Titanium dioxide paint provides a durable, UV-resistant surface ideal for outdoor applications but lacks the hardness and scratch resistance of PVD titanium coating. PVD titanium coating forms a thin, hard layer through physical vapor deposition, enhancing wear resistance and corrosion protection without adding significant weight. Choosing between the two depends on whether color durability or maximum surface hardness is the priority for the titanium pet product.
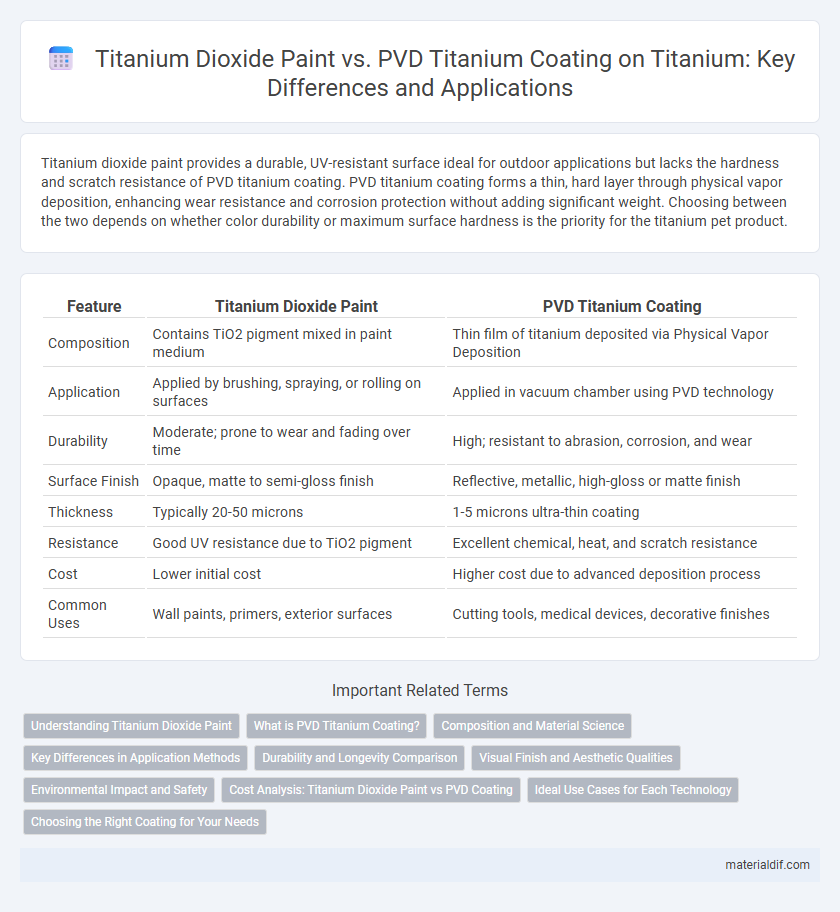
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Titanium Dioxide Paint | PVD Titanium Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains TiO2 pigment mixed in paint medium | Thin film of titanium deposited via Physical Vapor Deposition |
| Application | Applied by brushing, spraying, or rolling on surfaces | Applied in vacuum chamber using PVD technology |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to wear and fading over time | High; resistant to abrasion, corrosion, and wear |
| Surface Finish | Opaque, matte to semi-gloss finish | Reflective, metallic, high-gloss or matte finish |
| Thickness | Typically 20-50 microns | 1-5 microns ultra-thin coating |
| Resistance | Good UV resistance due to TiO2 pigment | Excellent chemical, heat, and scratch resistance |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to advanced deposition process |
| Common Uses | Wall paints, primers, exterior surfaces | Cutting tools, medical devices, decorative finishes |
Understanding Titanium Dioxide Paint
Titanium dioxide paint contains titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles that provide excellent opacity and UV protection, making it a popular choice for outdoor and industrial applications. This paint enhances durability and weather resistance by creating a reflective, protective layer that reduces surface degradation and color fading. Unlike PVD titanium coating, which deposits a thin metallic layer for decorative and functional purposes, titanium dioxide paint relies on pigment dispersion to achieve its protective and aesthetic effects.
What is PVD Titanium Coating?
