Graphite sheets offer superior thickness and durability, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced thermal management and mechanical strength. Graphite films are thinner and more flexible, providing excellent electrical conductivity and heat dissipation in compact electronic devices. Choosing between graphite sheet and film depends on the specific requirements for flexibility, thermal performance, and mechanical robustness.
Table of Comparison
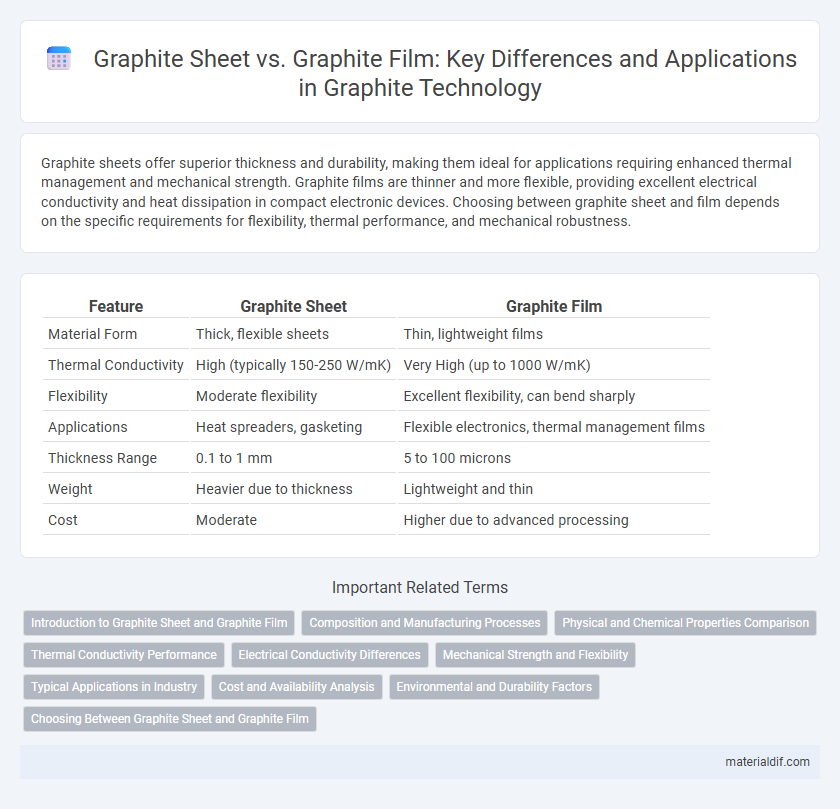
| Feature | Graphite Sheet | Graphite Film |
|---|---|---|
| Material Form | Thick, flexible sheets | Thin, lightweight films |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (typically 150-250 W/mK) | Very High (up to 1000 W/mK) |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | Excellent flexibility, can bend sharply |
| Applications | Heat spreaders, gasketing | Flexible electronics, thermal management films |
| Thickness Range | 0.1 to 1 mm | 5 to 100 microns |
| Weight | Heavier due to thickness | Lightweight and thin |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to advanced processing |
Introduction to Graphite Sheet and Graphite Film
Graphite sheets are flexible, multilayered materials known for excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, commonly used in heat dissipation applications. Graphite films, thinner and more uniform, provide higher thermal conductivity and superior flexibility, ideal for compact electronic devices. Both materials leverage graphite's anisotropic properties but differ in thickness and mechanical characteristics to suit specific industrial needs.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Graphite sheets are primarily composed of compressed natural graphite flakes and are manufactured through a lamination process that stacks and compresses these flakes into a dense, flexible layer. Graphite films, in contrast, are produced using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) techniques or exfoliation methods, resulting in ultra-thin, high-purity layers of graphite or graphene with superior thermal conductivity. The differences in composition and manufacturing processes directly impact their mechanical properties, thermal performance, and suitability for applications such as thermal management in electronics.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Graphite sheets exhibit high thermal conductivity and excellent flexibility due to their multilayered structure, while graphite films offer superior electrical conductivity and smoother surfaces thanks to their thinner, more uniform layers. Chemically, graphite sheets possess greater resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures, whereas graphite films are more reactive but provide enhanced surface area for catalytic applications. Both materials demonstrate strong chemical inertness with subtle differences in their microstructure influencing mechanical strength and thermal stability.
Thermal Conductivity Performance
Graphite sheets exhibit superior thermal conductivity due to their thicker structure and enhanced heat dissipation capabilities compared to graphite films, which are thinner and offer more flexible applications but lower overall thermal transfer. The thermal conductivity of graphite sheets typically ranges between 1500 to 2000 W/m*K, making them ideal for high-performance thermal management in electronics. Graphite films generally show thermal conductivity around 500 to 1000 W/m*K, balancing heat conduction with mechanical flexibility for wearable devices and flexible electronics.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Graphite sheets exhibit anisotropic electrical conductivity, offering high in-plane conductivity but limited through-plane conductivity due to their compressed fiber structure. Graphite films, formed by chemical vapor deposition or exfoliation, provide more uniform electrical conductivity with superior in-plane electron mobility and enhanced surface conductivity. These differences make graphite sheets suitable for applications requiring heat spreading and mechanical flexibility, while graphite films excel in high-performance electronic devices needing consistent electrical characteristics.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Graphite sheets exhibit higher mechanical strength due to their thicker, multi-layered structure, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and load-bearing capacity. Graphite films, being thinner and more flexible, offer superior bending performance and conformability, ideal for flexible electronics and thermal management in compact devices. The choice between graphite sheet and film depends on balancing rigidity and flexibility for specific industrial uses.
Typical Applications in Industry
Graphite sheets are commonly used in thermal management for electronics, providing high thermal conductivity and flexibility in heat dissipation within devices such as smartphones and laptops. Graphite films excel in applications requiring ultrathin heat spreaders, often found in aerospace and high-performance computing sectors where weight reduction and efficient thermal spreading are critical. Both materials are essential in industries prioritizing effective thermal regulation, but sheets offer structural adaptability while films provide minimal thickness and superior heat conduction.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Graphite sheets generally offer higher durability and thickness, making them more cost-effective for heavy-duty applications, while graphite films provide thinner, flexible layers suitable for precision electronics but at a higher price point. Availability of graphite sheets is more widespread due to their simpler manufacturing process, whereas graphite films often require specialized production, resulting in limited supply and fluctuating costs. Cost analysis favors graphite sheets for bulk industrial use, whereas graphite films command premium prices driven by niche demand and advanced material properties.
Environmental and Durability Factors
Graphite sheets exhibit superior durability compared to graphite films due to their thicker, more resilient structure, making them better suited for high-stress environments. Environmentally, graphite sheets are often manufactured with fewer chemical treatments, reducing toxic waste and enhancing eco-friendliness relative to graphite films. The enhanced mechanical stability and lower environmental impact position graphite sheets as a preferable choice in sustainable industrial applications.
Choosing Between Graphite Sheet and Graphite Film
Graphite sheets offer higher thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making them ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and durability. Graphite films, being thinner and more flexible, are suitable for compact electronic devices where space constraints and flexibility are critical. Selecting between graphite sheet and graphite film depends on the specific thermal management needs, space availability, and mechanical requirements of the application.
Graphite Sheet vs Graphite Film Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com