Mylar offers superior moisture resistance and a reflective surface that enhances light retention, making it ideal for pet containment and heating applications. In contrast, Tyvek excels in breathability and tear resistance, providing excellent durability and ventilation for pet enclosures. Choosing between Mylar and Tyvek depends on whether moisture barrier or airflow and durability are the primary concerns for your pet's environment.
Table of Comparison
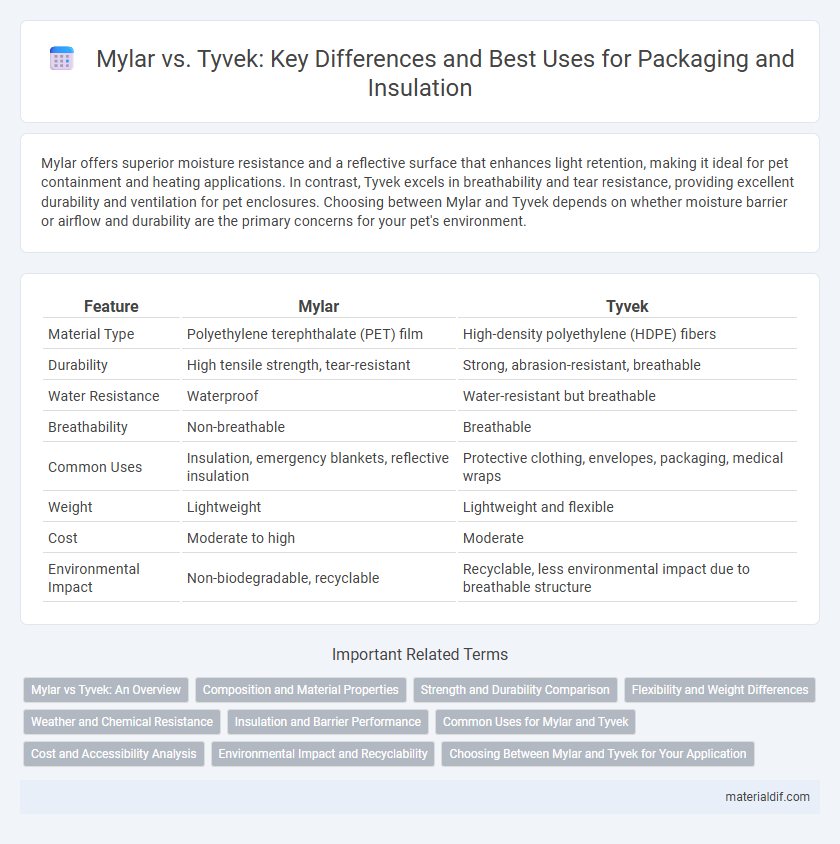
| Feature | Mylar | Tyvek |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) fibers |
| Durability | High tensile strength, tear-resistant | Strong, abrasion-resistant, breathable |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof | Water-resistant but breathable |
| Breathability | Non-breathable | Breathable |
| Common Uses | Insulation, emergency blankets, reflective insulation | Protective clothing, envelopes, packaging, medical wraps |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight and flexible |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Recyclable, less environmental impact due to breathable structure |
Mylar vs Tyvek: An Overview
Mylar is a polyester film known for its high tensile strength, chemical stability, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases, making it ideal for insulation and packaging applications. Tyvek, a spunbonded polyethylene material, offers superior tear resistance, breathability, and water repellency, often used for protective apparel and house wrap. While Mylar excels in providing airtight and moisture-barrier solutions, Tyvek is preferred for durability and breathability in construction and garment protection.
Composition and Material Properties
Mylar is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET), known for its high tensile strength, chemical stability, and excellent moisture and gas barrier properties. Tyvek, on the other hand, is a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) fiber material characterized by its lightweight, breathable, and water-resistant properties. While Mylar excels in durability and barrier performance for insulation and packaging, Tyvek is preferred for applications requiring breathability and tear resistance, such as protective clothing and envelopes.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Mylar offers superior tensile strength and resistance to tearing compared to Tyvek, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability. Tyvek, while durable, is known for its lightweight and breathable properties but has lower puncture resistance than Mylar. When evaluating long-term wear and environmental exposure, Mylar maintains its structural integrity better than Tyvek.
Flexibility and Weight Differences
Mylar exhibits greater flexibility and a lighter weight compared to Tyvek, making it ideal for applications requiring pliability and low mass. Tyvek, composed of high-density polyethylene fibers, is more rigid and heavier, offering enhanced durability but less adaptability. This contrast in flexibility and weight influences their suitability for packaging, insulation, and protective coverings.
Weather and Chemical Resistance
Mylar offers superior chemical resistance, making it highly effective against solvents, oils, and acids, while Tyvek provides excellent weather resistance due to its breathable, water-resistant properties ideal for outdoor applications. Mylar's dense polyester film structure provides a robust barrier against moisture and chemicals, whereas Tyvek's spunbonded polyethylene design excels at preventing water ingress while allowing vapor to escape. In environments requiring long-term exposure to harsh chemicals and moisture, Mylar is the preferred choice, whereas Tyvek is favored for breathable, water-resistant protection in varying weather conditions.
Insulation and Barrier Performance
Mylar provides exceptional insulation by reflecting up to 97% of radiant heat, making it highly effective for thermal management compared to Tyvek, which primarily serves as a breathable barrier with limited insulating properties. Tyvek excels in moisture resistance and air barrier performance but lacks the reflective quality that enhances Mylar's ability to reduce heat transfer. For applications requiring superior insulation and vapor barrier capabilities, Mylar offers a distinct advantage over Tyvek.
Common Uses for Mylar and Tyvek
Mylar, a polyester film known for its durability and moisture resistance, is commonly used in food packaging, insulation, and emergency blankets. Tyvek, made from high-density polyethylene fibers, excels in protective apparel, house wrap, and medical packaging due to its breathability and tear resistance. Both materials are favored in construction and protective applications but serve distinct functions based on their unique physical properties.
Cost and Accessibility Analysis
Mylar offers lower initial costs and wide availability through multiple consumer and industrial suppliers, making it a budget-friendly option for projects requiring durable, reflective materials. Tyvek generally commands higher prices due to its specialized properties like breathability and tear resistance, limiting its accessibility primarily to construction and protective applications. For cost-sensitive uses where accessibility is crucial, Mylar presents a more economical and readily obtainable choice compared to Tyvek.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Mylar, a polyester film, is less biodegradable than Tyvek, which is made from high-density polyethylene fibers and is more easily recyclable through specialized programs. Tyvek's porous structure allows for better environmental compatibility, as it decomposes more readily and can be repurposed in recycling streams that accept synthetic textiles. Mylar's durability and chemical resistance, while advantageous for certain uses, contribute to a longer environmental persistence, posing challenges for waste management and recycling efforts.
Choosing Between Mylar and Tyvek for Your Application
Mylar offers superior moisture and chemical resistance, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics and food products, while Tyvek excels in durability and breathability, suited for protective clothing and construction barriers. Evaluating project requirements such as environmental exposure, flexibility, and permeability guides the decision between Mylar's reflective, waterproof properties and Tyvek's tear resistance and air flow capabilities. Selecting the appropriate material ensures optimal performance, longevity, and protection tailored to specific application needs.
Mylar vs Tyvek Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com