Glass mat offers superior conformability and ease of molding, making it ideal for complex shapes and providing excellent impact resistance. Woven roving features a woven fabric structure that delivers higher tensile strength and stiffness, suitable for structural applications requiring load-bearing capacity. Choosing between glass mat and woven roving depends on the specific mechanical demands and shaping complexity of the composite component.
Table of Comparison
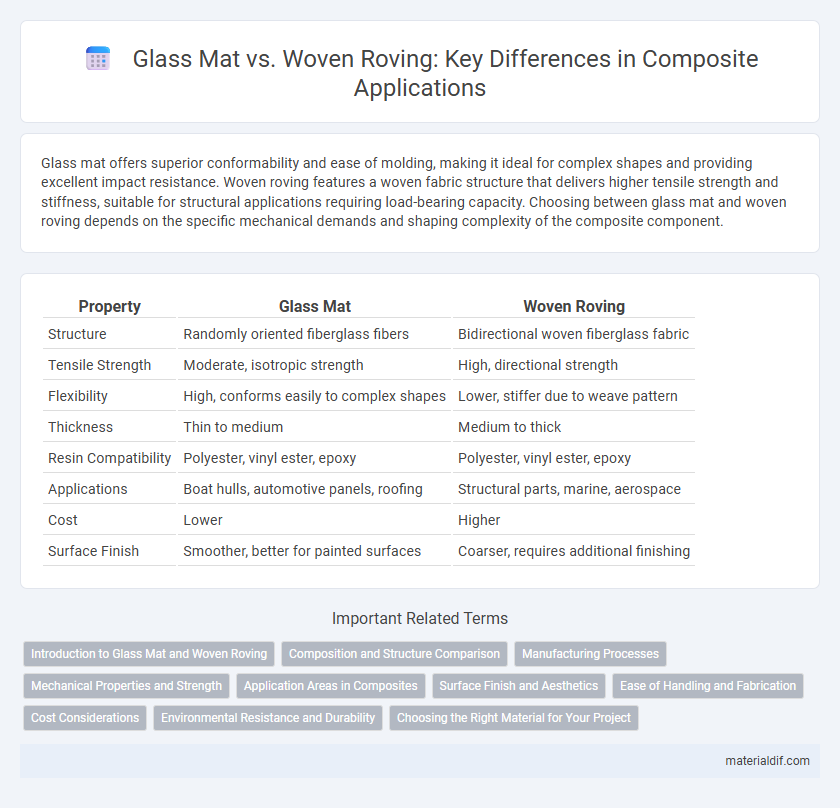
| Property | Glass Mat | Woven Roving |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Randomly oriented fiberglass fibers | Bidirectional woven fiberglass fabric |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate, isotropic strength | High, directional strength |
| Flexibility | High, conforms easily to complex shapes | Lower, stiffer due to weave pattern |
| Thickness | Thin to medium | Medium to thick |
| Resin Compatibility | Polyester, vinyl ester, epoxy | Polyester, vinyl ester, epoxy |
| Applications | Boat hulls, automotive panels, roofing | Structural parts, marine, aerospace |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, better for painted surfaces | Coarser, requires additional finishing |
Introduction to Glass Mat and Woven Roving
Glass mat is a non-woven reinforcement material composed of randomly oriented glass fibers held together by a binder, commonly used for its excellent surface finish and corrosion resistance in composite applications. Woven roving consists of interlaced glass fiber strands forming a fabric with enhanced mechanical strength, making it suitable for structural components requiring high load-bearing capacity. Both materials serve distinct purposes in composites, with glass mat offering ease of molding and woven roving providing dimensional stability and toughness.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Glass mat consists of randomly oriented chopped glass fibers bound together with a binder, creating a non-woven, isotropic structure ideal for uniform strength distribution. Woven roving features continuous glass fibers woven into a fabric with distinct warp and weft directions, providing higher tensile strength and stiffness along those fibers. The composition of glass mat enhances impact resistance and conformability, while woven roving delivers superior load-bearing capacity due to its organized fiber architecture.
Manufacturing Processes
Glass mat manufacturing involves the random orientation of chopped glass fibers held together by a binder, producing a uniform, non-directional reinforcement ideal for molded composite parts. Woven roving is created by interlacing continuous glass fiber strands in a controlled, directional pattern, enhancing strength and stiffness along specific axes. The distinct manufacturing processes influence composite performance, with glass mat favoring complex shapes and woven roving suited for high-load applications requiring predictable mechanical properties.
Mechanical Properties and Strength
Glass Mat composites provide excellent impact resistance and improved tensile strength due to their random fiber orientation, offering isotropic mechanical properties ideal for complex shapes. Woven Roving composites deliver superior stiffness and higher flexural strength from their unidirectional fiber patterns, optimizing the load-bearing capacity along fabric directions. The choice between Glass Mat and Woven Roving depends on specific strength requirements and mechanical load distributions in composite applications.
Application Areas in Composites
Glass mat is widely used in applications requiring excellent conformability and surface finish, such as automotive body panels and marine hulls, due to its random fiber orientation that provides isotropic strength. Woven roving offers superior directional strength and stiffness, making it ideal for structural components like boat decks, wind turbine blades, and sporting goods where load-bearing capacity is critical. Both materials serve crucial roles in composites, with glass mat preferred for ease of molding and surface smoothness, and woven roving chosen for enhanced mechanical performance in high-stress environments.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Glass mat offers a smoother surface finish with less visible texture, making it ideal for applications where a clean, uniform appearance is essential. Woven roving displays a distinct woven pattern that provides a textured, high-performance look but may require additional finishing to achieve a smooth aesthetic. The choice between glass mat and woven roving significantly influences the final product's visual appeal and surface quality in composite fabrication.
Ease of Handling and Fabrication
Glass mat offers superior ease of handling and fabrication compared to woven roving due to its random fiber orientation, which reduces fiber distortion and simplifies cutting and molding processes. The uniform surface of glass mat provides excellent conformity to complex shapes, minimizing air entrapment and enhancing resin flow during fabrication. In contrast, woven roving demands precise cutting along fiber directions, often requiring additional labor and skill to avoid distortion and maintain structural integrity.
Cost Considerations
Glass Mat composites generally offer lower material costs compared to Woven Roving due to their less complex manufacturing process and use of shorter fibers, making them cost-effective for large-scale applications. Woven Roving, with its higher material strength and fiber content, tends to have a higher unit price, but may reduce long-term expenses by enhancing durability and performance. Choosing between Glass Mat and Woven Roving depends on balancing initial expenditure with desired structural integrity and lifecycle cost efficiency.
Environmental Resistance and Durability
Glass Mat offers superior environmental resistance due to its random fiber orientation, enhancing impact absorption and preventing water ingress, leading to increased durability in humid and corrosive environments. Woven Roving exhibits excellent tensile strength and stiffness but is more susceptible to delamination and moisture penetration, which can reduce long-term durability under harsh environmental conditions. Choosing Glass Mat improves composite longevity in applications exposed to UV, chemicals, and varying temperatures, making it ideal for marine and automotive industries.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Glass mat offers superior conformability and excellent surface finish, making it ideal for complex shapes and molded parts, while woven roving provides higher strength and impact resistance suited for structural applications. Selecting the right composite reinforcement depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, surface appearance, and fabrication processes. Evaluate factors like mechanical properties, ease of handling, and cost-effectiveness to ensure optimal performance and longevity in your composite structure.
Glass Mat vs Woven Roving Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com