Pickled titanium undergoes an acid treatment that removes surface impurities and enhances corrosion resistance, making it ideal for environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. Non-pickled titanium retains its natural oxide layer but may have surface contaminants that can affect its performance over time. Choosing pickled titanium ensures improved durability and reliability for pet products subjected to wear and exposure.
Table of Comparison
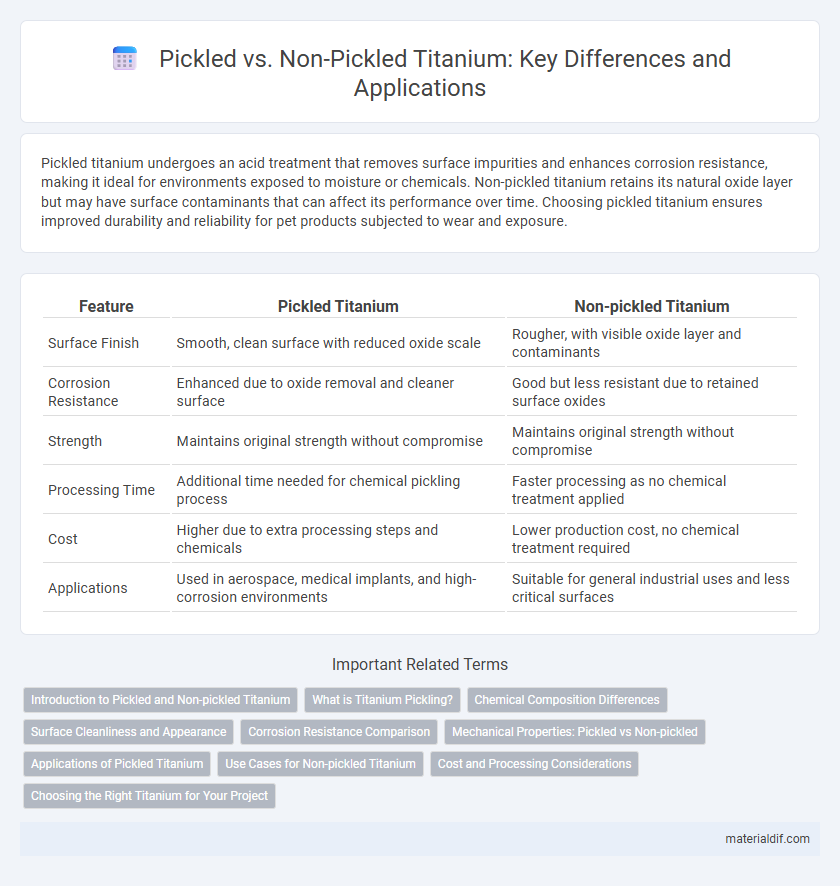
| Feature | Pickled Titanium | Non-pickled Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Smooth, clean surface with reduced oxide scale | Rougher, with visible oxide layer and contaminants |
| Corrosion Resistance | Enhanced due to oxide removal and cleaner surface | Good but less resistant due to retained surface oxides |
| Strength | Maintains original strength without compromise | Maintains original strength without compromise |
| Processing Time | Additional time needed for chemical pickling process | Faster processing as no chemical treatment applied |
| Cost | Higher due to extra processing steps and chemicals | Lower production cost, no chemical treatment required |
| Applications | Used in aerospace, medical implants, and high-corrosion environments | Suitable for general industrial uses and less critical surfaces |
Introduction to Pickled and Non-pickled Titanium
Pickled titanium undergoes a chemical treatment process that removes surface impurities, enhancing corrosion resistance and preparing the metal for further fabrication or finishing. Non-pickled titanium retains its natural oxide layer and surface contaminants, which can affect weld quality and surface appearance. Understanding the differences between pickled and non-pickled titanium is crucial for applications requiring high precision and durability.
What is Titanium Pickling?
Titanium pickling refers to a cleaning process that removes surface contaminants and oxides using an acid mixture, enhancing the metal's corrosion resistance and surface finish. This treatment is vital in industries requiring high-purity titanium, such as aerospace and medical fields, as it ensures optimal material performance and longevity. Non-pickled titanium retains its natural oxide layer and any surface impurities, which may affect bonding or coating applications.
Chemical Composition Differences
Pickled titanium undergoes an acid treatment that removes the surface oxide layer, resulting in a chemically cleaner and more reactive surface compared to non-pickled titanium. This process alters the elemental concentration at the surface, reducing contaminants such as iron and enhancing the exposure of pure titanium and its natural oxide, titanium dioxide. Non-pickled titanium retains a thicker oxide layer and surface impurities, which can affect corrosion resistance and surface reactivity.
Surface Cleanliness and Appearance
Pickled titanium undergoes an acid treatment to remove surface contaminants such as oxides and scale, resulting in a brighter, cleaner appearance with enhanced corrosion resistance. Non-pickled titanium retains its natural oxide layer and surface impurities, which can appear duller and less uniform in color. The pickling process significantly improves surface cleanliness, making pickled titanium ideal for applications requiring high aesthetic quality and superior hygiene.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Pickled titanium undergoes an acid treatment process that removes surface impurities and oxides, significantly enhancing its corrosion resistance compared to non-pickled titanium. This treatment results in a cleaner, smoother surface that reduces the risk of localized corrosion, especially in aggressive environments such as seawater or chemical processing. Non-pickled titanium, while still corrosion-resistant, may retain surface contaminants that compromise its durability under harsh conditions.
Mechanical Properties: Pickled vs Non-pickled
Pickled titanium exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to non-pickled titanium due to the removal of surface impurities and oxide layers, resulting in improved strength and fatigue resistance. The pickling process enhances the material's surface smoothness, which reduces stress concentrations and minimizes crack initiation under cyclic loading. Non-pickled titanium, with residual contaminants, typically shows lower tensile strength and reduced durability in demanding applications.
Applications of Pickled Titanium
Pickled titanium is extensively used in chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries due to its enhanced corrosion resistance and clean surface, which improves bonding with coatings and welding applications. Its surface treatment removes impurities and oxides, making it ideal for high-purity environments such as semiconductor manufacturing and marine applications. These qualities ensure longevity and reliability in harsh environments, distinguishing it from non-pickled titanium often used in less demanding structural applications.
Use Cases for Non-pickled Titanium
Non-pickled titanium is preferred in aerospace and medical industries due to its superior fatigue resistance and higher corrosion tolerance in less aggressive environments. Its non-treated surface maintains raw mechanical properties, making it ideal for structural components and implants requiring natural oxide layers for biocompatibility. Industrial applications favor non-pickled titanium where surface roughness enhances bonding with coatings or adhesives.
Cost and Processing Considerations
Pickled titanium undergoes acid treatment to remove surface contaminants, resulting in a cleaner finish but higher processing costs due to added chemical handling and waste disposal. Non-pickled titanium avoids this step, reducing manufacturing expenses while potentially retaining surface impurities that may affect performance in certain applications. Choosing between pickled and non-pickled titanium requires balancing cost-efficiency with desired surface quality and corrosion resistance.
Choosing the Right Titanium for Your Project
Pickled titanium undergoes an acid treatment that removes impurities, enhances corrosion resistance, and improves surface finish, making it ideal for projects requiring superior durability and aesthetic appeal. Non-pickled titanium retains its natural oxide layer, offering sufficient corrosion resistance but may have surface irregularities unsuitable for highly specialized applications. Selecting between pickled and non-pickled titanium depends on project requirements such as environmental exposure, desired finish quality, and mechanical performance.
Pickled Titanium vs Non-pickled Titanium Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com