Polypropylene fiber is a versatile material engineered for textiles and industrial applications, offering flexibility and durability, while polypropylene resin serves as the raw polymer used in molding and extrusion processes to create rigid plastic products. The fiber form undergoes specific treatments to enhance strength and elasticity, making it ideal for carpets, geotextiles, and ropes. In contrast, polypropylene resin is valued for its high melting point and chemical resistance, crucial for manufacturing containers, automotive parts, and packaging materials.
Table of Comparison
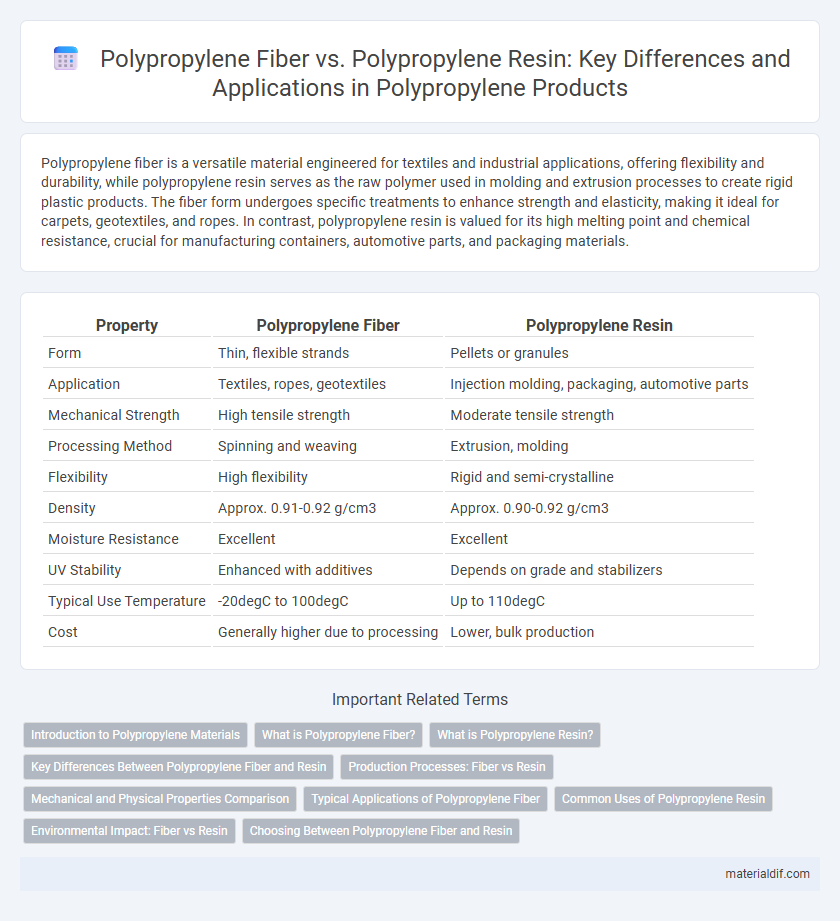
| Property | Polypropylene Fiber | Polypropylene Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Thin, flexible strands | Pellets or granules |
| Application | Textiles, ropes, geotextiles | Injection molding, packaging, automotive parts |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Processing Method | Spinning and weaving | Extrusion, molding |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Rigid and semi-crystalline |
| Density | Approx. 0.91-0.92 g/cm3 | Approx. 0.90-0.92 g/cm3 |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| UV Stability | Enhanced with additives | Depends on grade and stabilizers |
| Typical Use Temperature | -20degC to 100degC | Up to 110degC |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Lower, bulk production |
Introduction to Polypropylene Materials
Polypropylene fiber is a versatile synthetic material known for its high tensile strength, moisture resistance, and flexibility, commonly used in textiles and reinforcement applications. Polypropylene resin, a crystalline thermoplastic polymer, serves as the base material for producing fibers, films, and molded products, valued for its chemical resistance and low density. Both forms stem from polypropylene's polymerization process, but fibers emphasize durability and elasticity, while resin focuses on structural versatility and manufacturing efficiency.
