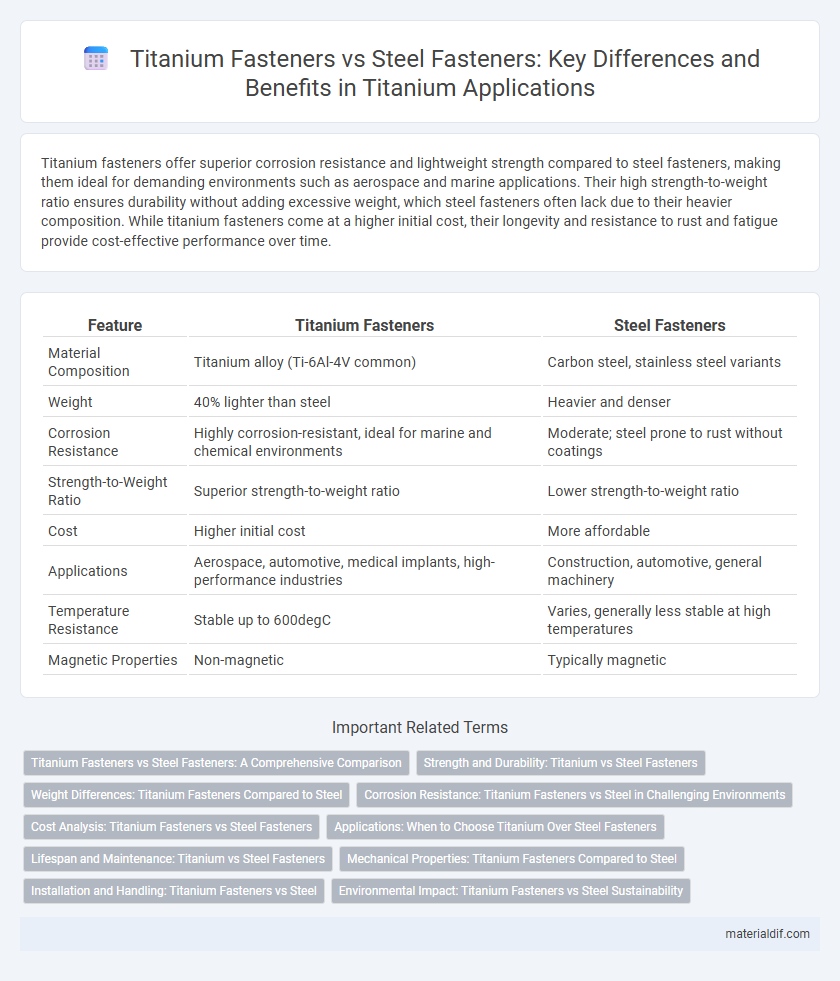
Titanium fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and lightweight strength compared to steel fasteners, making them ideal for demanding environments such as aerospace and marine applications. Their high strength-to-weight ratio ensures durability without adding excessive weight, which steel fasteners often lack due to their heavier composition. While titanium fasteners come at a higher initial cost, their longevity and resistance to rust and fatigue provide cost-effective performance over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Titanium Fasteners | Steel Fasteners |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V common) | Carbon steel, stainless steel variants |
| Weight | 40% lighter than steel | Heavier and denser |
| Corrosion Resistance | Highly corrosion-resistant, ideal for marine and chemical environments | Moderate; steel prone to rust without coatings |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Superior strength-to-weight ratio | Lower strength-to-weight ratio |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | More affordable |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, medical implants, high-performance industries | Construction, automotive, general machinery |
| Temperature Resistance | Stable up to 600degC | Varies, generally less stable at high temperatures |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Typically magnetic |
Titanium Fasteners vs Steel Fasteners: A Comprehensive Comparison
Titanium fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and a high strength-to-weight ratio compared to steel fasteners, making them ideal for aerospace, marine, and medical applications where durability and weight savings are critical. While steel fasteners provide greater cost efficiency and are widely available, they tend to be heavier and more prone to rust, especially in harsh environments. Titanium's non-magnetic properties and excellent fatigue resistance further enhance its performance over steel, despite a higher initial investment.
