Seamless titanium offers superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to welded titanium, as it lacks any weak points or joints. Welded titanium, while more cost-effective and easier to manufacture, may be prone to stress concentrations at the welds, potentially compromising durability over time. Choosing seamless titanium ensures enhanced longevity and reliability, making it ideal for high-performance pet products requiring maximum resilience.
Table of Comparison
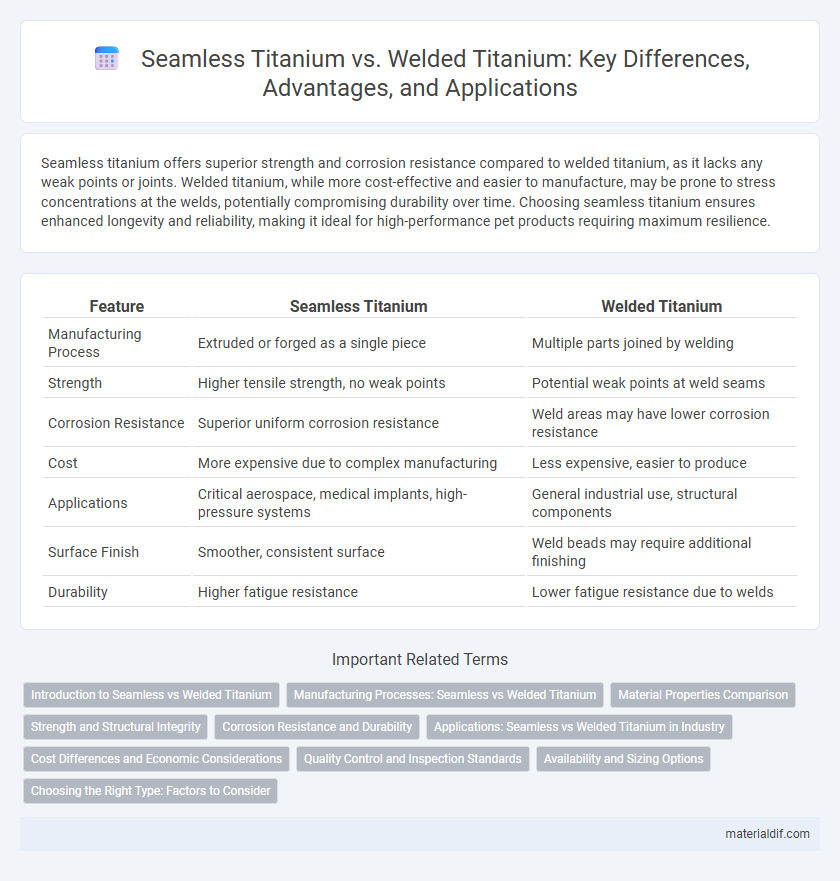
| Feature | Seamless Titanium | Welded Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Extruded or forged as a single piece | Multiple parts joined by welding |
| Strength | Higher tensile strength, no weak points | Potential weak points at weld seams |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior uniform corrosion resistance | Weld areas may have lower corrosion resistance |
| Cost | More expensive due to complex manufacturing | Less expensive, easier to produce |
| Applications | Critical aerospace, medical implants, high-pressure systems | General industrial use, structural components |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, consistent surface | Weld beads may require additional finishing |
| Durability | Higher fatigue resistance | Lower fatigue resistance due to welds |
Introduction to Seamless vs Welded Titanium
Seamless titanium is produced through a forging or extrusion process, resulting in a uniform, defect-free structure that offers superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to welded titanium. Welded titanium involves joining metal pieces through fusion techniques, which can introduce weak points and variability in mechanical properties along the weld seams. Selecting seamless titanium enhances performance in aerospace, medical, and chemical industries where material integrity is critical.
