Titanium foil offers a thin, flexible solution ideal for delicate applications requiring precise contouring, while titanium mesh provides a rigid, porous structure that promotes tissue integration and stability in reconstructive procedures. Mesh's open design enhances vascularization and bone growth, making it suitable for load-bearing areas, whereas foil's smooth surface minimizes tissue irritation and suits protective barriers. Choosing between the two depends on the specific surgical requirements, balancing flexibility, strength, and biological compatibility.
Table of Comparison
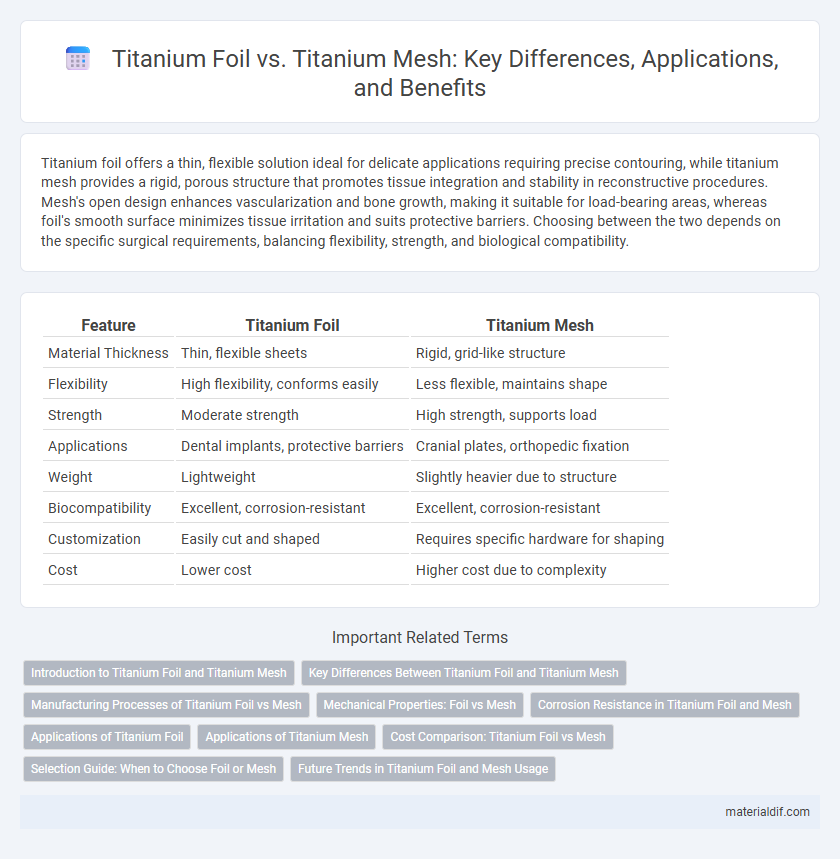
| Feature | Titanium Foil | Titanium Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Material Thickness | Thin, flexible sheets | Rigid, grid-like structure |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, conforms easily | Less flexible, maintains shape |
| Strength | Moderate strength | High strength, supports load |
| Applications | Dental implants, protective barriers | Cranial plates, orthopedic fixation |
| Weight | Lightweight | Slightly heavier due to structure |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, corrosion-resistant | Excellent, corrosion-resistant |
| Customization | Easily cut and shaped | Requires specific hardware for shaping |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to complexity |
Introduction to Titanium Foil and Titanium Mesh
Titanium foil is a thin, flexible sheet of titanium widely used in aerospace, medical implants, and electronics for its lightweight strength and excellent corrosion resistance. Titanium mesh consists of interconnected strands forming a grid-like structure, commonly utilized for bone repair, reinforcement in construction, and filtration due to its durability and porosity. Both materials leverage titanium's biocompatibility and mechanical properties but differ significantly in form and application versatility.
