Aerospace titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to commercial titanium, making it ideal for high-performance applications in aircraft and spacecraft. Commercial titanium, while still strong and corrosion-resistant, is typically produced with less stringent standards and lower alloy content, reducing its suitability for extreme environments. Both types share core titanium properties, but aerospace-grade titanium undergoes specialized processing to meet rigorous safety and durability requirements.
Table of Comparison
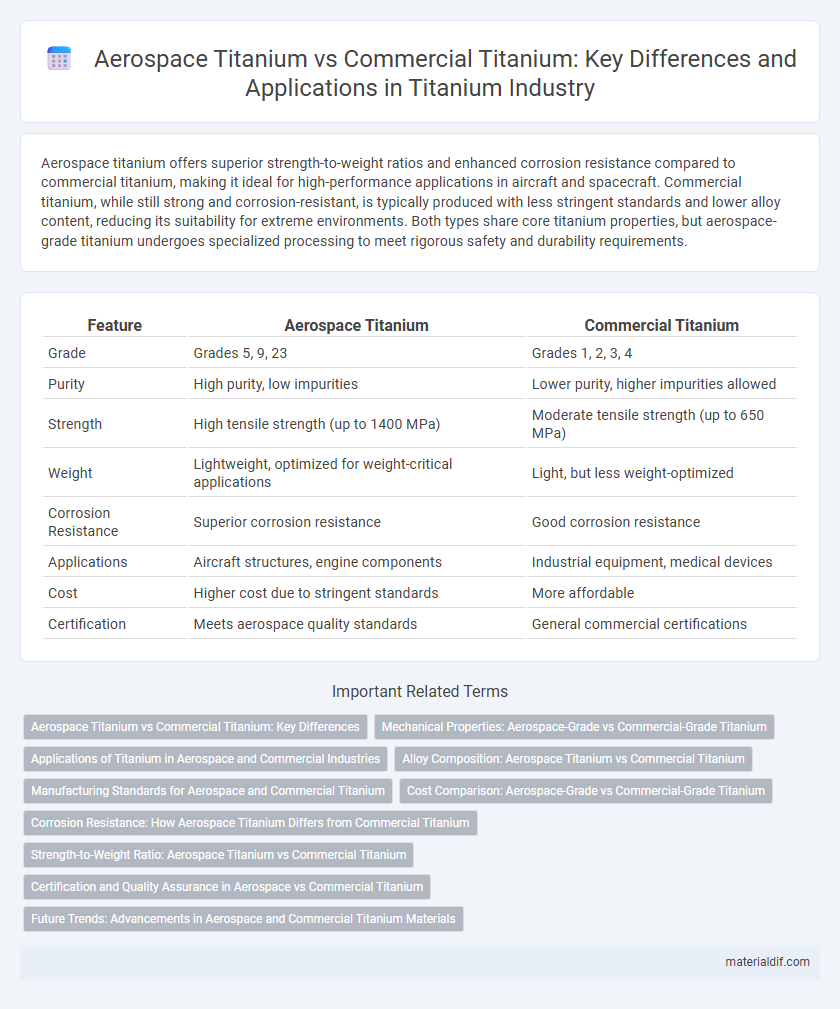
| Feature | Aerospace Titanium | Commercial Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Grade | Grades 5, 9, 23 | Grades 1, 2, 3, 4 |
| Purity | High purity, low impurities | Lower purity, higher impurities allowed |
| Strength | High tensile strength (up to 1400 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (up to 650 MPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight, optimized for weight-critical applications | Light, but less weight-optimized |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior corrosion resistance | Good corrosion resistance |
| Applications | Aircraft structures, engine components | Industrial equipment, medical devices |
| Cost | Higher cost due to stringent standards | More affordable |
| Certification | Meets aerospace quality standards | General commercial certifications |
Aerospace Titanium vs Commercial Titanium: Key Differences
Aerospace titanium exhibits superior strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance compared to commercial-grade titanium, making it essential for critical aircraft components. Commercial titanium typically has lower purity and mechanical properties, suited for less demanding applications such as consumer goods and industrial equipment. Stringent quality control and certifications differentiate aerospace titanium, ensuring reliability under extreme aerospace conditions.
Mechanical Properties: Aerospace-Grade vs Commercial-Grade Titanium
Aerospace-grade titanium alloys, such as Ti-6Al-4V, exhibit superior mechanical properties including higher tensile strength (up to 1,100 MPa) and enhanced fatigue resistance compared to commercial-grade titanium, which generally has lower tensile strength around 550 MPa. The controlled microstructure and alloying elements in aerospace titanium result in improved fracture toughness and creep resistance, essential for extreme aerospace environments. In contrast, commercial titanium prioritizes corrosion resistance and is suitable for less mechanically demanding applications, lacking the high-performance characteristics required for aerospace structural components.
