Titanium wire offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility compared to nickel wire, making it ideal for long-term use in pet accessories and medical applications. While nickel wire is more flexible and affordable, it may cause allergic reactions in some pets due to nickel sensitivity. Choosing titanium wire ensures durability and safety, especially for pets with metal allergies.
Table of Comparison
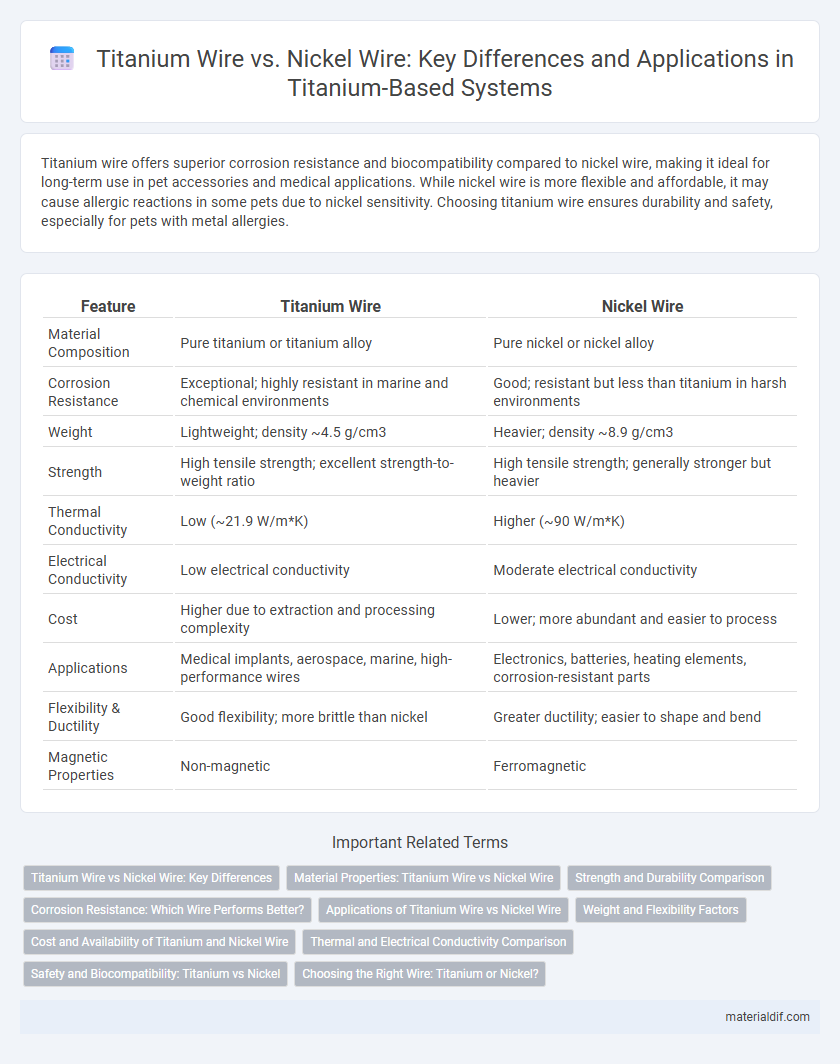
| Feature | Titanium Wire | Nickel Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure titanium or titanium alloy | Pure nickel or nickel alloy |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional; highly resistant in marine and chemical environments | Good; resistant but less than titanium in harsh environments |
| Weight | Lightweight; density ~4.5 g/cm3 | Heavier; density ~8.9 g/cm3 |
| Strength | High tensile strength; excellent strength-to-weight ratio | High tensile strength; generally stronger but heavier |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (~21.9 W/m*K) | Higher (~90 W/m*K) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low electrical conductivity | Moderate electrical conductivity |
| Cost | Higher due to extraction and processing complexity | Lower; more abundant and easier to process |
| Applications | Medical implants, aerospace, marine, high-performance wires | Electronics, batteries, heating elements, corrosion-resistant parts |
| Flexibility & Ductility | Good flexibility; more brittle than nickel | Greater ductility; easier to shape and bend |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Ferromagnetic |
Titanium Wire vs Nickel Wire: Key Differences
Titanium wire offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility compared to nickel wire, making it ideal for medical implants and aerospace applications. Nickel wire boasts higher electrical conductivity and lower cost but may cause allergic reactions and degrade in harsh environments. The choice between titanium and nickel wire depends on specific requirements for strength, conductivity, and environmental resilience.
