CNC machined titanium offers precise, intricate detailing and superior strength due to its subtractive manufacturing process, making it ideal for high-performance pet accessories requiring durability. Laser cut titanium excels in speed and cost-efficiency, producing clean, accurate cuts suitable for simpler designs with less complex geometry. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance of precision, strength, and production cost for titanium pet products.
Table of Comparison
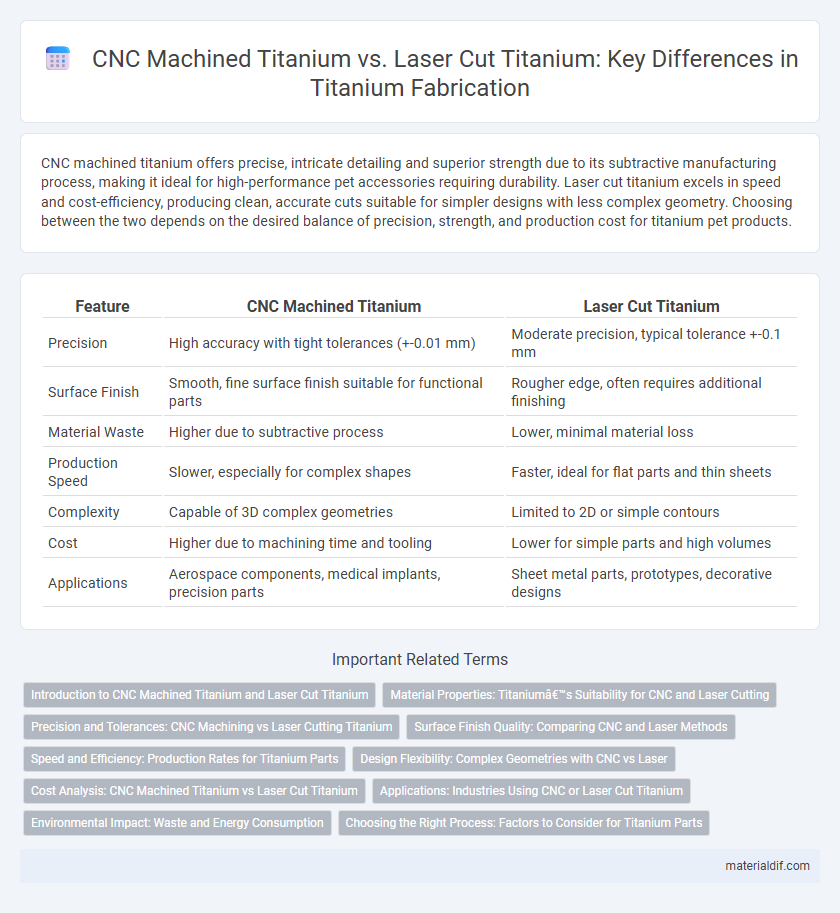
| Feature | CNC Machined Titanium | Laser Cut Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High accuracy with tight tolerances (+-0.01 mm) | Moderate precision, typical tolerance +-0.1 mm |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, fine surface finish suitable for functional parts | Rougher edge, often requires additional finishing |
| Material Waste | Higher due to subtractive process | Lower, minimal material loss |
| Production Speed | Slower, especially for complex shapes | Faster, ideal for flat parts and thin sheets |
| Complexity | Capable of 3D complex geometries | Limited to 2D or simple contours |
| Cost | Higher due to machining time and tooling | Lower for simple parts and high volumes |
| Applications | Aerospace components, medical implants, precision parts | Sheet metal parts, prototypes, decorative designs |
Introduction to CNC Machined Titanium and Laser Cut Titanium
CNC machined titanium involves a precise, computer-controlled process that shapes titanium blocks into complex components with high accuracy and smooth finishes. Laser cut titanium utilizes focused laser beams to cut or engrave titanium sheets, offering rapid production and minimal material waste. Both methods highlight titanium's exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties, but differ in application scope and surface quality.