Applications of Titanium in Aerospace and Commercial Industries
Titanium's high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance make it ideal for aerospace applications, including aircraft structural components, engine parts, and fasteners, where durability and lightweight materials are critical. In commercial industries, titanium is widely used for medical implants, chemical processing equipment, and sports equipment due to its biocompatibility and resistance to extreme environments. The distinct grade variations and alloy compositions cater specifically to the demanding mechanical and environmental requirements of aerospace versus commercial uses.
Alloy Composition: Aerospace Titanium vs Commercial Titanium
Aerospace titanium alloys, such as Ti-6Al-4V, contain higher concentrations of aluminum and vanadium, enhancing strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue performance critical for aerospace applications. In contrast, commercial titanium grades like Grade 2 focus on purity and ductility with lower alloying elements, making them suitable for general-purpose use in industries such as automotive and medical implants. The precise alloy composition differences directly impact mechanical properties and suitability for high-performance versus standard commercial environments.
Manufacturing Standards for Aerospace and Commercial Titanium
Aerospace titanium is manufactured under stringent standards such as AMS 4902 and MIL-T-9046, ensuring exceptional strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion performance critical for aircraft components. Commercial titanium follows ASTM B265 specifications, prioritizing cost-efficiency and general structural applications with less rigorous quality control compared to aerospace grades. The manufacturing processes for aerospace titanium involve precise forging, heat treatment, and non-destructive testing to meet aerospace industry's demanding safety and reliability criteria.
Cost Comparison: Aerospace-Grade vs Commercial-Grade Titanium
Aerospace-grade titanium, known for its superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced corrosion resistance, commands a significantly higher price than commercial-grade titanium due to stringent quality control and specialized alloy compositions like Ti-6Al-4V. Commercial-grade titanium, primarily used in industrial and consumer products, offers cost efficiency with acceptable performance but lacks the high fatigue resistance and precise mechanical properties necessary for aerospace applications. The cost premium for aerospace titanium reflects its critical role in aircraft structural components, where safety and longevity are paramount, leading to prices that can be two to three times higher than commercial-grade variants.
Corrosion Resistance: How Aerospace Titanium Differs from Commercial Titanium
Aerospace titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to commercial titanium due to its higher purity levels and specialized alloying elements like aluminum and vanadium, which enhance oxidation resistance and strength. Its microstructure is precisely controlled through advanced manufacturing processes to optimize resistance against high-temperature oxidative environments commonly experienced in aerospace applications. Commercial titanium, while corrosion-resistant, often contains more impurities and lacks these targeted alloys, resulting in comparatively lower durability in harsh, corrosive settings.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aerospace Titanium vs Commercial Titanium
Aerospace titanium alloys, such as Ti-6Al-4V, exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to commercial-grade titanium, making them essential for high-performance aerospace applications where weight savings and structural integrity are critical. These aerospace alloys typically provide tensile strengths exceeding 900 MPa while maintaining low density around 4.43 g/cm3, significantly outperforming commercial titanium grades that have lower strength thresholds and less consistent material properties. The optimized metallurgical composition and advanced processing techniques used in aerospace titanium enhance fatigue resistance and fracture toughness, ensuring reliability in demanding environments beyond the capabilities of standard commercial titanium.
Certification and Quality Assurance in Aerospace vs Commercial Titanium
Aerospace titanium undergoes rigorous certification processes including adherence to AS9100 standards and stringent quality assurance protocols to ensure superior mechanical properties and traceability for critical applications. Commercial titanium, while tested for general strength and corrosion resistance, follows less stringent certifications primarily aligned with ASTM standards, allowing for broader but less specialized uses. Quality control in aerospace focuses heavily on non-destructive testing, metallurgical analysis, and traceability to guarantee performance under extreme conditions, unlike commercial titanium which prioritizes cost-efficiency and moderate durability.
Future Trends: Advancements in Aerospace and Commercial Titanium Materials
Advancements in aerospace titanium focus on developing ultra-high strength alloys and improved corrosion resistance to meet stringent performance and safety standards, enabling lighter, more fuel-efficient aircraft. Commercial titanium trends emphasize cost-effective production methods and enhanced recyclability, supporting sustainable construction and medical applications. Future innovations combine additive manufacturing with novel titanium composites to expand functionality across both aerospace and commercial sectors.
Aerospace Titanium vs Commercial Titanium Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com