Acrylic bending involves heating a flat acrylic sheet until it becomes pliable and then shaping it into curved forms, ideal for custom displays and protective barriers. Acrylic molding, on the other hand, uses a process where molten acrylic is injected or cast into a mold to create complex shapes and detailed designs with high precision. Choosing between bending and molding depends on the desired end product's complexity, production volume, and cost considerations.
Table of Comparison
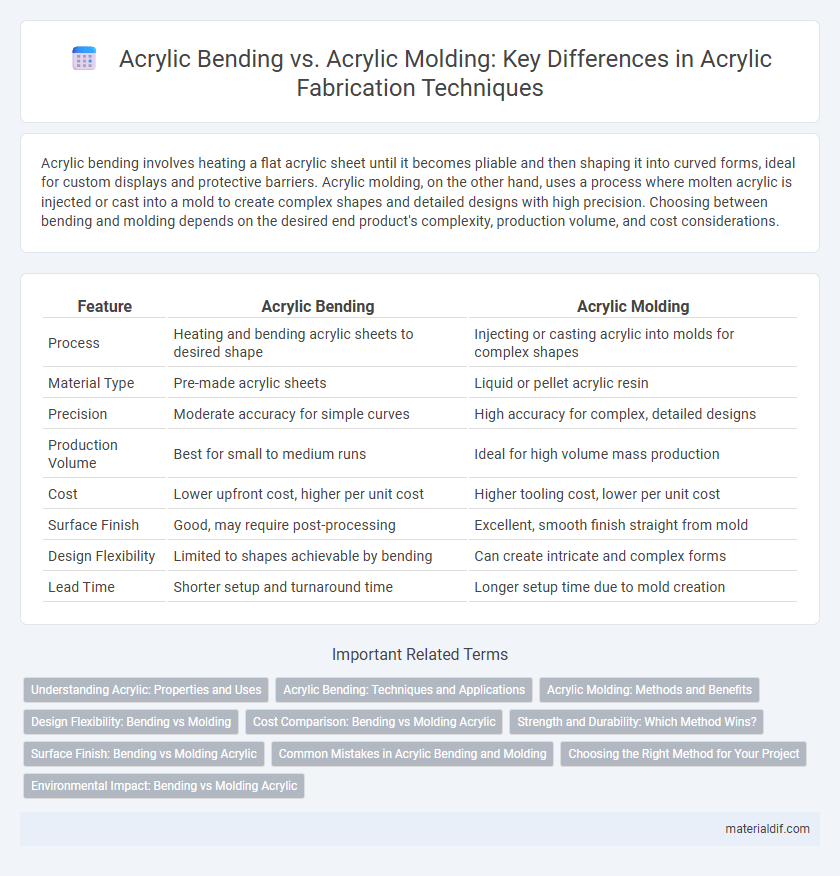
| Feature | Acrylic Bending | Acrylic Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heating and bending acrylic sheets to desired shape | Injecting or casting acrylic into molds for complex shapes |
| Material Type | Pre-made acrylic sheets | Liquid or pellet acrylic resin |
| Precision | Moderate accuracy for simple curves | High accuracy for complex, detailed designs |
| Production Volume | Best for small to medium runs | Ideal for high volume mass production |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost, higher per unit cost | Higher tooling cost, lower per unit cost |
| Surface Finish | Good, may require post-processing | Excellent, smooth finish straight from mold |
| Design Flexibility | Limited to shapes achievable by bending | Can create intricate and complex forms |
| Lead Time | Shorter setup and turnaround time | Longer setup time due to mold creation |
Understanding Acrylic: Properties and Uses
Acrylic bending involves heating sheets of acrylic to a pliable state for shaping, preserving its clarity and durability, ideal for custom display cases and light fixtures. Acrylic molding, including injection and casting methods, forms complex shapes by pouring or injecting molten acrylic into molds, widely used in automotive parts and consumer products. Understanding the distinct thermal and mechanical properties of acrylic, such as its high impact resistance and UV stability, is crucial for selecting the appropriate fabrication technique in design and manufacturing applications.
