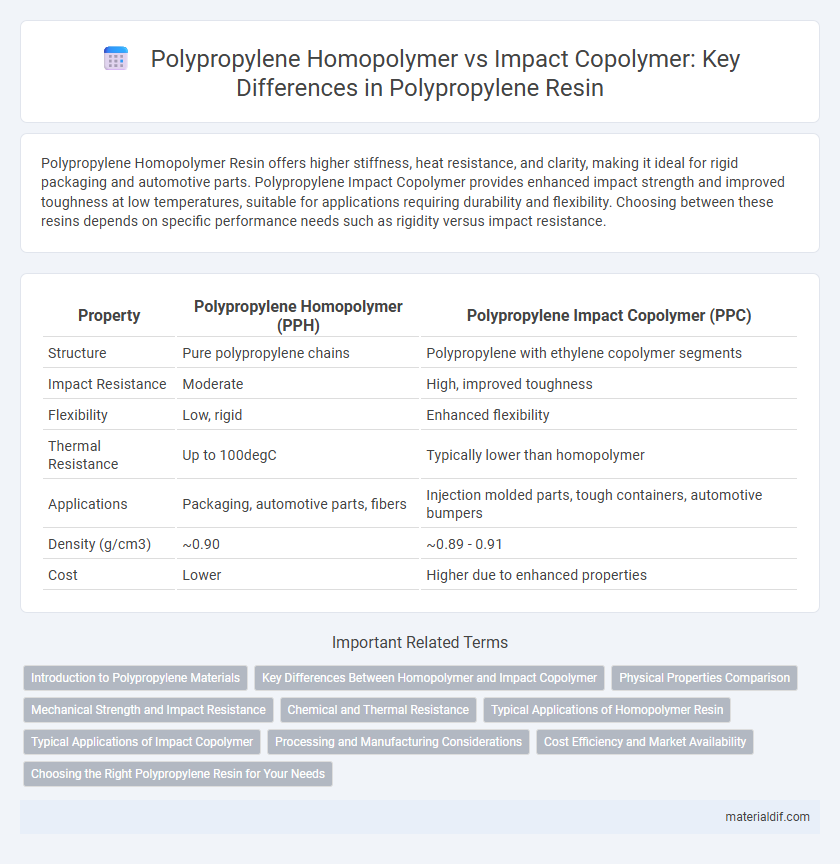
| Property | Polypropylene Homopolymer (PPH) | Polypropylene Impact Copolymer (PPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Pure polypropylene chains | Polypropylene with ethylene copolymer segments |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High, improved toughness |
| Flexibility | Low, rigid | Enhanced flexibility |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | Typically lower than homopolymer |
| Applications | Packaging, automotive parts, fibers | Injection molded parts, tough containers, automotive bumpers |
| Density (g/cm3) | ~0.90 | ~0.89 - 0.91 |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Polypropylene Materials
Polypropylene homopolymer resin features a crystalline structure that provides high tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring rigidity and durability. Polypropylene impact copolymer combines homopolymer polypropylene with an ethylene-propylene rubber phase, enhancing impact resistance and flexibility, particularly at low temperatures. These materials serve diverse industries, with homopolymers used in automotive parts and packaging, while impact copolymers excel in consumer goods and injection molding applications.
Key Differences Between Homopolymer and Impact Copolymer
Polypropylene Homopolymer Resin exhibits higher stiffness and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring rigidity and dimensional stability, whereas Polypropylene Impact Copolymer incorporates ethylene segments to enhance impact resistance and toughness at low temperatures. Homopolymers typically display higher melting points and superior chemical resistance, while impact copolymers provide improved flexibility and enhanced impact performance in cold environments. These key differences drive the selection between homopolymer for structural components and impact copolymer for uses demanding durability under dynamic stress.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene Homopolymer resin features higher tensile strength and rigidity, making it ideal for applications requiring stiffness and heat resistance. In contrast, Polypropylene Impact Copolymer exhibits superior impact resistance and flexibility, due to its ethylene content, enhancing durability in low-temperature environments. Density values for homopolymer range from 0.90 to 0.91 g/cm3, while impact copolymers typically have densities between 0.895 and 0.905 g/cm3, influencing their mechanical performance and processing behavior.
Mechanical Strength and Impact Resistance
Polypropylene Homopolymer Resin exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile and flexural properties, making it ideal for rigid applications requiring durability. Polypropylene Impact Copolymer offers enhanced impact resistance due to its rubber-modified structure, providing better toughness and performance under sudden stress or low temperatures. The choice between homopolymer and impact copolymer depends on the specific balance needed between stiffness and impact durability in the end-use application.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
Polypropylene homopolymer resin exhibits superior chemical resistance, maintaining stability against acids, bases, and organic solvents, whereas polypropylene impact copolymer offers enhanced toughness but slightly reduced chemical resistance due to its ethylene content. Thermal resistance is higher in polypropylene homopolymer resin, with a melting point around 160-170degC, while impact copolymers typically have a slightly lower melting point, reducing their maximum service temperature. Both materials provide excellent thermal insulation, but homopolymers are preferred for applications requiring greater heat endurance and chemical stability.
Typical Applications of Homopolymer Resin
Polypropylene Homopolymer Resin is predominantly utilized in applications requiring high rigidity and tensile strength, such as automotive parts, packaging films, and consumer goods. Its superior chemical resistance and low moisture absorption make it ideal for food containers and medical devices. Compared to Impact Copolymer, homopolymer resin excels in products demanding stiffness and dimensional stability.
Typical Applications of Impact Copolymer
Polypropylene Impact Copolymer is commonly used in automotive parts, consumer goods, and packaging due to its enhanced toughness and impact resistance compared to Homopolymer resin. It is ideal for products requiring improved durability under stress, such as automotive bumpers, appliance housings, and protective cases. The material's balance of stiffness and impact strength makes it suitable for both rigid and flexible applications where higher performance is essential.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Polypropylene homopolymer resin offers higher stiffness and tensile strength, making it suitable for applications requiring rigid structures, while impact copolymer provides enhanced toughness and impact resistance due to its ethylene content. Processing homopolymer typically requires higher melt temperatures and offers better heat deflection, whereas impact copolymer allows for improved flexibility and energy absorption during molding but may necessitate adjusted cooling rates to prevent warpage. Manufacturers must balance processing conditions such as melt flow index, injection molding parameters, and end-use mechanical requirements when choosing between these two polypropylene grades.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polypropylene homopolymer resin offers superior stiffness and tensile strength at a generally lower cost, making it more cost-efficient for applications requiring rigidity and chemical resistance. Polypropylene impact copolymer provides enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, which can justify its higher price in markets demanding durability and toughness under stress. Market availability favors homopolymer resin due to its widespread use in packaging and automotive parts, while impact copolymer is more specialized, resulting in variable regional supply and pricing.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene Resin for Your Needs
Polypropylene homopolymer resin offers higher tensile strength and rigidity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and stiffness, such as automotive parts and packaging. Polypropylene impact copolymer, with enhanced impact resistance and flexibility, suits products needing better toughness at low temperatures, like toys and storage containers. Selecting the right polypropylene resin depends on balancing mechanical properties and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance in specific applications.
Polypropylene Homopolymer Resin vs Polypropylene Impact Copolymer Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com