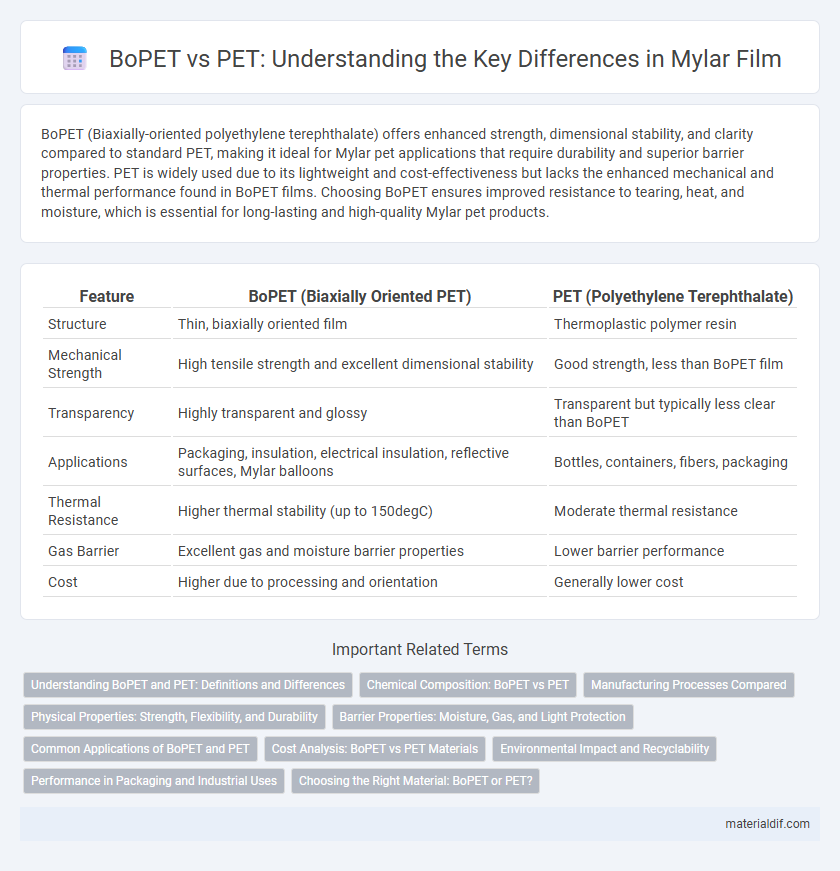
BoPET (Biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate) offers enhanced strength, dimensional stability, and clarity compared to standard PET, making it ideal for Mylar pet applications that require durability and superior barrier properties. PET is widely used due to its lightweight and cost-effectiveness but lacks the enhanced mechanical and thermal performance found in BoPET films. Choosing BoPET ensures improved resistance to tearing, heat, and moisture, which is essential for long-lasting and high-quality Mylar pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | BoPET (Biaxially Oriented PET) | PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Thin, biaxially oriented film | Thermoplastic polymer resin |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability | Good strength, less than BoPET film |
| Transparency | Highly transparent and glossy | Transparent but typically less clear than BoPET |
| Applications | Packaging, insulation, electrical insulation, reflective surfaces, Mylar balloons | Bottles, containers, fibers, packaging |
| Thermal Resistance | Higher thermal stability (up to 150degC) | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Gas Barrier | Excellent gas and moisture barrier properties | Lower barrier performance |
| Cost | Higher due to processing and orientation | Generally lower cost |
Understanding BoPET and PET: Definitions and Differences
BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) is a highly durable film made by stretching PET film in both the machine and transverse directions, enhancing strength, clarity, and barrier properties compared to standard PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate). PET refers to the base polymer commonly used in fibers and packaging, while BoPET is a specific processed form designed to optimize mechanical and optical performance. The key differences between BoPET and PET lie in their manufacturing process and resulting properties, with BoPET offering improved dimensional stability, tensile strength, and moisture resistance.
Chemical Composition: BoPET vs PET
BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) and PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) share the same fundamental chemical composition, consisting of repeating units of ethylene terephthalate derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. The key difference lies in BoPET's biaxial orientation process, which aligns polymer chains in both the machine and transverse directions, enhancing mechanical strength, thermal stability, and dimensional stability without altering the molecular structure. This orientation process transforms standard PET into a film with improved chemical resistance and barrier properties, essential for packaging and insulation applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) differs from standard PET primarily through its manufacturing process, which involves biaxial orientation by stretching the polymer film both machine and transverse directions. This biaxial stretching enhances tensile strength, dimensional stability, and barrier properties compared to conventional PET films produced by simple extrusion or casting methods. The controlled heat-setting stage in BoPET manufacturing locks in molecular alignment, resulting in superior mechanical and optical characteristics ideal for packaging, insulation, and electronic applications.
Physical Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) exhibits superior tensile strength and enhanced flexibility compared to standard PET due to its biaxial orientation process, which aligns polymer chains in two directions. This orientation significantly improves dimensional stability and resistance to tearing, making BoPET more durable under mechanical stress. Standard PET typically shows lower strength and flexibility, leading to reduced lifespan in applications requiring repeated stress or bending.
Barrier Properties: Moisture, Gas, and Light Protection
BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) offers superior barrier properties compared to standard PET, providing enhanced moisture, gas, and light protection. The biaxial orientation process significantly improves BoPET's density and crystallinity, reducing permeability and increasing resistance to oxygen and water vapor transmission. This makes BoPET an ideal material for packaging sensitive products requiring extended shelf life and protection from environmental factors.
Common Applications of BoPET and PET
BoPET, a highly oriented polyester film, is widely used in packaging, electrical insulation, and solar panel substrates due to its excellent dimensional stability and barrier properties. PET, known for its versatility, is commonly applied in textile fibers, beverage bottles, and food containers because of its strength, transparency, and recyclability. Both materials serve crucial roles in industries like packaging and electronics, with BoPET favored for specialized film applications and PET dominating in fibers and containers.
Cost Analysis: BoPET vs PET Materials
BoPET typically costs more than standard PET due to its enhanced manufacturing process, which imparts superior barrier properties, tensile strength, and dimensional stability. While PET is more economical for bulk applications, BoPET's higher price is justified in industries demanding durability and performance, such as electronics and packaging. Cost analysis must factor in long-term benefits like extended product lifespan and reduced material waste, which often offset BoPET's upfront expenses.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) offers superior environmental benefits compared to standard PET due to its enhanced durability and resistance, which extends product life and reduces waste. Both BoPET and PET are recyclable, but BoPET's crystallinity and film structure often require specialized recycling processes, limiting its circular lifecycle in some regions. The reduction in raw material usage and energy consumption during BoPET production contributes to a lower carbon footprint relative to conventional PET packaging.
Performance in Packaging and Industrial Uses
BoPET offers superior tensile strength and dimensional stability compared to standard PET, making it ideal for high-performance packaging applications requiring durability and clarity. Its excellent barrier properties enhance protection against moisture, gases, and contaminants, extending shelf life in food and pharmaceutical packaging. Industrial uses benefit from BoPET's heat resistance and electrical insulation, outperforming conventional PET in demanding environments.
Choosing the Right Material: BoPET or PET?
BoPET (Biaxially Oriented Polyethylene Terephthalate) offers superior dimensional stability, clarity, and tensile strength compared to standard PET, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and excellent barrier properties. PET is more cost-effective and suitable for general packaging and consumer goods, where flexibility and lower strength are acceptable. Selecting between BoPET and PET depends on balancing performance requirements like tear resistance, moisture barrier, and transparency against budget constraints and intended use.
BoPET vs PET Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com