Material Properties: Titanium Wire vs Nickel Wire
Titanium wire offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications where durability and lightweight materials are crucial. Nickel wire excels in electrical conductivity and thermal resistance, often utilized in electronics and heating elements due to its stable performance under high temperatures. Both metals provide unique mechanical properties, but titanium's biocompatibility and superior strength distinguish it from nickel's conductivity and heat tolerance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium wire exhibits superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to nickel wire, making it ideal for applications demanding both high tensile strength and lightweight materials. Its excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue durability outperform nickel wire, ensuring longer lifespan under harsh environmental conditions. Nickel wire, while strong and flexible, tends to degrade faster under cyclic stress and corrosive exposure relative to titanium.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Wire Performs Better?
Titanium wire offers superior corrosion resistance compared to nickel wire, making it ideal for harsh environments such as marine and chemical processing industries. Its ability to form a stable oxide layer prevents oxidation and degradation over time, whereas nickel wire is more prone to corrosion, especially in acidic or saline conditions. This enhanced durability extends the lifespan of titanium wire in applications requiring consistent performance under corrosive exposure.
Applications of Titanium Wire vs Nickel Wire
Titanium wire is extensively used in aerospace, medical implants, and marine environments due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Nickel wire finds applications in electrical heating elements, battery manufacturing, and corrosion-resistant alloys because of its high electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance. The choice between titanium and nickel wire depends on specific application requirements such as mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and electrical properties.
Weight and Flexibility Factors
Titanium wire is significantly lighter than nickel wire, with a density of about 4.5 g/cm3 compared to nickel's 8.9 g/cm3, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical. Titanium also offers superior flexibility and corrosion resistance, maintaining strength without brittleness under repeated bending. Nickel wire, while heavier and less flexible, provides higher electrical conductivity but sacrifices the lightweight and durable benefits seen in titanium.
Cost and Availability of Titanium and Nickel Wire
Titanium wire is significantly more expensive than nickel wire due to the complex extraction and processing required for titanium, making nickel wire a more cost-effective choice for many industrial applications. While titanium wire offers superior corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio, nickel wire is widely available and produced at a larger scale, resulting in lower prices and easier procurement. The limited supply and higher production costs of titanium wire contribute to its premium pricing compared to the more abundant and affordable nickel wire.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Titanium wire exhibits significantly lower thermal and electrical conductivity compared to nickel wire, with thermal conductivities of approximately 21.9 W/m*K for titanium and 90.9 W/m*K for nickel. Nickel wire's electrical conductivity is around 14.3% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), whereas titanium's is much lower, roughly 1.0% IACS, making nickel preferable in applications requiring efficient heat or electrical transfer. The lower conductivity of titanium wire makes it ideal for corrosion-resistant, high-strength applications where thermal and electrical conduction are less critical.
Safety and Biocompatibility: Titanium vs Nickel
Titanium wire offers superior biocompatibility and corrosion resistance compared to nickel wire, making it safer for medical and dental applications where prolonged skin or tissue contact occurs. Nickel wire can release ions that may trigger allergic reactions or toxicity in sensitive individuals, while titanium's inert nature minimizes adverse biological responses. Medical-grade titanium wire is widely preferred for implants and prosthetics due to its excellent safety profile and reduced risk of inflammation or hypersensitivity.
Choosing the Right Wire: Titanium or Nickel?
Titanium wire offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making it ideal for aerospace, medical implants, and jewelry applications. Nickel wire provides superior electrical conductivity and flexibility, suitable for electronic components and heating elements. Selecting between titanium and nickel wire depends on the specific requirements of durability, conductivity, and environmental exposure in the intended application.
Titanium Wire vs Nickel Wire Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com