What is Polypropylene Fiber?
Polypropylene fiber is a synthetic fiber derived from polypropylene resin, characterized by its high tensile strength, lightweight nature, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. It is commonly used in textiles, automotive components, and construction materials due to its durability and flexibility. Unlike polypropylene resin, which is the raw plastic material, polypropylene fiber undergoes specialized processing to create fine strands suitable for fabric and reinforcement applications.
What is Polypropylene Resin?
Polypropylene resin is a thermoplastic polymer derived from propylene monomers, widely used as the raw material for producing various polypropylene products, including fibers, films, and molded items. It features a high melting point, chemical resistance, and durability, making it suitable for applications in packaging, automotive parts, and textiles. Unlike polypropylene fiber, which is a spun form of the resin designed for fabric and nonwoven uses, the resin serves as the foundational material processed through extrusion or injection molding.
Key Differences Between Polypropylene Fiber and Resin
Polypropylene fiber is a long, thin filament derived from polypropylene resin, primarily used for textiles, ropes, and geotextiles due to its flexibility and strength. Polypropylene resin, in granular form, serves as the raw material for producing various polypropylene products through molding and extrusion processes. The key differences lie in their physical forms, applications, and manufacturing stages, with fiber being a processed end-product and resin acting as the foundational polymer.
Production Processes: Fiber vs Resin
Polypropylene fiber production involves a melt-spinning process where molten polypropylene is extruded through spinnerets to form continuous filaments that are then drawn and crimped for enhanced strength and flexibility. In contrast, polypropylene resin is produced through polymerization of propylene monomers using catalysts such as Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts, resulting in solid pellets or granules used as raw material in various molding and extrusion applications. The fiber production emphasizes controlled extrusion and post-spinning treatments, whereas resin production centers on catalyst selection and polymerization conditions to determine molecular weight and isotacticity.
Mechanical and Physical Properties Comparison
Polypropylene fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for reinforcing materials and textiles, whereas polypropylene resin offers superior stiffness and impact resistance suitable for molded products. The fiber form provides enhanced elongation and resilience under dynamic stress, while the resin delivers higher hardness and thermal resistance in solid-state applications. Both forms share chemical inertness and moisture resistance, but the fiber's physical structure allows for better breathability compared to the dense, rigid nature of the resin.
Typical Applications of Polypropylene Fiber
Polypropylene fiber is widely used in textiles, geotextiles, and reinforcement materials due to its high tensile strength, chemical resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Typical applications include upholstery fabrics, carpet backing, nonwoven fabrics for medical and hygiene products, and concrete reinforcement fibers for improved structural durability. In contrast, polypropylene resin is primarily used for injection molding and extrusion in producing automotive parts, packaging containers, and household goods.
Common Uses of Polypropylene Resin
Polypropylene resin is widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and durability. It serves as a raw material for producing containers, bottles, and furniture components, offering excellent moisture barrier properties. In contrast, polypropylene fiber is primarily employed in textiles, carpets, and geotextiles for its strength and flexibility.
Environmental Impact: Fiber vs Resin
Polypropylene fiber and polypropylene resin differ in their environmental impact mainly due to their applications and life cycles. Polypropylene fiber, often used in textiles and geotextiles, tends to have a longer lifespan and can contribute to microplastic pollution if not properly managed. Polypropylene resin, primarily utilized in packaging and molded products, is more frequently recycled, reducing landfill waste but still presents challenges related to production emissions and end-of-life disposal.
Choosing Between Polypropylene Fiber and Resin
Polypropylene fiber offers high tensile strength, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for textile and reinforcement applications. Polypropylene resin, characterized by its thermoplastic properties and ease of molding, is preferred for producing plastic parts, packaging, and automotive components. Selecting between polypropylene fiber and resin depends on the end-use requirements, such as mechanical strength, flexibility, and processing methods.
Polypropylene Fiber vs Polypropylene Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com