Titanium wire offers superior flexibility and strength, making it ideal for intricate pet accessories and durable collars. In contrast, titanium strip provides a broader, flat surface perfect for engraving pet identification tags with clear, lasting text. Choosing between titanium wire and strip depends on whether flexibility or surface area is the priority for your pet's needs.
Table of Comparison
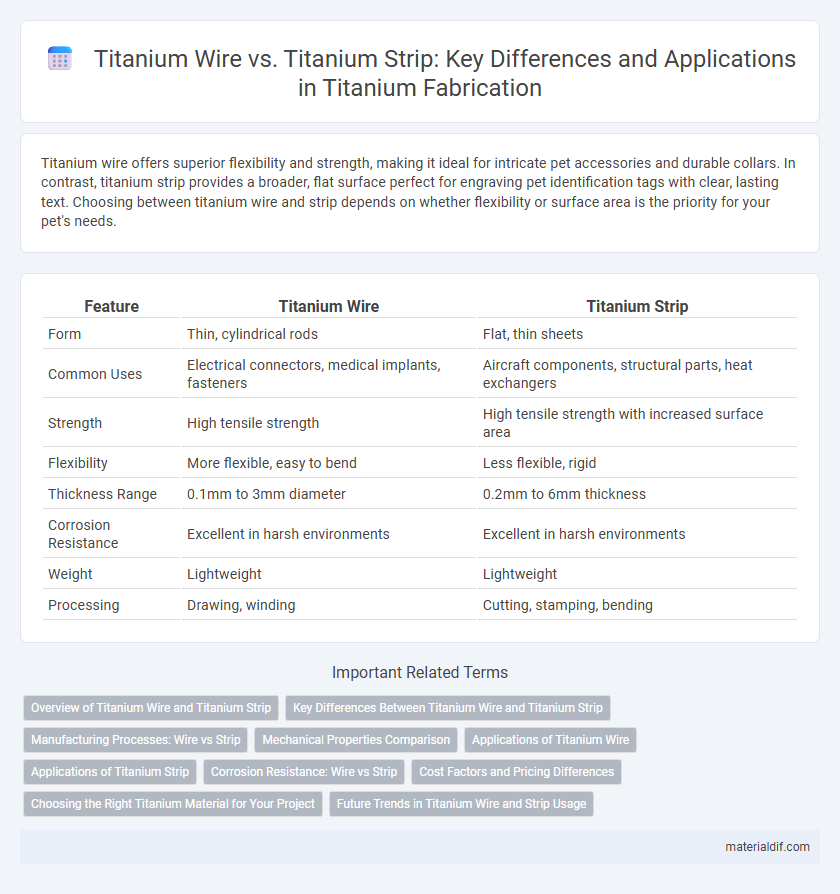
| Feature | Titanium Wire | Titanium Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Thin, cylindrical rods | Flat, thin sheets |
| Common Uses | Electrical connectors, medical implants, fasteners | Aircraft components, structural parts, heat exchangers |
| Strength | High tensile strength | High tensile strength with increased surface area |
| Flexibility | More flexible, easy to bend | Less flexible, rigid |
| Thickness Range | 0.1mm to 3mm diameter | 0.2mm to 6mm thickness |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in harsh environments | Excellent in harsh environments |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Processing | Drawing, winding | Cutting, stamping, bending |
Overview of Titanium Wire and Titanium Strip
Titanium wire offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for medical devices, aerospace fasteners, and precision engineering applications. Titanium strip, characterized by its flat and thin sheet form, provides superior surface finish and is commonly used in manufacturing components like gaskets, springs, and architectural materials. Both titanium wire and strip leverage titanium's lightweight and biocompatible properties but differ in form factor and application scope, with wire suited for intricate or load-bearing uses and strip favored for structural and surface-specific roles.
Key Differences Between Titanium Wire and Titanium Strip
Titanium wire and titanium strip differ primarily in shape and application, with wire being a thin, flexible cylindrical form ideal for precision work such as medical devices and aerospace components. Titanium strip features a flat, rectangular cross-section offering greater surface area and rigidity, suited for structural uses, heat exchangers, and electronic components. The manufacturing process also varies; wire typically undergoes drawing to achieve thin gauges, while strip is rolled or milled to precise thicknesses.
Manufacturing Processes: Wire vs Strip
Titanium wire manufacturing involves processes such as hot rolling, drawing, and annealing to achieve high tensile strength and flexibility, suitable for medical devices and aerospace components. Titanium strip production primarily uses hot rolling followed by cold rolling and finishing treatments to create flat, uniform sheets with precise thickness, ideal for structural applications and corrosion-resistant uses. Both wire and strip require controlled environments and specialized equipment to maintain titanium's purity and mechanical properties during fabrication.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Titanium wire exhibits higher tensile strength and enhanced flexibility compared to titanium strip, making it ideal for applications requiring precise deformation and durability. In contrast, titanium strip offers superior surface finish and dimensional stability, which is essential for structural components subject to consistent stress. The choice between titanium wire and strip depends on the balance between mechanical resilience and geometric precision needed for specific engineering tasks.
Applications of Titanium Wire
Titanium wire is extensively used in medical implants, aerospace components, and electrical applications due to its high strength, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. It is ideal for manufacturing surgical instruments, orthodontic braces, and precision fasteners where durability and lightweight properties are critical. In contrast, titanium strip is often utilized for structural parts and heat exchangers, emphasizing flat form factors rather than the fine, flexible properties required in wire applications.
Applications of Titanium Strip
Titanium strip is widely used in aerospace, medical devices, and chemical processing industries due to its superior strength, corrosion resistance, and flexibility. Its flat and uniform shape makes it ideal for manufacturing intricate parts, such as springs, fasteners, and heat exchangers that require precise dimensions. Titanium strip's excellent weldability and fatigue resistance enhance its application in environments exposed to high stress and temperature variations.
Corrosion Resistance: Wire vs Strip
Titanium wire exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance due to its uniform surface area and minimal exposure to environmental elements, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate shapes. Titanium strip, while also highly resistant to corrosion, offers a broader surface area that may be more susceptible to localized corrosion if not properly coated or finished. Both forms maintain the inherent corrosion-resistant properties of titanium, but wire's shape advantage often results in superior long-term durability in harsh environments.
Cost Factors and Pricing Differences
Titanium wire typically costs more than titanium strips due to the intricate manufacturing processes required to produce fine, uniform diameters, which involve precise drawing and annealing techniques. In contrast, titanium strips benefit from more straightforward rolling and cutting methods, resulting in lower production costs and competitive pricing. Market demand, material thickness, and alloy grade also significantly influence the price variance between titanium wire and strips.
Choosing the Right Titanium Material for Your Project
Titanium wire offers exceptional flexibility and strength, making it ideal for intricate applications requiring precision and durability, such as medical instruments and aerospace components. Titanium strip provides a broader surface area and consistent thickness, suitable for structural parts and heat exchangers where uniform strength and corrosion resistance are critical. Selecting titanium wire or strip depends on the specific project requirements, including mechanical stress, flexibility needs, and fabrication methods to optimize performance and longevity.
Future Trends in Titanium Wire and Strip Usage
Emerging advancements in additive manufacturing and biomedical implants are driving increased demand for titanium wire due to its superior flexibility and strength-to-weight ratio. Titanium strips are gaining traction in aerospace and automotive industries, where enhanced corrosion resistance and formability enable lightweight structural components. Future trends indicate a growing shift toward hybrid applications combining titanium wire and strip to optimize mechanical performance and cost-efficiency.
Titanium Wire vs Titanium Strip Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com