Strength and Durability: Titanium vs Steel Fasteners
Titanium fasteners exhibit a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to steel fasteners, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet durable components. Their corrosion resistance significantly enhances durability, especially in harsh environments where steel fasteners are prone to rust and degradation. Despite steel's higher tensile strength in some grades, titanium fasteners maintain structural integrity longer due to their exceptional fatigue resistance and minimal corrosion impact.
Weight Differences: Titanium Fasteners Compared to Steel
Titanium fasteners weigh approximately 40% less than steel fasteners, offering significant weight savings in aerospace, automotive, and marine applications where reducing mass is crucial. Despite their lighter weight, titanium fasteners maintain comparable tensile strength to steel, ensuring durability and reliability under high-stress conditions. This optimal strength-to-weight ratio enhances fuel efficiency and performance by minimizing the overall load without sacrificing structural integrity.
Corrosion Resistance: Titanium Fasteners vs Steel in Challenging Environments
Titanium fasteners exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to steel fasteners, making them ideal for challenging environments such as marine, chemical processing, and aerospace applications. Their naturally forming oxide layer prevents rust and degradation, significantly extending service life in highly corrosive conditions. Steel fasteners, even when coated, are more prone to corrosion, leading to frequent maintenance and potential structural failure.
Cost Analysis: Titanium Fasteners vs Steel Fasteners
Titanium fasteners typically cost 3 to 4 times more than steel fasteners due to higher raw material expenses and complex manufacturing processes. Despite the initial investment, titanium's superior corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio often result in lower lifecycle costs in aerospace and marine applications. Steel fasteners offer a more economical upfront price but may incur higher maintenance and replacement expenses in corrosive or high-stress environments.
Applications: When to Choose Titanium Over Steel Fasteners
Titanium fasteners are ideal for aerospace, marine, and chemical processing applications where corrosion resistance and weight reduction are critical. Steel fasteners are preferred in construction and automotive industries due to their higher strength-to-cost ratio and broad availability. Choose titanium fasteners for environments involving extreme temperatures or exposure to saltwater, where durability and long-term performance outweigh initial cost.
Lifespan and Maintenance: Titanium vs Steel Fasteners
Titanium fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and a lifespan up to twice as long as steel fasteners, especially in harsh environments such as marine or chemical exposure. Steel fasteners require regular maintenance, including coating or galvanization, to prevent rust and ensure durability, whereas titanium fasteners typically remain maintenance-free. The reduced need for maintenance and longer lifespan of titanium fasteners lower total lifecycle costs despite their higher initial price.
Mechanical Properties: Titanium Fasteners Compared to Steel
Titanium fasteners exhibit a superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to steel fasteners, offering high tensile strength while being significantly lighter. They provide excellent corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments, reducing the risk of material degradation and fastening failure. While steel fasteners often have higher absolute strength, titanium's combination of mechanical strength and low density makes it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications requiring lightweight durability.
Installation and Handling: Titanium Fasteners vs Steel
Titanium fasteners offer superior corrosion resistance and lower weight, making them easier to handle during installation compared to steel fasteners, which are heavier and prone to rust. The lower thermal conductivity of titanium reduces heat transfer during tightening, minimizing the risk of thermal expansion and ensuring consistent preload. Steel fasteners require careful corrosion protection and often more torque to achieve secure fastening, whereas titanium fasteners provide enhanced durability with less maintenance.
Environmental Impact: Titanium Fasteners vs Steel Sustainability
Titanium fasteners exhibit superior sustainability compared to steel, primarily due to their corrosion resistance that extends lifespan and reduces replacement frequency. The lower density of titanium also results in lighter components, contributing to energy savings in transportation and installation. Although titanium extraction requires significant energy, its recyclability and reduced environmental degradation during use underscore its overall eco-friendly advantage over steel fasteners.
Titanium Fasteners vs Steel Fasteners Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com