Mylar film offers excellent moisture resistance and electrical insulation, making it ideal for packaging and insulation in electronic components. Polyimide film provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, suitable for high-temperature environments and flexible electronics. Selecting between Mylar and polyimide depends on the specific application requirements for temperature endurance and mechanical durability.
Table of Comparison
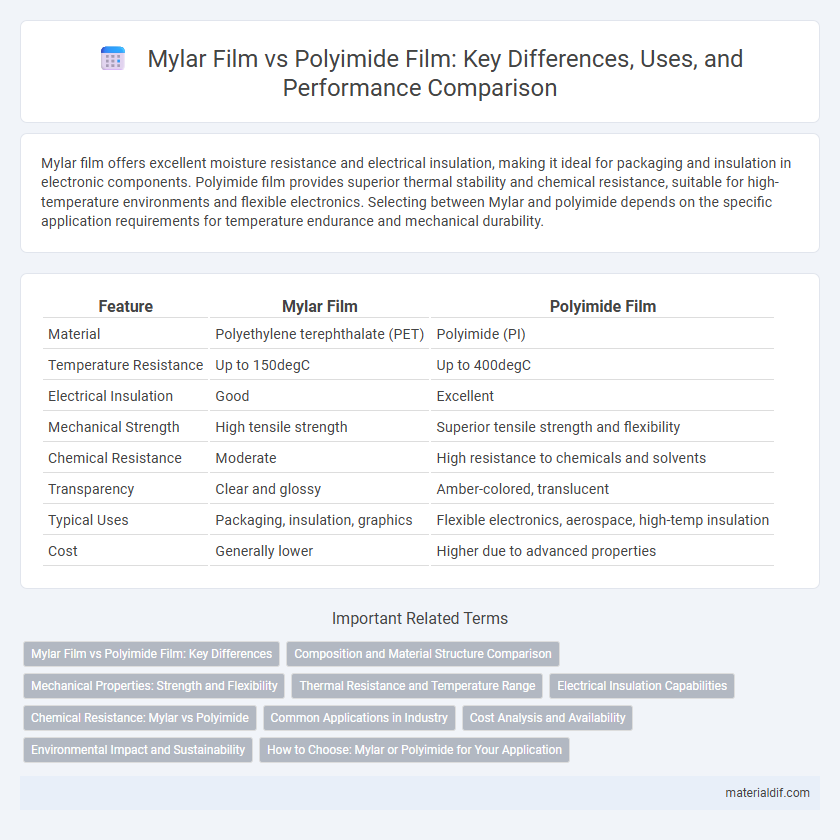
| Feature | Mylar Film | Polyimide Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Polyimide (PI) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 150degC | Up to 400degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Superior tensile strength and flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Transparency | Clear and glossy | Amber-colored, translucent |
| Typical Uses | Packaging, insulation, graphics | Flexible electronics, aerospace, high-temp insulation |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to advanced properties |
Mylar Film vs Polyimide Film: Key Differences
Mylar film, made from biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), offers high tensile strength, excellent dimensional stability, and good electrical insulation, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and clarity. In contrast, polyimide film is known for its superior thermal stability, chemical resistance, and can withstand extreme temperatures up to 400degC, which suits high-performance electronics and aerospace uses. The key differences lie in their temperature tolerance, mechanical properties, and cost, with Mylar being more cost-effective and polyimide excelling in harsh environments.
Composition and Material Structure Comparison
Mylar film, a type of biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), features a crystalline polyester structure that provides excellent tensile strength, chemical stability, and dimensional stability. In contrast, polyimide film is composed of aromatic polyimide polymers characterized by highly stable imide linkages, delivering superior thermal resistance and flexibility at elevated temperatures. While Mylar excels in clarity and moisture barrier properties due to its polyester matrix, polyimide films offer enhanced electrical insulation and durability in harsh environments thanks to their heterocyclic imide ring structure.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Mylar film exhibits high tensile strength and moderate flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and resistance to tearing. Polyimide film outperforms Mylar in thermal stability while offering superior flexibility and excellent mechanical strength, especially at elevated temperatures. The choice between Mylar and polyimide films depends on the specific mechanical demands and environmental conditions of the intended use.
Thermal Resistance and Temperature Range
Mylar film, made from biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), offers excellent thermal resistance up to 150degC, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate heat tolerance. Polyimide film outperforms Mylar with a higher thermal resistance, enduring continuous use up to 260degC and short-term exposure to even higher temperatures. The significantly broader temperature range of polyimide film makes it ideal for high-performance electronic insulation and aerospace applications compared to Mylar film.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Mylar film, composed of biaxially oriented polyethylene terephthalate (BoPET), offers excellent electrical insulation with high dielectric strength, making it ideal for applications requiring reliable insulation under moderate thermal conditions. Polyimide film, known for its superior thermal stability and exceptional dielectric properties, maintains robust electrical insulation even at elevated temperatures up to 400degC, outperforming Mylar in demanding electronic and aerospace environments. Both films provide strong insulation, but polyimide's enhanced heat resistance and electrical performance make it preferable for high-temperature, high-voltage applications.
Chemical Resistance: Mylar vs Polyimide
Mylar film, a polyester film, offers excellent resistance to water, alkalis, and mild acids but can degrade when exposed to strong solvents and high temperatures. Polyimide film, known for its superior thermal stability, chemically resists a broad range of solvents, acids, and alkalis, maintaining integrity under harsh chemical environments. This makes polyimide film more suitable for applications requiring prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals compared to Mylar.
Common Applications in Industry
Mylar film is widely used in packaging, electrical insulation, and graphic arts due to its excellent tensile strength and clarity, while polyimide film is preferred in high-temperature electronics, aerospace, and flexible printed circuits for its superior thermal stability and chemical resistance. Industries utilize Mylar for food packaging and solar films because of its moisture barrier properties, whereas polyimide films are essential in wire insulation and flexible electronics owing to their ability to withstand extreme heat. Both films are critical in industrial applications but are selected based on temperature tolerance and mechanical properties required.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Mylar film offers a cost-effective alternative to polyimide film, with prices typically 30-50% lower, making it suitable for budget-sensitive applications. Polyimide film, while more expensive due to its superior thermal and chemical resistance, often requires longer lead times and limited supplier availability compared to Mylar, which is widely produced and easily sourced globally. Companies balancing cost and performance frequently opt for Mylar film in large-volume projects where extreme durability is not critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mylar film, a polyester-based material, generally has lower environmental impact compared to polyimide film due to its recyclability and lower energy requirements during production. Polyimide film offers superior thermal and chemical resistance but is less recyclable and involves more complex manufacturing processes that contribute to higher carbon emissions. Selecting Mylar film supports sustainability goals by promoting material recovery and reducing ecological footprint in applications like packaging and electrical insulation.
How to Choose: Mylar or Polyimide for Your Application
Mylar film offers excellent dimensional stability, high tensile strength, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for packaging, insulation, and printing applications requiring clarity and durability. Polyimide film excels in extreme temperature resistance, chemical stability, and electrical insulation properties, suited for aerospace, electronics, and high-performance industrial uses. Evaluate your application's environmental conditions, thermal demands, and mechanical stresses to determine whether the balanced properties of Mylar or the superior thermal resilience of polyimide better meet your performance and budget requirements.
Mylar Film vs Polyimide Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com