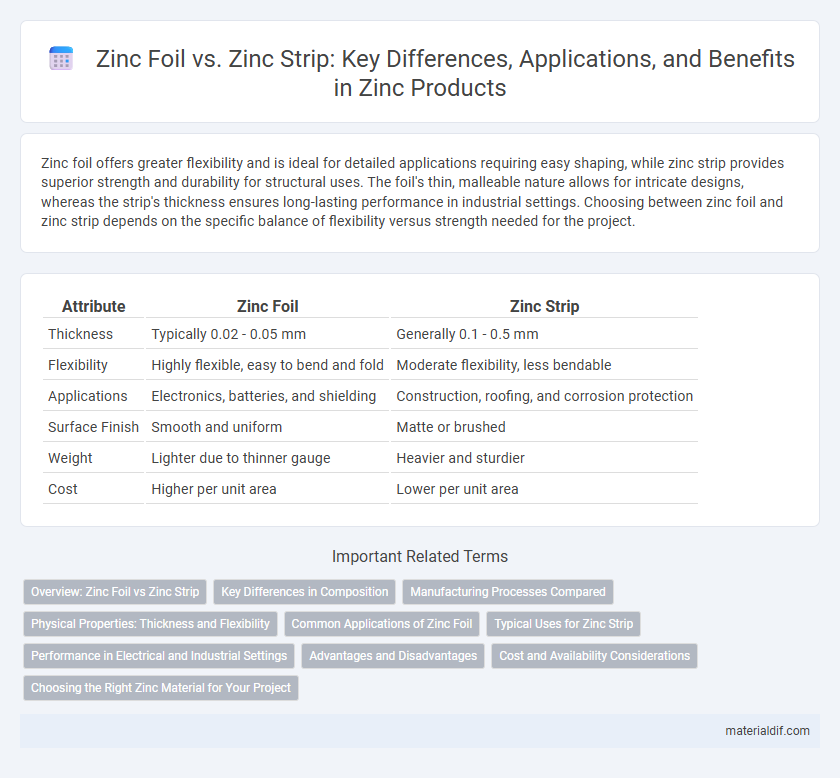
Zinc foil offers greater flexibility and is ideal for detailed applications requiring easy shaping, while zinc strip provides superior strength and durability for structural uses. The foil's thin, malleable nature allows for intricate designs, whereas the strip's thickness ensures long-lasting performance in industrial settings. Choosing between zinc foil and zinc strip depends on the specific balance of flexibility versus strength needed for the project.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Zinc Foil | Zinc Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Typically 0.02 - 0.05 mm | Generally 0.1 - 0.5 mm |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, easy to bend and fold | Moderate flexibility, less bendable |
| Applications | Electronics, batteries, and shielding | Construction, roofing, and corrosion protection |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and uniform | Matte or brushed |
| Weight | Lighter due to thinner gauge | Heavier and sturdier |
| Cost | Higher per unit area | Lower per unit area |
Overview: Zinc Foil vs Zinc Strip
Zinc foil offers a thin, flexible form ideal for precise applications like battery electrodes and chemical experiments, while zinc strip is thicker and more rigid, suitable for construction, galvanization, and corrosion resistance tasks. Zinc foil typically ranges from 0.01 mm to 0.05 mm in thickness, providing high surface area and malleability, whereas zinc strips commonly measure 0.1 mm to several millimeters for enhanced durability. Both forms provide excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion protection, but the choice depends on the required mechanical strength and application specificity.
Key Differences in Composition
Zinc foil is characterized by its thin, flexible sheet form with a purity level typically around 99.9%, designed for applications requiring easy molding and lightweight protection. Zinc strip, in contrast, is thicker, more rigid, and often produced with slight alloying elements to enhance strength and durability for structural uses. The key compositional difference lies in the foil's ultra-pure, malleable zinc content versus the strip's fortified, thicker zinc blend tailored for mechanical resilience.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Zinc foil is typically produced through a cold rolling process that achieves ultra-thin, flexible sheets ideal for applications requiring high precision and finesse. Zinc strips are manufactured by hot rolling thicker zinc slabs followed by annealing to enhance strength and durability, making them suitable for structural uses. The distinct manufacturing techniques result in differences in texture, thickness, and mechanical properties, influencing their respective industrial applications.
Physical Properties: Thickness and Flexibility
Zinc foil exhibits significantly greater flexibility due to its reduced thickness, typically ranging from 0.02 to 0.1 mm, allowing for easy bending and shaping without cracking. In contrast, zinc strips are thicker, generally between 0.3 to 1.5 mm, resulting in increased rigidity and reduced malleability for applications requiring structural stability. The thin gauge of zinc foil makes it ideal for precision wrapping and corrosion resistance, whereas thicker zinc strips provide enhanced mechanical strength and durability.
Common Applications of Zinc Foil
Zinc foil is extensively used in applications requiring flexible, thin, and highly malleable metal for corrosion protection, such as in battery manufacturing and metal encapsulation. Its conformability makes it ideal for wrapping and sealing electronic components and for use in thin-film solar cells where precision layering is critical. Unlike zinc strips, which are thicker and used for structural or grounding purposes, zinc foil excels in roles demanding lightweight shielding and efficient coverage.
Typical Uses for Zinc Strip
Zinc strip is commonly used in corrosion protection, galvanic anodes, and chemical experiments due to its consistent thickness and flexibility. It serves as a reliable material in battery manufacturing and electroplating processes where precise control over zinc deposition is essential. Unlike zinc foil, zinc strip offers enhanced durability and ease of cutting, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring strength and stability.
Performance in Electrical and Industrial Settings
Zinc foil offers superior flexibility and a higher surface area, enhancing its conductivity and corrosion resistance in electrical applications compared to zinc strip. Zinc strip, with its rigid structure, provides greater mechanical strength and durability, making it ideal for industrial settings requiring robustness and longevity. Both materials excel in specific performance criteria, with foil preferred for intricate electrical components and strip favored for heavy-duty industrial uses.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Zinc foil offers superior flexibility and ease of molding, making it ideal for detailed applications such as corrosion protection in batteries and chemical reactions. Zinc strips provide greater mechanical strength and are better suited for structural uses, but they may be less adaptable to curved surfaces. While zinc foil is more expensive and prone to tearing, zinc strips offer durability at a lower cost, balancing performance and price depending on the application's requirements.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Zinc foil typically offers a higher cost due to its thinness and manufacturing precision, making it suitable for specialized applications requiring flexibility. Zinc strips are generally more affordable and widely available, favored for bulk use in construction, galvanizing, and cathodic protection. Availability of zinc strips in various thicknesses and widths ensures easier sourcing for industrial-scale projects compared to zinc foil.
Choosing the Right Zinc Material for Your Project
Zinc foil offers superior flexibility and thinness, ideal for intricate applications requiring precise layering or wrapping. Zinc strips provide greater rigidity and strength, making them suitable for structural uses or projects demanding durability. Selecting the right zinc material depends on project requirements such as flexibility, thickness, and mechanical strength to ensure optimal performance.
Zinc Foil vs Zinc Strip Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com