Titanium foil offers superior flexibility and is ideal for applications requiring lightweight and thin material, such as packaging and medical uses. Titanium plates provide greater strength and rigidity, making them suitable for structural components and heavy-duty industrial applications. Choosing between titanium foil and plate depends on the specific requirements for thickness, durability, and formability in your project.
Table of Comparison
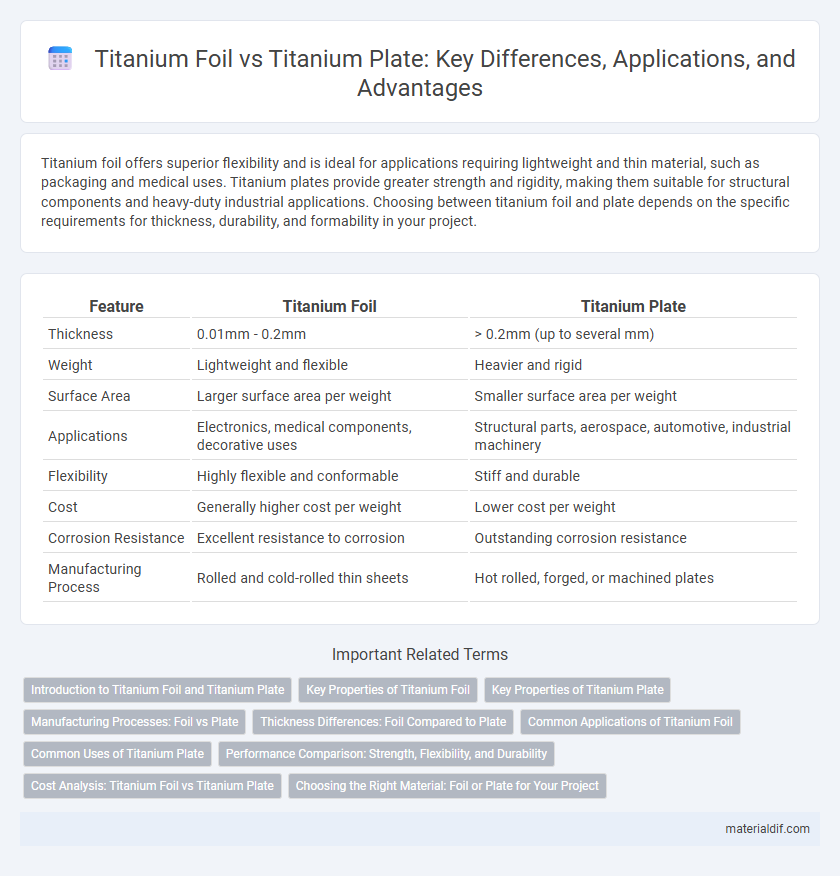
| Feature | Titanium Foil | Titanium Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.01mm - 0.2mm | > 0.2mm (up to several mm) |
| Weight | Lightweight and flexible | Heavier and rigid |
| Surface Area | Larger surface area per weight | Smaller surface area per weight |
| Applications | Electronics, medical components, decorative uses | Structural parts, aerospace, automotive, industrial machinery |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and conformable | Stiff and durable |
| Cost | Generally higher cost per weight | Lower cost per weight |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to corrosion | Outstanding corrosion resistance |
| Manufacturing Process | Rolled and cold-rolled thin sheets | Hot rolled, forged, or machined plates |
Introduction to Titanium Foil and Titanium Plate
Titanium foil features a thin, flexible form factor ideal for applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials, commonly used in aerospace, medical implants, and electronics. Titanium plates are thicker and provide higher structural strength and durability, making them suitable for construction, automotive components, and heavy-duty industrial applications. Both titanium foil and plates leverage titanium's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, differing primarily in thickness and mechanical properties for diverse engineering needs.
Key Properties of Titanium Foil
Titanium foil offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, superior corrosion resistance, and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications where precise thinness is required. Its high tensile strength combined with lightweight properties enables efficient performance in heat exchangers and chemical processing equipment. Compared to titanium plates, titanium foil provides enhanced malleability and conductivity, facilitating easier integration into complex designs and electronic components.
Key Properties of Titanium Plate
Titanium plate offers superior strength and durability compared to titanium foil, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring robust structural support. Its thicker gauge provides enhanced corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments such as marine or chemical processing industries. The high tensile strength and excellent weldability of titanium plates enable their use in aerospace, automotive, and construction sectors where reliability and performance are critical.
Manufacturing Processes: Foil vs Plate
Titanium foil is produced primarily through a cold rolling process that repeatedly compresses and thins the metal to achieve thicknesses typically under 0.5 mm, enabling excellent flexibility and precision for applications like aerospace and medical devices. Titanium plate, in contrast, is manufactured using hot rolling or forging techniques that involve heating the metal above its recrystallization temperature, resulting in thicker, stronger sheets generally exceeding 0.5 mm ideal for structural components and heavy-duty industrial uses. The manufacturing processes impact mechanical properties, with foil offering enhanced surface finish and corrosion resistance, while the plate provides superior strength and durability.
Thickness Differences: Foil Compared to Plate
Titanium foil typically ranges from 0.025 mm to 0.3 mm in thickness, making it significantly thinner and more flexible than titanium plate, which generally starts at around 1.0 mm and can exceed several centimeters. The reduced thickness of titanium foil enhances its suitability for applications requiring lightweight, malleable materials, such as electronic components and chemical processing surfaces. In contrast, titanium plates provide greater structural strength and rigidity, ideal for aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery components where durability is critical.
Common Applications of Titanium Foil
Titanium foil is widely used in aerospace and electronics industries due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for heat exchangers, capacitors, and surface protection layers. Unlike thicker titanium plates, foil's thinness allows it to be used in medical implants, such as dental and surgical devices, where flexibility and biocompatibility are critical. Its precise thickness and malleability also serve critical roles in chemical processing equipment and battery manufacturing.
Common Uses of Titanium Plate
Titanium plate is widely used in aerospace, marine, and industrial applications due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. Common uses include structural components, pressure vessels, and shipbuilding, where durability and performance under extreme conditions are critical. Unlike titanium foil, which is thinner and suited for shielding or heat exchangers, titanium plates provide the robust thickness necessary for load-bearing and protective applications.
Performance Comparison: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
Titanium foil offers superior flexibility and lighter weight compared to titanium plate, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate shaping and minimal mass. Titanium plates provide greater strength and enhanced durability, suitable for structural components subjected to high stress and wear. Performance-wise, choosing between foil and plate depends on balancing the need for strength versus flexibility in demanding environments such as aerospace, medical implants, and industrial manufacturing.
Cost Analysis: Titanium Foil vs Titanium Plate
Titanium foil typically costs more per unit weight than titanium plate due to its thin gauge and specialized manufacturing processes, such as rolling and annealing to achieve flexibility and precision thickness. Titanium plates offer a lower cost advantage for bulk applications because they are thicker, easier to produce, and require less processing time, making them more economical for structural uses. When analyzing overall project expenses, selecting titanium foil or plate depends on the balance between material cost, mechanical properties, and specific application requirements.
Choosing the Right Material: Foil or Plate for Your Project
Titanium foil offers exceptional flexibility and thinness, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant layers such as aerospace insulation or medical implants. Titanium plates provide superior strength and rigidity, best suited for structural components in industries like marine engineering or automotive manufacturing. Selecting between foil and plate depends on project requirements for thickness, mechanical strength, and formability, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Titanium Foil vs Titanium Plate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com