Material Properties: Titanium’s Suitability for CNC and Laser Cutting
Titanium's exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance make it highly suitable for both CNC machining and laser cutting processes. CNC machining leverages titanium's toughness to create precise, complex shapes with excellent surface finishes, while laser cutting efficiently handles titanium's reflective properties and high melting point to produce clean, accurate cuts with minimal thermal distortion. Understanding titanium's material properties, such as its high tensile strength (up to 434 MPa) and thermal conductivity (around 21.9 W/m*K), is crucial to optimizing manufacturing techniques for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications.
Precision and Tolerances: CNC Machining vs Laser Cutting Titanium
CNC machined titanium offers superior precision with tolerances typically within +-0.001 inch, making it ideal for complex components requiring high accuracy. Laser cut titanium provides faster cutting speeds but generally maintains tolerances around +-0.005 inch, which suits less intricate parts. The choice depends on the specific application's tolerance demands and the level of detail required in the titanium components.
Surface Finish Quality: Comparing CNC and Laser Methods
CNC machined titanium offers a superior surface finish characterized by smooth, precise contours and minimal roughness due to controlled cutting tools and consistent feed rates. Laser cut titanium often features a slightly rougher edge with heat-affected zones and microscopic burrs resulting from focused thermal energy during cutting. For applications demanding high surface quality and tight tolerances, CNC machining is preferred over laser cutting.
Speed and Efficiency: Production Rates for Titanium Parts
CNC machined titanium offers consistent precision with moderate production speeds, making it ideal for complex, high-tolerance parts requiring detailed finishes. Laser cut titanium excels in speed and efficiency for producing flat or simpler shapes, significantly increasing production rates with minimal material waste. Manufacturing workflows optimize by selecting laser cutting for rapid prototyping or batch production, while CNC machining is preferred for intricate components demanding dimensional accuracy.
Design Flexibility: Complex Geometries with CNC vs Laser
CNC machined titanium offers superior design flexibility by enabling the creation of intricate and complex geometries with high precision, making it ideal for detailed automotive, aerospace, and medical components. Laser cutting titanium provides efficient shaping for simpler, flat profiles but is limited when producing three-dimensional or highly detailed parts. The choice between CNC machining and laser cutting depends on the complexity of the design, with CNC machining better suited for precision and versatility in complex titanium structures.
Cost Analysis: CNC Machined Titanium vs Laser Cut Titanium
CNC machined titanium typically incurs higher costs due to prolonged tooling time, complex setup, and precise material removal processes, resulting in greater labor and machine expenses. Laser cut titanium offers cost efficiency for simpler designs with faster production speeds and minimal post-processing, reducing overall operational costs. Volume and tolerances critically impact cost-effectiveness, with CNC machining favored for detailed, low to medium volume parts and laser cutting optimized for high-volume, less intricate components.
Applications: Industries Using CNC or Laser Cut Titanium
CNC machined titanium is widely used in aerospace and medical industries due to its precision and ability to create complex, high-strength components such as turbine blades and surgical implants. Laser cut titanium is preferred in automotive and electronics sectors for producing intricate, high-quality parts with minimal thermal distortion, including heat shields and circuit components. Both methods support industries requiring lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials but differ in application based on precision needs and production volume.
Environmental Impact: Waste and Energy Consumption
CNC machined titanium generates more material waste compared to laser cutting, as the subtractive process removes significant amounts of metal during shaping. Laser cutting titanium offers higher precision with minimal scrap, reducing raw material usage and lowering environmental footprint. Energy consumption for laser cutting titanium tends to be lower per unit of production, making it a more sustainable choice in titanium fabrication.
Choosing the Right Process: Factors to Consider for Titanium Parts
Selecting the right process for titanium parts depends on factors such as precision requirements, surface finish, and production volume. CNC machining offers high dimensional accuracy and superior surface quality, ideal for complex geometries and tight tolerances. Laser cutting excels in rapid prototyping and cost-effective production of flat titanium sheets but may require secondary finishing for detailed applications.
CNC Machined Titanium vs Laser Cut Titanium Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com