PVD titanium coating is a physical vapor deposition process that creates a thin, durable layer of titanium or titanium compounds on surfaces, enhancing corrosion resistance and wear durability. Unlike titanium dioxide paint, which is a pigment-based coating primarily for color and UV protection, PVD coatings provide functional benefits such as increased hardness and chemical stability. This technology is widely used in medical devices, automotive parts, and consumer products for its superior performance and longevity.
Composition and Material Science
Titanium dioxide paint primarily consists of TiO2 particles suspended in a polymer matrix, offering excellent UV resistance and opacity due to the high refractive index of titanium dioxide pigment. In contrast, PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) titanium coating involves the deposition of a thin, pure titanium or titanium alloy layer onto a substrate through vapor phase processes, resulting in a dense, adherent, and highly durable metallic film. The material science of PVD coatings emphasizes atomic-level bonding and crystalline structure control, enhancing hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear performance beyond what titanium dioxide paint's composite polymer structure can achieve.
Key Differences in Application Methods
Titanium dioxide paint is applied through traditional methods such as brushing, spraying, or rolling, allowing for easy and cost-effective surface coverage primarily in architectural and automotive industries. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) titanium coating involves vaporizing titanium in a vacuum chamber to deposit a thin, durable film on substrates, offering superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and precision for applications in aerospace and medical devices. The key difference lies in paint being a liquid-based application forming a pigment layer, whereas PVD creates a metallurgical bond with the substrate at an atomic level, resulting in enhanced performance characteristics.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Titanium dioxide paint offers moderate durability with resistance to UV light and corrosion but tends to degrade over time under harsh environmental conditions. PVD titanium coating provides superior longevity due to its atomic-level bonding and enhanced hardness, resulting in exceptional wear resistance and prolonged lifespan. The PVD process ensures a denser, more durable surface that outperforms traditional titanium dioxide paint in both abrasion resistance and resistance to chemical damage.
Visual Finish and Aesthetic Qualities
Titanium dioxide paint offers a bright, opaque finish with excellent opacity and UV resistance but lacks the metallic luster and depth found in PVD titanium coatings. PVD titanium coatings provide a highly durable, reflective surface with superior scratch resistance, delivering a sleek, metallic aesthetic that enhances visual depth and color vibrancy. The PVD process allows for a variety of color options and finishes that maintain their brilliance over time, making it ideal for premium applications requiring both strength and refined appearance.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Titanium dioxide paint contains microparticles that can pose environmental hazards due to runoff and potential inhalation risks, while PVD titanium coating utilizes physical vapor deposition to create a solid, non-toxic layer with minimal environmental emissions. The PVD process reduces waste and avoids harmful solvents commonly found in paints, enhancing workplace safety and reducing ecological footprint. In contrast, titanium dioxide paint may contribute to air and water pollution, raising concerns over long-term exposure and ecosystem health.
Cost Analysis: Titanium Dioxide Paint vs PVD Coating
Titanium dioxide paint offers a cost-effective solution for surface protection and aesthetic enhancement, typically priced significantly lower than PVD titanium coating. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) titanium coating involves advanced technology and higher material costs, leading to greater upfront expenditure but providing superior durability and resistance. Long-term cost analysis favors PVD coating for applications requiring enhanced wear resistance and longevity, despite its initial higher investment compared to titanium dioxide paint.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Technology
Titanium dioxide paint excels in applications requiring high UV resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for exterior surfaces exposed to harsh weather and pollutants. PVD titanium coating offers superior hardness and wear resistance, suited for precision components in aerospace, medical instruments, and decorative finishes needing durable, scratch-resistant protection. Selecting between these technologies depends on whether the priority is surface protection from environmental degradation or enhanced mechanical performance.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Needs
Titanium dioxide paint offers excellent UV protection and corrosion resistance ideal for outdoor applications, while PVD titanium coating provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and a decorative metallic finish suitable for high-performance and luxury goods. Assessing environmental exposure, durability requirements, and aesthetic preferences helps determine the optimal coating choice. For demanding industrial uses, PVD coating excels in longevity, whereas titanium dioxide paint is cost-effective for general protective purposes.
Titanium Dioxide Paint vs PVD Titanium Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com