Key Differences Between Titanium Foil and Titanium Mesh
Titanium foil is a thin, flexible sheet used primarily for surface protection and lightweight structural applications, offering excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Titanium mesh consists of interwoven or perforated strands, providing high strength and rigidity with enhanced fixation capabilities in medical implants and aerospace components. The key differences lie in their form factor, mechanical properties, and application areas, with foil favoring coverage and mesh optimizing strength and integration.
Manufacturing Processes of Titanium Foil vs Mesh
Titanium foil is produced through rolling and annealing processes that reduce thick titanium slabs into thin, flexible sheets with smooth surfaces ideal for precise industrial applications. Titanium mesh, in contrast, is manufactured by weaving or laser cutting titanium wires or sheets into porous, grid-like structures that offer enhanced strength and breathability for medical implants and aerospace uses. The choice of manufacturing method directly influences the mechanical properties, thickness uniformity, and application suitability of titanium foil versus mesh.
Mechanical Properties: Foil vs Mesh
Titanium foil offers superior flexibility and uniform strength, making it ideal for applications requiring precise contouring and consistent load distribution. Titanium mesh provides enhanced mechanical ventilation and structural support, with a higher strength-to-weight ratio due to its porous design. The choice between foil and mesh depends on balancing tensile strength, elasticity, and the need for rigidity in specific engineering or medical uses.
Corrosion Resistance in Titanium Foil and Mesh
Titanium foil exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance due to its uniform and dense oxide layer, providing superior protection against harsh environments compared to titanium mesh. While titanium mesh maintains good corrosion resistance, its perforated structure increases surface area exposure, potentially accelerating localized corrosion under aggressive conditions. Optimal corrosion resistance in titanium applications is achieved by selecting foil for environments requiring maximum chemical stability and mesh when flexibility and weight reduction are prioritized alongside corrosion protection.
Applications of Titanium Foil
Titanium foil is extensively used in aerospace and medical industries for applications requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials with excellent strength-to-weight ratios. It serves as a barrier layer in electronics, offers flexibility in manufacturing medical implants, and is preferred for chemical processing equipment due to its superior resistance to aggressive environments. Its thin profile allows for easy shaping and layering, making it ideal for specialized engineering and high-performance industrial uses.
Applications of Titanium Mesh
Titanium mesh is extensively used in medical applications such as cranial and maxillofacial reconstructive surgery due to its superior strength, flexibility, and biocompatibility. Its porous structure allows for tissue integration and bone regeneration, making it ideal for implant fixation and fracture stabilization. Compared to titanium foil, mesh provides enhanced mechanical support while facilitating vascularization and reducing implant weight.
Cost Comparison: Titanium Foil vs Mesh
Titanium foil generally costs less than titanium mesh due to its simpler manufacturing process and lower material usage. Titanium mesh requires precise weaving or welding, increasing production expenses and overall price. When budgeting for medical implants or industrial applications, the cost-effectiveness of titanium foil makes it a preferred option over titanium mesh.
Selection Guide: When to Choose Foil or Mesh
Titanium foil offers a smooth, flexible surface ideal for applications requiring corrosion resistance and lightweight shielding, making it suitable for electronic components and medical implants. Titanium mesh provides superior strength, ventilation, and structural support, commonly chosen for aerospace parts, filtration systems, and reconstructive surgery frameworks. Selecting between foil and mesh depends on the need for either a continuous barrier or a porous, reinforced structure tailored to specific engineering or biomedical uses.
Future Trends in Titanium Foil and Mesh Usage
Titanium foil is increasingly favored for its lightweight, high strength, and flexibility in aerospace and medical implant industries, driving innovations in ultra-thin, corrosion-resistant applications. Titanium mesh usage is expanding in reconstructive surgery and additive manufacturing due to its excellent biocompatibility and structural support, with future trends emphasizing customization through 3D printing technologies. Emerging developments focus on enhancing surface treatments and alloy compositions to optimize performance and multifunctionality in both titanium foil and mesh across advanced technological fields.
Titanium Foil vs Titanium Mesh Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com