UV-stabilized polypropylene offers enhanced resistance to degradation caused by exposure to sunlight, extending the material's lifespan in outdoor applications. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene tends to become brittle and discolored when exposed to ultraviolet rays, limiting its durability and performance. Selecting UV-stabilized polypropylene ensures better retention of mechanical properties and appearance over time in environments with significant UV exposure.
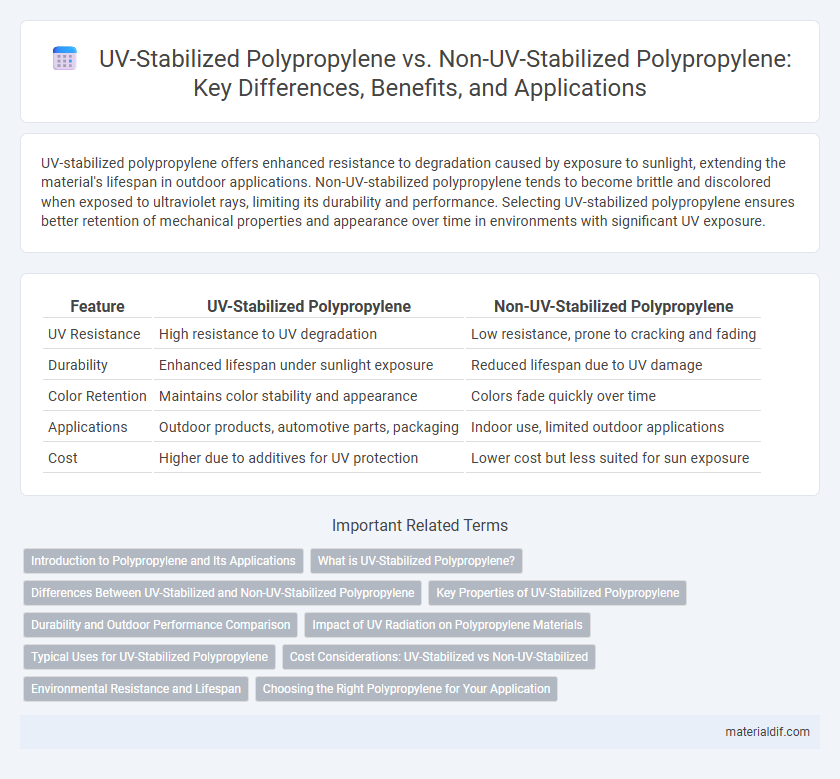
Table of Comparison
| Feature | UV-Stabilized Polypropylene | Non-UV-Stabilized Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| UV Resistance | High resistance to UV degradation | Low resistance, prone to cracking and fading |
| Durability | Enhanced lifespan under sunlight exposure | Reduced lifespan due to UV damage |
| Color Retention | Maintains color stability and appearance | Colors fade quickly over time |
| Applications | Outdoor products, automotive parts, packaging | Indoor use, limited outdoor applications |
| Cost | Higher due to additives for UV protection | Lower cost but less suited for sun exposure |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Its Applications
Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and durability. UV-stabilized polypropylene contains additives that protect the material from degradation caused by ultraviolet radiation, extending its lifespan in outdoor applications such as automotive components and outdoor furniture. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene lacks these additives, making it suitable primarily for indoor use where exposure to sunlight is limited, ensuring cost-effectiveness without compromising performance in controlled environments.
What is UV-Stabilized Polypropylene?
UV-stabilized polypropylene contains additives that protect the polymer from degradation caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation, enhancing its durability and resistance to fading, cracking, and loss of mechanical properties when exposed to sunlight. This stabilization extends the service life of polypropylene products in outdoor applications such as automotive parts, piping, and packaging. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene lacks these protective additives, making it more susceptible to photo-oxidative damage and reduced performance under prolonged UV exposure.
Differences Between UV-Stabilized and Non-UV-Stabilized Polypropylene
UV-stabilized polypropylene incorporates additives like UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) that significantly enhance its resistance to ultraviolet radiation, preventing degradation and extending its lifespan in outdoor applications. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene lacks these protective additives, making it prone to photodegradation, discoloration, brittleness, and loss of mechanical properties upon prolonged UV exposure. The difference in performance is critical for applications requiring durability and weather resistance, such as automotive parts, outdoor furniture, and packaging.
Key Properties of UV-Stabilized Polypropylene
UV-stabilized polypropylene contains additives such as UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) that protect the polymer from photodegradation caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation. This stabilization enhances its resistance to color fading, brittleness, and loss of mechanical strength, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Compared to non-UV-stabilized polypropylene, UV-stabilized variants maintain durability, tensile strength, and impact resistance under prolonged sunlight exposure.
Durability and Outdoor Performance Comparison
UV-stabilized polypropylene exhibits enhanced durability by resisting degradation from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation, significantly extending its outdoor lifespan compared to non-UV-stabilized polypropylene. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene tends to yellow, become brittle, and lose mechanical properties rapidly when exposed to sunlight, limiting its use in outdoor applications. The incorporation of UV stabilizers maintains the polymer's tensile strength and surface integrity, making UV-stabilized polypropylene the preferred choice for outdoor products such as automotive parts, decking, and outdoor furniture.
Impact of UV Radiation on Polypropylene Materials
UV-stabilized polypropylene incorporates additives that absorb or deflect ultraviolet radiation, preventing polymer chain degradation and maintaining mechanical properties under prolonged sun exposure. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene experiences polymer chain scission and surface embrittlement when exposed to UV radiation, leading to reduced tensile strength and increased brittleness. This degradation negatively affects the durability and lifespan of polypropylene products used in outdoor applications.
Typical Uses for UV-Stabilized Polypropylene
UV-stabilized polypropylene is commonly used in outdoor applications such as automotive parts, roofing membranes, and garden furniture due to its enhanced resistance to degradation from ultraviolet light exposure. This type of polypropylene maintains its physical properties and appearance when subjected to prolonged sunlight, making it ideal for construction materials and agricultural films. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene is typically limited to indoor or low-exposure environments where UV resistance is not critical.
Cost Considerations: UV-Stabilized vs Non-UV-Stabilized
UV-stabilized polypropylene incurs higher initial costs due to the addition of specialized UV inhibitors and stabilizers that protect against photodegradation, extending the material's lifespan under sun exposure. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene offers a lower upfront price but may require more frequent replacement or maintenance when used outdoors, increasing long-term expenses. Evaluating total life-cycle costs favors UV-stabilized polypropylene in applications exposed to direct sunlight, where durability and reduced degradation translate into better cost efficiency.
Environmental Resistance and Lifespan
UV-stabilized polypropylene exhibits enhanced environmental resistance by incorporating additives that absorb or block harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing polymer degradation such as cracking and discoloration. This stabilization significantly extends the material's lifespan, making it suitable for prolonged outdoor applications exposed to sunlight and harsh weather conditions. In contrast, non-UV-stabilized polypropylene degrades faster under UV exposure, resulting in reduced durability and a shorter service life when used in similar environments.
Choosing the Right Polypropylene for Your Application
UV-stabilized polypropylene contains additives that protect against degradation from ultraviolet light, making it ideal for outdoor applications exposed to sunlight. Non-UV-stabilized polypropylene lacks these additives and is more suitable for indoor use or environments with minimal UV exposure. Selecting the right polypropylene depends on the specific environmental conditions and longevity requirements of your application.
UV-Stabilized Polypropylene vs Non-UV-Stabilized Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com