Acrylic Bending: Techniques and Applications
Acrylic bending involves heating sheets of acrylic plastic to a pliable state before shaping them using techniques like strip heating, hot air bending, or infrared heating, allowing precise curves and angles. This process is widely applied in architectural designs, display cases, and custom protective screens due to its clarity and durability. Compared to acrylic molding, bending offers quicker turnaround times and cost-effective solutions for creating large, seamless bends without compromising the material's optical properties.
Acrylic Molding: Methods and Benefits
Acrylic molding encompasses various techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, and casting, each tailored to produce precise shapes and complex designs with excellent surface finishes. These methods offer benefits including high production efficiency, enhanced structural integrity, and the ability to create intricate details that are difficult to achieve through bending. Compared to acrylic bending, molding ensures superior durability and consistency, making it ideal for mass production and custom applications in industries like automotive, signage, and optics.
Design Flexibility: Bending vs Molding
Acrylic bending offers design flexibility through precise, custom curves and shapes formed by heating solid sheets, ideal for prototypes and small-scale projects. Acrylic molding enables complex, intricate designs with uniform wall thickness by injecting molten acrylic into molds, suited for mass production and detailed geometries. While bending allows on-demand adjustments and simpler tooling, molding provides greater consistency and scalability for advanced shapes.
Cost Comparison: Bending vs Molding Acrylic
Acrylic bending typically incurs lower upfront costs due to simpler equipment and quicker setup times, making it cost-effective for small batches or custom shapes. Acrylic molding involves higher initial expenses for mold fabrication and machinery but offers significant cost advantages in large-scale production through faster output and consistent quality. Choosing between acrylic bending and molding depends on production volume and budget, with bending favoring low-volume, flexible designs and molding suited for high-volume, repeatable manufacturing.
Strength and Durability: Which Method Wins?
Acrylic molding typically offers superior strength and durability compared to acrylic bending due to the uniform molecular structure formed during the molding process, which reduces stress points and potential weak spots. Bending acrylic involves applying heat to reshape sheets, often causing localized stress that may lead to cracking or weakening over time. For applications demanding long-lasting durability and structural integrity, molded acrylic parts are generally the more reliable choice.
Surface Finish: Bending vs Molding Acrylic
Acrylic bending typically results in a smooth, polished edge with minimal surface imperfections due to localized heating, which preserves the clarity and gloss of the material. In contrast, acrylic molding can produce parts with more varied surface finishes depending on the mold quality and cooling rate, often requiring post-processing to achieve a flawless appearance. Surface finish in molding may exhibit slight texture or flow lines, whereas bending maintains a consistent, high-gloss transparency essential for aesthetic applications.
Common Mistakes in Acrylic Bending and Molding
Common mistakes in acrylic bending include overheating that causes bubbles and burns, uneven heating leading to cracks, and improper clamping resulting in deformation. In acrylic molding, errors often arise from incorrect temperature control which can cause warping or incomplete curing, improper mold design causing inconsistent shapes, and using unsuitable acrylic grades that affect the final product's strength and clarity. Precise temperature management, tool calibration, and material selection are critical to avoiding defects in both bending and molding processes.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Acrylic bending offers precise control for creating seamless curves and is ideal for custom displays or signage requiring smooth, continuous shapes. Acrylic molding, however, suits mass production by enabling complex, repeatable forms with consistent quality using heat and pressure. Selecting the right method depends on project scale, design complexity, and budget constraints to achieve optimal results.
Environmental Impact: Bending vs Molding Acrylic
Acrylic bending produces less waste by heating and reshaping pre-formed sheets, minimizing material loss and energy consumption compared to acrylic molding, which involves melting raw acrylic pellets and forming them into shapes, often generating higher emissions and scraps. Bending processes typically require lower temperatures, reducing carbon footprint relative to the energy-intensive molding methods such as injection or compression molding. Choosing acrylic bending over molding supports eco-friendly manufacturing by conserving resources and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions tied to acrylic fabrication.
Acrylic Bending vs Acrylic Molding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com