Manufacturing Processes: Seamless vs Welded Titanium
Seamless titanium is manufactured through a hot extrusion or rotary piercing process, creating a single, continuous piece with uniform grain structure, enhancing strength and corrosion resistance. Welded titanium involves joining multiple pieces using advanced welding techniques such as electron beam or laser welding, which may introduce heat-affected zones and potential stress points. The seamless process results in higher integrity and reliability for critical applications, while welded titanium allows for more complex shapes and cost-effective production.
Material Properties Comparison
Seamless titanium offers superior uniformity and enhanced corrosion resistance due to its continuous grain structure, making it ideal for high-stress applications where strength and durability are critical. Welded titanium, while cost-effective and versatile for complex shapes, may exhibit localized weaknesses at the weld seams, potentially reducing overall fatigue resistance and impacting mechanical properties. The choice between seamless and welded titanium must consider factors such as tensile strength, fatigue endurance, and exposure to corrosive environments to ensure optimal material performance.
Strength and Structural Integrity
Seamless titanium exhibits superior strength and structural integrity compared to welded titanium due to the absence of joints or welds that can act as weak points under stress. The uniform grain structure in seamless titanium enhances its resistance to fatigue and corrosion, making it ideal for high-pressure applications. Welded titanium, while cost-effective, may experience reduced durability and potential failure risks at the welded seams when subjected to extreme conditions.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Seamless titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to the absence of weld joints, which are potential sites for corrosion and structural weaknesses. Welded titanium, while generally strong, may have compromised durability in harsh environments because weld zones can be prone to micro-cracks and galvanic corrosion. In marine and chemical applications, seamless titanium is preferred for its enhanced longevity and consistent performance under corrosive stress.
Applications: Seamless vs Welded Titanium in Industry
Seamless titanium is preferred in aerospace and medical industries due to its superior strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high pressure, making it ideal for critical components such as aircraft engine parts and surgical implants. Welded titanium, offering cost efficiency and design flexibility, is commonly used in chemical processing equipment, heat exchangers, and marine applications where complex shapes and larger sizes are required. Industrial applications choose seamless titanium for high-performance, load-bearing environments, while welded titanium suits fabrication of large structures with moderate stress demands.
Cost Differences and Economic Considerations
Seamless titanium typically incurs higher production costs due to its complex manufacturing process involving extrusion or rotary piercing, leading to superior strength and corrosion resistance compared to welded titanium. Welded titanium, produced by joining sheets or plates, offers a more cost-effective solution with lower material waste and faster fabrication times, making it economically advantageous for large-scale projects with less critical structural demands. Cost considerations must balance the application requirements, where seamless titanium justifies its premium through enhanced performance, while welded titanium provides a budget-friendly alternative without compromising basic functionality.
Quality Control and Inspection Standards
Seamless titanium tubes offer superior quality control through uniform grain structure and absence of weld defects, ensuring enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Welded titanium tubes require rigorous inspection standards such as radiographic and ultrasonic testing to identify potential weld flaws like porosity or cracks that could compromise structural integrity. Compliance with ASTM B337 and AMS 4901 standards is critical in both processes to guarantee the highest reliability in aerospace, medical, and chemical industry applications.
Availability and Sizing Options
Seamless titanium tubing offers limited size availability, typically produced in standard diameters suited for high-pressure applications, ensuring superior strength and corrosion resistance. Welded titanium tubes have a broader range of sizing options and wall thicknesses due to their fabrication process, providing flexibility for custom dimensions and complex shapes. Availability of welded titanium is generally higher, making it more accessible for applications requiring specific sizes or large volume orders.
Choosing the Right Type: Factors to Consider
Seamless titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and strength due to its uniform structure, making it ideal for high-pressure and critical applications. Welded titanium provides flexibility in design and cost-effectiveness for larger or complex shapes but may have lower chemical resistance at the weld seams. When choosing between seamless and welded titanium, consider factors such as application pressure, corrosion environment, fabrication complexity, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Seamless Titanium vs Welded Titanium Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com