Titanium mesh offers superior strength and stability compared to titanium wire, making it ideal for complex structural support in medical and dental applications. It provides enhanced biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term durability without causing adverse reactions in pet implants. While titanium wire is flexible and easier to manipulate, titanium mesh's rigid framework promotes better tissue integration and healing in veterinary procedures.
Table of Comparison
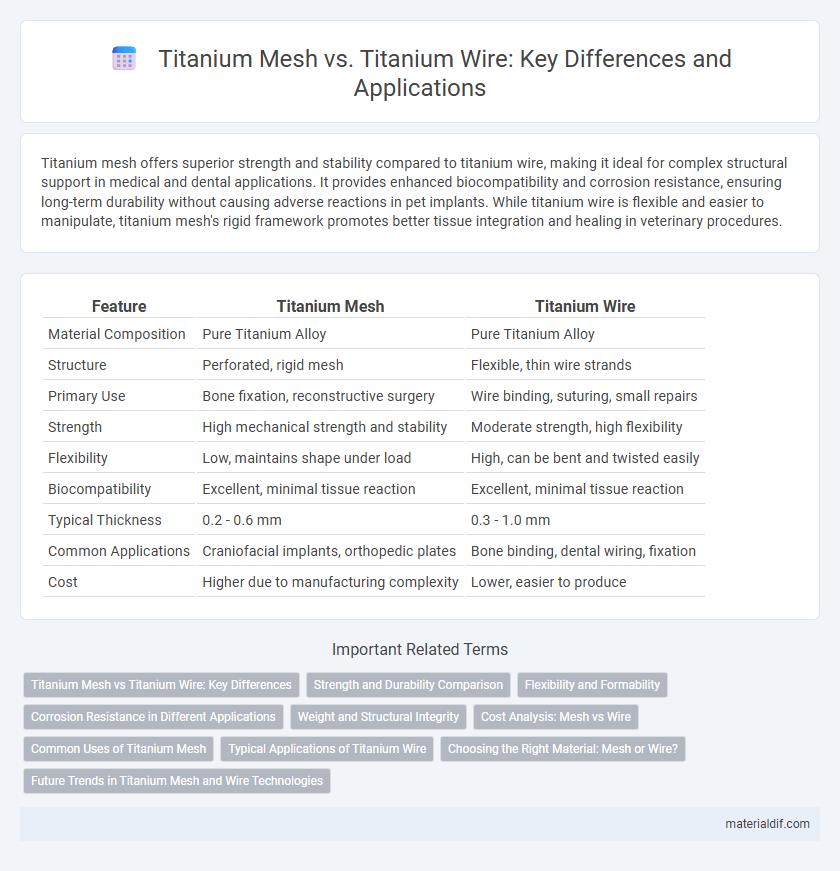
| Feature | Titanium Mesh | Titanium Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure Titanium Alloy | Pure Titanium Alloy |
| Structure | Perforated, rigid mesh | Flexible, thin wire strands |
| Primary Use | Bone fixation, reconstructive surgery | Wire binding, suturing, small repairs |
| Strength | High mechanical strength and stability | Moderate strength, high flexibility |
| Flexibility | Low, maintains shape under load | High, can be bent and twisted easily |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent, minimal tissue reaction | Excellent, minimal tissue reaction |
| Typical Thickness | 0.2 - 0.6 mm | 0.3 - 1.0 mm |
| Common Applications | Craniofacial implants, orthopedic plates | Bone binding, dental wiring, fixation |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing complexity | Lower, easier to produce |
Titanium Mesh vs Titanium Wire: Key Differences
Titanium mesh provides superior structural support and flexibility in bone reconstruction compared to titanium wire, which is primarily used for simple fixation tasks. The porous design of titanium mesh allows for better tissue integration and reduced risk of infection, while titanium wire offers ease of contouring and is cost-effective for minor stabilization. Choosing between titanium mesh and wire depends on the complexity of the surgical procedure and desired biomechanical properties.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium mesh offers superior strength and durability compared to titanium wire due to its interconnected lattice structure, which distributes stress more evenly and resists deformation under load. In tensile tests, titanium mesh demonstrates higher yield strength and greater fatigue resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term structural integrity. Titanium wire, while flexible and easier to shape, typically exhibits lower tensile strength and reduced durability in high-stress environments.
Flexibility and Formability
Titanium mesh offers superior flexibility and ease of contouring for complex anatomical structures compared to titanium wire, enabling precise adaptation in medical and industrial applications. Its interwoven design allows for uniform stress distribution and enhanced formability without compromising strength. Titanium wire, while strong and malleable, lacks the same degree of pliability and adaptability, making it less suitable for intricate shaping requirements.
Corrosion Resistance in Different Applications
Titanium mesh exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to titanium wire due to its uniform structure and greater surface area, which enhances its passivation layer stability in harsh environments. In marine and biomedical applications, titanium mesh's enhanced corrosion resistance ensures longer durability and biocompatibility, minimizing metal ion release and potential tissue reactions. Titanium wire, while corrosion-resistant, may develop localized corrosion points under mechanical stresses, making mesh preferable for critical structural and implant uses.
Weight and Structural Integrity
Titanium mesh offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to titanium wire, providing enhanced structural integrity without adding significant weight. Its interlocking grid design distributes stress evenly, making it ideal for applications requiring robust load-bearing capacity. Titanium wire, while lighter, lacks the uniform strength and rigidity of mesh, making it less suitable for high-stress structural uses.
Cost Analysis: Mesh vs Wire
Titanium mesh typically incurs higher costs due to complex manufacturing processes and precision required for medical and aerospace applications, whereas titanium wire is generally more affordable and versatile for simpler structural uses. Cost analysis must factor in production scale, material thickness, and application-specific requirements, with wire benefiting from lower raw material waste and easier fabrication. Choosing between mesh and wire hinges on balancing cost efficiency against mechanical performance criteria.
Common Uses of Titanium Mesh
Titanium mesh is commonly used in medical applications such as cranial and maxillofacial surgery due to its rigidity and biocompatibility, providing strong support for bone regeneration. Unlike titanium wire, which is often utilized for suturing or fixation in orthopedic procedures, titanium mesh offers a structured framework ideal for reconstructive surgeries and implant stabilization. Its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make titanium mesh an essential material in both clinical and dental implantology.
Typical Applications of Titanium Wire
Titanium wire is commonly utilized in medical and aerospace industries due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. Its flexibility and ability to be formed into fine gauges make it ideal for surgical sutures, orthopedic implants, and precision wiring in electronic devices. Unlike titanium mesh, which is preferred for structural reinforcement in cranial and maxillofacial surgeries, titanium wire is favored for applications requiring intricate shapes and precise tension control.
Choosing the Right Material: Mesh or Wire?
Titanium mesh offers superior structural support and flexibility for complex anatomical contours, making it ideal in craniofacial and orthopedic reconstructive surgeries. Titanium wire provides ease of manipulation and cost-effectiveness but lacks the rigidity and stability of mesh, which is crucial for long-term fixation. Selecting between titanium mesh and wire depends on the specific clinical requirements, emphasizing stability, anatomical conformity, and biomechanical demands.
Future Trends in Titanium Mesh and Wire Technologies
Future trends in titanium mesh and wire technologies emphasize enhanced biocompatibility and improved mechanical strength for medical and aerospace applications. Innovations include nano-coating techniques to increase corrosion resistance and the integration of smart sensors within titanium wire for real-time structural health monitoring. Advanced manufacturing methods, such as additive manufacturing and laser sintering, are driving personalized and complex titanium mesh designs with superior performance characteristics.
Titanium Mesh vs Titanium Wire Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com