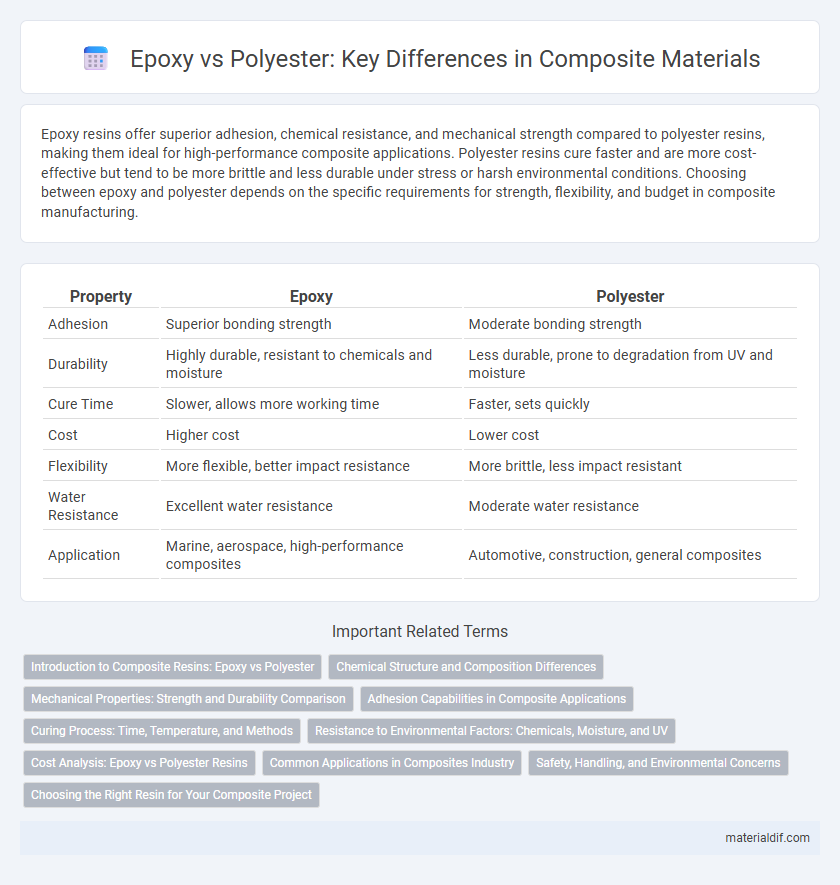
Epoxy resins offer superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polyester resins, making them ideal for high-performance composite applications. Polyester resins cure faster and are more cost-effective but tend to be more brittle and less durable under stress or harsh environmental conditions. Choosing between epoxy and polyester depends on the specific requirements for strength, flexibility, and budget in composite manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Epoxy | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion | Superior bonding strength | Moderate bonding strength |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to chemicals and moisture | Less durable, prone to degradation from UV and moisture |
| Cure Time | Slower, allows more working time | Faster, sets quickly |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Flexibility | More flexible, better impact resistance | More brittle, less impact resistant |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water resistance | Moderate water resistance |
| Application | Marine, aerospace, high-performance composites | Automotive, construction, general composites |
Introduction to Composite Resins: Epoxy vs Polyester
Composite resins play a crucial role in determining the mechanical properties and durability of composite materials, with epoxy and polyester being the most widely used types. Epoxy resin is known for its superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace and marine industries. Polyester resin offers cost-effectiveness and faster curing times, commonly used in automotive and construction sectors where moderate strength and ease of processing are required.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Epoxy resins consist of epoxide groups that form strong covalent bonds during curing, resulting in a highly cross-linked thermoset polymer with superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance. Polyester resins are composed of unsaturated polyesters that react with styrene monomers, producing a less cross-linked network with lower adhesive properties and increased brittleness. The chemical structure of epoxy resins features epoxide rings that enable tougher, more durable composites compared to the ester groups in polyester resins, which contribute to their lower performance and susceptibility to moisture.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability Comparison
Epoxy composites exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to polyester, with higher tensile strength and better adhesion contributing to enhanced durability. Epoxy's molecular structure provides greater resistance to fatigue, impact, and environmental degradation, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Polyester composites, while more cost-effective, generally have lower strength and are more prone to microcracking and hydrolytic damage under prolonged stress.
Adhesion Capabilities in Composite Applications
Epoxy resins exhibit superior adhesion capabilities in composite applications due to their strong chemical bonding with various substrates, resulting in enhanced mechanical performance and durability. Polyester resins, while more cost-effective, offer comparatively weaker adhesion, often limiting their effectiveness in high-stress or load-bearing composite structures. The enhanced molecular interaction of epoxy contributes to improved resistance against moisture and environmental degradation, making it the preferred choice for demanding composite applications.
Curing Process: Time, Temperature, and Methods
Epoxy composites cure through a chemical reaction that typically takes 24 to 48 hours at room temperature, with heat acceleration possible between 60degC and 80degC to reduce curing time to a few hours. Polyester composites cure faster, often within 30 minutes to an hour at room temperature, but require precise control of initiators like MEKP and temperature around 20degC to 25degC for optimal polymerization. The curing methods for epoxy often involve controlled thermal ramps and post-curing stages, whereas polyester curing relies heavily on exothermic reaction management to prevent defects such as shrinkage and brittleness.
Resistance to Environmental Factors: Chemicals, Moisture, and UV
Epoxy composites exhibit superior resistance to chemicals, moisture, and UV exposure compared to polyester composites, making them ideal for harsh environmental conditions. Epoxy's dense molecular structure provides enhanced barrier properties against water absorption and chemical degradation. Polyester resins are more prone to hydrolysis and UV-induced brittleness, limiting their durability in chemically aggressive or high UV environments.
Cost Analysis: Epoxy vs Polyester Resins
Epoxy resins generally have a higher initial cost compared to polyester resins due to their superior adhesive properties and chemical resistance, which contribute to longer product lifespan and reduced maintenance expenses. Polyester resins, being more affordable and widely available, are preferred for budget-sensitive projects but often entail higher lifecycle costs because of lower durability and susceptibility to environmental degradation. Evaluating total cost of ownership, epoxy resins offer better value in high-performance composite applications despite the greater upfront investment.
Common Applications in Composites Industry
Epoxy resins are widely used in aerospace and automotive composites due to their superior mechanical properties and excellent adhesion, making them ideal for high-performance structural components. Polyester resins dominate in marine and construction applications because of their cost-effectiveness and good resistance to water and chemicals, often utilized in boat hulls and building panels. Both materials serve critical roles in the composites industry, with epoxy preferred for demanding environments and polyester favored for economical, large-scale production.
Safety, Handling, and Environmental Concerns
Epoxy resins exhibit lower volatility and produce fewer hazardous fumes compared to polyester resins, enhancing user safety during handling and application. Polyester resins contain styrene, a volatile organic compound with significant health risks, requiring adequate ventilation and protective gear to minimize exposure. Environmentally, epoxy produces less hazardous waste and has lower emissions, making it a more sustainable choice for composite manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Resin for Your Composite Project
Epoxy resins offer superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength compared to polyester resins, making them ideal for high-performance composite applications such as aerospace and marine industries. Polyester resins are more cost-effective and cure faster, suitable for general-purpose projects with moderate strength requirements like automotive body panels and fiberglass tanks. Assess project-specific factors such as budget, durability, environmental exposure, and curing time to determine the optimal resin choice for composite fabrication.
Epoxy vs Polyester Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com